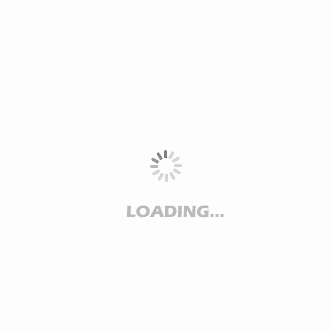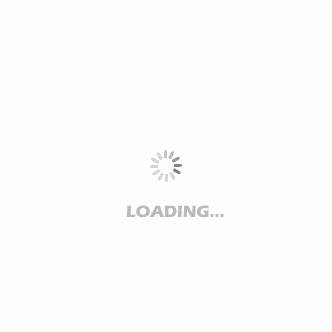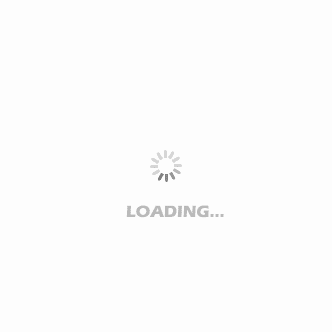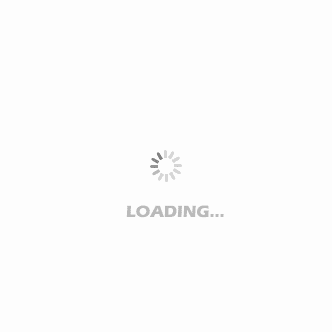
"Cheap aggrenox caps 25/200mg overnight delivery, treatment xanthelasma eyelid".
By: O. Redge, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., Ph.D.
Co-Director, University of Massachusetts Medical School
Adolescents completed a measure of benefit finding related to their diabetes at T1-4 with six-month intervals symptoms rheumatic fever discount aggrenox caps 25/200mg with visa, and a measure assessing identity exploration and commitment at T5 treatment 5th disease buy aggrenox caps pills in toronto, one year later medicine 93 3109 order aggrenox caps now. Through the use of latent growth curve modeling medications via g tube order aggrenox caps on line amex, T5 identity scores were regressed on intercept and slope terms of benefit finding through T1-4, simultaneously controlling for age, gender, illness duration, pump status (insulin injections vs. Identity exploration (but not commitment) at T5 was uniquely and positively predicted by both the intercept and slope terms of benefit finding. Higher initial levels and increases over time in benefit finding positively predicted identity exploration one year later. Identity exploration is a key developmental challenge for adolescents on the road to adulthood. This task can prove especially challenging for adolescents confronted with a chronic illness. The present results indicated that if these adolescents experience benefit finding when dealing with their diabetes, they are more inclined to thoroughly explore different identity alternatives later on in adolescence. In sum, benefit finding may constitute a process facilitating optimal identity formation in adolescents with a chronic illness. This study examined if adolescents experience different changes in benefit-finding as they age, and if certain developmental trajectories are associated with more positive diabetes-related outcomes. Participants were 252 adolescents with type 1 diabetes (ages 10-14 at Time 1, 46% boys) who took part in a five-wave longitudinal study spanning 3 years. Adolescents completed a measure of benefit finding related to their diabetes at times 1-4, each 6 months apart. The first class (27%) scored very low on benefit-finding initially and decreased over time. The second class (57%) had moderate levels of benefit-finding initially and decreased slightly over time. The third class (16%) scored very high on benefit-finding initially and remained stable over time. Overall, findings suggest that adolescents who consistently experience high levels of benefitfinding in diabetes may have better treatment adherence later. It is possible that benefitfinding serves as a protective factor for those dealing with a chronic illness, and may motivate adolescents to more closely follow the regimens suggested by their providers. Interestingly, sex differences emerged, as parent-reported adherence was significant for males (r=-. Executive function may be especially important in adolescence, when responsibility over diabetes increases. Young children with T1D are at greater risk for nocturnal hypoglycemia and parents often wake children at night to check their blood glucose, disturbing both child and parent sleep. In turn, insufficient and poor quality sleep contribute to poor glycemic control in adolescents and young adults with T1D, yet few studies have sought to examine the characteristics of sleep in young children with T1D who may be at risk for these adverse effects. Children also wore actigraphy (Philips Actiwatch) at bedtime for 10 days as an objective measure of activity and rest to estimate sleep patterns. In addition, these children and their parents are not meeting recommendations for total amounts of sleep (American Academy of Sleep Medicine). Brief, behavioral interventions have shown promise in decreasing sleep latency in other pediatric populations, with improved overall amount and quality of sleep. Although we had a relatively small sample, this was the first study to objectively measure sleep in young children with T1D, highlighting the potentially high rates of sleep disturbance in this population. In an attempt to understand why teens, especially those of underrepresented groups such as Latinos, are at an increased risk for engaging in sexual risk behaviors. It has also been posited that early steady dating provides a context for many adolescent sexual experiences. However, the link between early dating behaviors and subsequent sex initiation among Latino youth has yet to be examined. Moreover, in light of evidence of the Hispanic Paradox partly explaining Latino health outcomes, variations across generational migration status should also be examined. Additionally, we examined the moderating role of generational migration status among first- (18. Findings have important implications for addressing early sexual initiation and may provide evidence of the Hispanic Paradox in this area. Researchers posit, however, that partners and relational factors likely influence the use of contraceptives.
