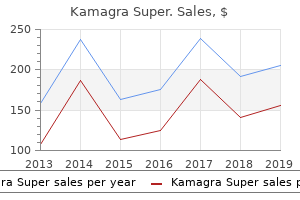
"Order kamagra super 160mg mastercard, erectile dysfunction drug".
By: R. Pedar, M.A., M.D., Ph.D.
Co-Director, University of Chicago Pritzker School of Medicine
To address individual nutrition needs based on personal and cultural preferences erectile dysfunction drugs free trial buy cheap kamagra super 160 mg online, health literacy and numeracy erectile dysfunction funny images cost of kamagra super, access to healthful foods impotence medication cheap kamagra super online master card, willingness and ability to make behavioral changes natural erectile dysfunction treatment remedies purchase kamagra super us, and existing barriers to change 3. To maintain the pleasure of eating by providing nonjudgmental messages about food choices while limiting food choices only when indicated by scientific evidence 4. To provide an individual with diabetes the practical tools for developing healthy eating patterns rather than focusing on individual macronutrients, micronutrients, or single foods Eating Patterns, Macronutrient Distribution, and Meal Planning Evidence suggests that there is not an ideal percentage of calories from carbohydrate, protein, and fat for people with diabetes. Therefore, macronutrient distribution should be based on an individualized assessment of current eating patterns, preferences, and metabolic goals. It is important that each member of the health care D ia be the s As so Goals of Nutrition Therapy for Adults With Diabetes ci a Reimbursement tio participation may be due to lack of referral or other identified barriers such as logistical issues (accessibility, timing, costs) and the lack of a perceived benefit (52). Because of the progressive nature of type 2 diabetes, behavior modification alone may not be adequate to maintain euglycemia over time. However, after medication is initiated, nutrition therapy continues to be an important component and should be integrated with the overall treatment plan (55). A variety of eating patterns are acceptable for the management of diabetes (41,58,60). Until the evidence surrounding comparative benefits of different eating patterns in specific individuals strengthens, health care providers should focus on the key factors that are common among the patterns: 1) emphasize nonstarchy vegetables, 2) minimize added sugars and refined grains, and 3) choose whole foods over highly processed foods to the extent possible (41). The Mediterraneanstyle (61,62), low-carbohydrate (63 65), and vegetarian or plant-based (66,67) eating patterns are all examples of healthful eating patterns that have shown positive results in research, but individualized meal planning should focus on personal preferences, needs, and goals. Reducing overall carbohydrate intake for individuals with diabetes has demonstrated the most evidence for improving glycemia and may be applied in a variety of eating patterns that meet individual needs and preferences. For individuals with type 2 diabetes not meeting glycemic targets or for whom reducing glucose-lowering drugs is a priority, reducing overall carbohydrate intake with a low- or very-low-carbohydrate eating pattern is a viable option (6365). As research studies on some low-carbohydrate eating plans generally indicate challenges with long-term sustainability, it is important to reassess and individualize meal plan guidance regularly for those interested in this approach. This eating pattern is not recommended at this time for women who are pregnant or lactating, people n care. Therefore, carbohydrate sources high in protein should be avoided when trying to treat or prevent hypoglycemia. Eating plans should emphasize nonstarchy vegetables, minimal added sugars, fruits, whole grains, as well as dairy products. The importance of glucose monitoring after drinking alcoholic beverages to reduce hypoglycemia risk should be emphasized. For those who consume sugarsweetened beverages regularly, a low-calorie or nonnutritive-sweetened beverage may serve as a short-term replacement strategy, but overall, people are encouraged to decrease both sweetened and nonnutritive-sweetened beverages and use other alternatives, with an emphasis on water intake. There is inadequate research in type 1 diabetes to support one eating pattern over another at this time. The diabetes plate method is commonly used for providing basic meal planning guidance (70) and provides a visual guide showing how to portion calories (featuring a 9-inch plate) and carbohydrates (by limiting them to what fits in one-quarter of the plate) and places an emphasis on low-carbohydrate (or nonstarchy) vegetables. Providing a visual/ small graphic of the diabetes plate method is preferred, as descriptions of the concept can be confusing when unfamiliar. Weight Management Management and reduction of weight is important for people with type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, or prediabetes and overweight or obesity. Lifestyle intervention programs should be intensive and have frequent follow-up to achieve significant reductions in excess body weight and improve clinical indicators. There is strong and consistent evidence that modest persistent weight loss can delay the progression from prediabetes to type 2 diabetes (58,71,72) (see Section 3 "Prevention or Delay of Type 2 Diabetes," doi. In prediabetes, the weight loss goal is 710% for preventing progression to type 2 diabetes (73). In conjunction with lifestyle therapy, medication-assisted weight loss can be considered for people at risk for type 2 diabetes when needed to achieve and sustain 710% weight loss (74,75). People with prediabetes at a healthy weight should also be considered for lifestyle intervention involving both aerobic and resistance exercise (73,76,77) and a healthy eating plan, such as a Mediterranean-style eating pattern (78). For many individuals with overweight and obesity with type 2 diabetes, 5% weight loss is needed to achieve beneficial outcomes in glycemic control, lipids, and blood pressure (79).