The campaign sought to educate motorcycle riders about the dangers of drinking and riding medications ms treatment cheap 25/200 mg aggrenox caps free shipping, encourage them to make safer choices brazilian keratin treatment 25/200 mg aggrenox caps visa, and provide impaired motorcycle riders with secure storage of their motorcycles so that they could find safe transport home symptoms week by week safe aggrenox caps 25/200mg. A coalition was established that included motorcycle riders treatment yeast uti buy line aggrenox caps, tavern owners, law enforcement, and local businesses, and substantial media attention was obtained at the program kick-off. While there is evidence that riders were willing to leave their motorcycles in secure storage containers, only small changes in rider behavior and alcohol-related motorcycle crashes were observed following the program (Aguilar & Delehanty, 2009). Motorcycles Rider groups can play critical roles in planning and implementing activities to reduce drinking and riding. Some State and local rider groups sponsor alcohol-free events or adopt alcohol-free policies. It also is not known how many States have included messages directed to motorcyclists in their overall alcohol-impaired driving campaigns. Effectiveness: There are no evaluations of the safety effectiveness of any drinking and riding campaigns. Costs: A good campaign will require substantial funds to conduct market research, design and test messages, and place campaign material where it will reach motorcyclists frequently. Time to implement: A good campaign will require at least 6 months to research, design, test, and implement. Most States will waive the skill test, and sometimes the knowledge test, for motorcyclists who have completed approved motorcycle rider training courses. This is perhaps not surprising given the variability of licensing tests and procedures. A companion report (Baer, Baldi, & Cook, 2005) describes training and licensing programs and actions to promote training and licensing. Maryland used the additional strategy of comparing their vehicle registration and driver licensing files. The letter reminded each registered owner that a motorcycle endorsement was required of anyone operating the registered motorcycle. This quick and inexpensive strategy caused 1,700 owners to become licensed within 4 months. A randomized controlled experiment of this intervention suggested that while the method did increase licensure, a large percentage remained unlicensed (Braver et al. Effective July 22, 2007, the State of Washington added an authorization to impound vehicles operated by drivers without a proper endorsement (including, but not limited to , motorcycles). Maryland and Pennsylvania have "one-stop shops" that provide a motorcycle endorsement immediately upon successful completion of a State-approved motorcycle rider training course or test, without having to wait after receiving a permit. Use: All States require motorcycle riders to obtain a motorcycle license or endorsement to ride on public highways. Less than half of responding States indicated that they enforce laws relating to improperly licensed motorcyclists (Baer et al. Effectiveness: the effectiveness of current licensing and testing on crashes and safety has not been evaluated. The costs of changing the licensing tests and procedures depend on the extent of changes and the amount of retraining needed for licensing examiners as well as what portion of costs are covered by licensing fees. Time to implement: Developing new policies to encourage higher rates of full motorcycle licensure (including limiting the number of times a provisional license may be renewed, administrative practices such as adding testing times and locations, or training motorcycle license examiners), or procedures such as waiving the skills test for those who have passed an approved training course, would likely require 6 to 12 months to implement. Enforcement of motorcycle licensing requirements could occur more readily, if requirements for full licensure are clear enough to enforce. According to the Motorcycle Safety Foundation (2010), 5 of the 31 States responding to their 2010 survey had some form of graduated licensing. Evaluations in New Zealand and evidence from Quebec suggest that they may do the same for motorcyclists (Mayhew & Simpson, 2001). In Utah, motorcycle endorsements are restricted to motorcycles no larger than the size of the motorcycle used for the skills test, or used during the approved State training course (substitute). This requires cooperation on the part of multiple agencies, including those responsible for collecting and analyzing crash data and those responsible for training and licensing. Forty-seven States have State-operated and legislated education and training programs and the other 3 have privately operated programs (Baer, Cook, & Baldi, 2005). Sixty percent of the 44 States that responded to a survey question from Baer et al.