The guidelines for fish are as follows: cook the fish to an internal temperature of 145єF for 15 seconds; to 155єF for comminuted fish erectile dysfunction diabetes qof purchase on line kamagra super, such as fish cakes erectile dysfunction causes in early 20s buy cheap kamagra super on-line, and 165єF for stuffed fish erectile dysfunction and diabetes pdf kamagra super 160 mg on line. Commercial processors and retailers may use a specific deep-freeze process to kill parasites in fish products that are served without thorough cooking low libido erectile dysfunction treatment purchase 160 mg kamagra super visa. Two cases occurred in New Orleans, well outside the endemic area, reflecting the likelihood of interstate commerce of commercial fish containing the parasite. In some villages in eastern Siberia, more than 90% of the human population is infected with this worm. Diagnosis Differential diagnosis is indicated by gastrointestinal symptoms and a history of eating fresh raw or undercooked salmonids from endemic areas. The eggs are difficult to distinguish from those of Diphyllobothrium latum; however, the treatment for both infections is the same. Treatment Nanophyetiasis is a mild illness, and the worms will pass naturally, if the practice of eating undercooked fish is stopped. Food Analysis There are no established methods for detection of Nanophyetus salmincola cysts in fish flesh. Praziquantel for treatment of human Nanophyetus salmincola (Troglotrema salmincola) infection. Human nanophyetiasis: transmission by handling naturally infected coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch). National Center for Biotechnology Information, Taxonomy Database: Digenea Bad Bug Book Foodborne Pathogenic Microorganisms and Natural Toxins Eustrongylides species 1. Organism For Consumers: A Snapshot Five cases of infection with this worm, which humans can get by eating raw or undercooked fish, are known to have occurred in the U. Four were in fishermen who ate live minnows, one of many kinds of freshwater or saltwater fish that can carry the worm. In humans, the worms can cause severe pain within 24 hours after being eaten, as they work their way into the bowel wall. There may be some risk of infection of the sterile area that holds the bowel, if worms break through the bowel wall and into the sterile area that holds the bowel and infect that area with bowel bacteria. Disease the disease (eustrongylidiasis) is caused by these worms when contaminated live or raw fish are consumed and the larval nematode penetrates the wall of the human intestine. Mortality: None known Infective dose: One live larval worm can cause an infection. Onset: Symptoms develop within 24 hours after a contaminated live or raw fish is eaten. Symptoms: In the five cases reported, penetration of the worm into the gut wall was accompanied by severe abdominal pain. Complications: the abdominal pain is similar to appendicitis, and four of the five reported cases required investigative surgery. During surgery, worms were found in the peritoneal cavity or in the process of penetrating the gut wall. Intestinal damage and inflammation can occur during gut penetration, and other tissues could be damaged during any subsequent larval migration. The disease has the potential to cause bacterial infection of the peritoneal cavity from intestinal contents or the worm itself. In one suspected case in which surgery was not performed, the symptoms resolved in 4 days. The eggs may be eaten by, and the larvae develop in, an oligochaete worm that lives in fresh or brackish water (an intermediate host). Birds become infected by eating contaminated fish, worms, or other intermediate hosts (amphibians and reptiles also have been reported as intermediate hosts). While the parasite cannot complete its life cycle in humans, it may attach to , and penetrate, the wall of the human digestive tract. Target populations the target populations are consumers of raw or undercooked fish that have not been previously frozen to kill parasites. Four of the five cases reported resulted from fishermen swallowing live, whole minnows used for bait. Sources and prevention Eustrongylides larvae are found in the flesh and viscera of a wide variety of fish from fresh, brackish, or salt waters.
Generic 160mg kamagra super with visa. How to recover your Nitric oxide using the Humming Mask.