Tailoring narratives more closely to individuals or adding audio to the narratives could reduce the time and cognitive burden associated with reading each narrative story symptoms 24 hour flu generic 25/200 mg aggrenox caps overnight delivery. Phase 2 of the study then focused on implementing the resulting four-session curriculum symptoms 5-6 weeks pregnant buy aggrenox caps australia, An Active Approach to Diabetes Self-Management medicine wheel images purchase aggrenox caps 25/200 mg with amex, in local community centers and examining its early acceptability symptoms after flu shot order aggrenox caps 25/200mg without prescription, feasibility, and effectiveness in producing clinical and psychosocial outcomes of interest. In addition, results indicate that both participants and community liaisons were highly satisfied with the intervention. Little is known about the daily challenges facing emerging adults with type 1 diabetes. We examined the types of daily stressors experienced by high school seniors as they transitioned into emerging adulthood. Adolescents with type 1 diabetes completed a 2-week daily diary in their senior year of high school (late adolescents) and one year later (emerging adults) (N=219; 60% female; 77% nonHispanic White, 12% Hispanic). Shifts in daily stress have implications for diabetes outcomes, as evidenced by work stress associations with poor glycemic control in emerging adults. Findings illuminate the stressful context of daily diabetes management during emerging adulthood, and may guide programs to facilitate better adjustment across this important transition. Dysthymia, Adjustment Disorder with Depressed Mood and Depressive Disorder Not Otherwise Specified). Stress associated with the burden of diabetes (diabetes distress) has been associated with worse diabetes control. We examined the relationship between diabetes distress, social support, and glycemic control in a sample of low-income African Americans with T2D living in Alabama. Methods: A sample of 120 low-income African American adults with uncontrolled T2D (HbA1c 7. Linear regression analyses tested for bivariate associations and also tested whether perceived support mediated the relationship between diabetes distress and glycemic control. In the final mediation model, perceived support did not significantly mediate the relationship between diabetes distress and change in glycemic control. Conclusions: Although analyses found no mediation of social support on the relationship between diabetes distress and glycemic control in this small study, it was observed that social support from family/friends was associated with less diabetes distress. These relationships should be examined in a larger sample and in intervention trials designed to improve social support. Youth with T1D (n = 80, aged 12-16 yrs) participated in an 18-month, randomized trial of a family-based behavioral nutrition intervention. All questions were assigned to predefined categories (etiology, treatment/procedure/self-management, diagnosis, prognosis/ risk, diet/exercise, symptom/side effect, self-motivation, and other) and agreement between what patients asked and what physicians expected was analyzed. Patients asked questions of etiology and symptoms/side effect while physicians expected patients to ask prognosis/ risk, treatment/procedure/self-management and diet/exercise. We speculate that psychological factors (patients may not want to discuss uncomfortable prognosis or outcome) and time constraint during the visit (physicians may not have time explaining etiology) play important roles although the causes of mismatch will be investigated in the future. Methods: Mixed method design was used for an in-depth understanding of the benefits and barriers of program effectiveness. Trained health coaches led educational sessions and provided weekly quick and easy tips to attain the desired health-related behavior. A community-based participatory research was used to culturally tailor the curriculum. Program participants included adults with dysglycemia (pre-diabetes or had diabetes). The benefits and barriers survey gathered information related to health literacy, and benefits and barriers of program participation followed by a focus group. The majority of target audience did not perceive transportation and community location as barriers to participation. Additionally, program participation allowed the majority of participants to change their lifestyles (88. Physical activity (and sleep) was measured using a wrist-worn accelerometer over 6-days. The average activity count/minute during waking hours was used to create 2 groups (n=20 each) of the most and least active subjects.
25/200 mg aggrenox caps mastercard. CREST syndrome - causes symptoms diagnosis treatment pathology.