Interoccasion pharmacokinetic variability is high erectile dysfunction effexor xr generic 160 mg kamagra super with amex, thus requiring serum level monitoring erectile dysfunction at age 35 generic kamagra super 160mg mastercard. Side effects include fever erectile dysfunction vacuum pumps australia buy kamagra super no prescription, skin lesions erectile dysfunction medication ratings cheap 160mg kamagra super with amex, skin necrosis (especially in protein C deficiency), anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, hemorrhage, and hemoptysis. A cohort study of 319 children found that infants < 1 yr required an average daily dose of 0. Pregnancy category is "D" for women with mechanical heart valves and "X" for all others indications. Use in combination with lamivudine or emtricitabine and with either one of the following: lopinavir/ritonavir, atazanavir/ ritonavir, darunavir/ritonavir, raltegravir, etravirine, or etravirine Ч 28 days. Dosage reduction is recommended in severe renal impairment and may be necessary in hepatic dysfunction. Seizures, confusion, rash, myositis, myopathy (use > 1 yr), hepatitis, and elevated liver enzymes have been reported. Macrocytosis is noted after 4 wk of therapy and can be used as an indicator of compliance. Effects of interacting drugs include increased toxicity (acyclovir and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole); increased hematological toxicity (ganciclovir, interferon-, and marrow suppressive drugs); and granulocytopenia (drugs which affect glucuronidation). Methadone, atovaquone, cimetidine, valproic acid, probenecid, and fluconazole may increase levels of zidovudine. Despite manufacturer recommendations of administering oral doses 30 min prior to or 1 hr after meals, doses may be administered with food. Patients with excessive losses (burns) or impaired absorption require higher doses. May decrease the absorption of penicillamine, tetracycline, and fluoroquinolones. Nasal (safety of an average of >4 headaches in a 30 day period has not been established; see remarks): 12 yr and adult: Start with 2. Patients with multiple cardiovascular risk factors and negative cardiovascular evaluation should have their first dose administered in a medically supervised facility. Common adverse reactions for all dosage forms unless otherwise indicated include nausea, taste alteration (nasal route), xerostomia, dizziness, hyperesthesia (nasal route), paresthesia, somnolence, sensation of hot and cold, throat pain, and asthenia (oral route). Then increase by 25 mg/kg/24 hr every 24 day until seizures disappear, up to a maximum of 20 mg/kg/24 hr. Additional dosage increments of 100 mg/24 hr can be made at 2 wk intervals to allow attainment of steady-state levels. Common side effects of drowsiness, ataxia, anorexia, gastrointestinal discomfort, headache, rash, and pruritis usually occur early in therapy and can be minimized with slow dose titration. Children are at increased risk for hyperthermia and oligohydrosis, especially in warm or hot weather. Although not fully delineated, therapeutic serum levels of 2030 mg/L have been suggested as higher rates of adverse reactions have been seen at levels > 30 mg/L. Use with caution in renal or hepatic impairment; slower dose titration and more frequent monitoring is recommended. National Institutes of Health: National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute Expert Panel. Clinical practice guidelines: Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma. The Management of CommunityAcquired Pneumonia in Infants and Children Older Than 3 Months of Age: Clinical Practice Guidelines by the Pediatric Infectious Disease Society and the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Updated Guidance for Palivizumab Prophylaxis Among Infants and Young Children at Increased Risk of Hospitalization for Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection. National High Blood Pressure Education Program Working Group on High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents. The Fourth Report on the Diagnosis, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents.
Ocular toxicity has been reported in adults taking ethambutol experimental erectile dysfunction drugs buy kamagra super with paypal, but changes in visual acuity have not been detected in infants exposed to ethambutol in utero erectile dysfunction quick natural remedies cheap kamagra super 160mg amex. However impotence stress generic kamagra super 160 mg visa, studies evaluating quinolone use in pregnant women did not find an increased risk of birth defects or congenital musculoskeletal abnormalities impotent rage definition discount kamagra super 160mg line. Ethionamide has been associated with an increased risk for several anomalies in rats after high-dose exposure but not in mice and rabbits. No data are available from animal studies or reports of cycloserine use in humans during pregnancy. A prospective study of the risk of tuberculosis among intravenous drug users with human immunodeficiency virus infection. Effect of highly active antiretroviral therapy on incidence of tuberculosis in South Africa: a cohort study. Isoniazid plus antiretroviral therapy to prevent tuberculosis: a randomised double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Risk factors for active tuberculosis after antiretroviral treatment initiation in Abidjan. Tuberculosis infection in the United States: prevalence estimates from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2011-2012. Trends in tuberculosis/human immunodeficiency virus comorbidity, United States, 1993-2004. Priorities for the treatment of latent tuberculosis infection in the United States. A controlled trial of isoniazid in persons with anergy and human immunodeficiency virus infection who are at high risk for tuberculosis. Comparison of T-cell-based assay with tuberculin skin test for diagnosis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in a school tuberculosis outbreak. Meta-analysis: new tests for the diagnosis of latent tuberculosis infection: areas of uncertainty and recommendations for research. Interferon-gamma release assays and tuberculin skin testing for diagnosis of latent tuberculosis infection in healthcare workers in the United States. Predictive value of interferon-gamma release assays for incident active tuberculosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Updated guidelines for using interferon gamma release assays to detect Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection-United States, 2010. A trial of three regimens to prevent tuberculosis in Ugandan adults infected with the human immunodeficiency virus. Adverse events with 4 months of rifampin therapy or 9 months of isoniazid therapy for latent tuberculosis infection: a randomized trial. Adherence to treatment of latent tuberculosis infection in a clinical population in New York City. Latent tuberculosis infection: updated and consolidated guidelines for programmatic management. Self-administered versus directly observed once-weekly isoniazid and rifapentine treatment of latent tuberculosis infection: a randomized trial. Update of recommendations for use of once-weekly isoniazid-rifapentine regimen to treat latent Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Four months of rifampin or nine months of isoniazid for latent tuberculosis in adults. Risk factors for hepatotoxicity associated with rifampin and pyrazinamide for the treatment of latent tuberculosis infection: experience from three public health tuberculosis clinics. Pyrazinamide and rifampin vs isoniazid for the treatment of latent tuberculosis: improved completion rates but more hepatotoxicity. Optimizing tuberculosis diagnosis in human immunodeficiency virusinfected inpatients meeting the criteria of seriously ill in the World Health Organization algorithm. Impact of human immunodeficiency virus infection on clinical and radiographic presentation. Variation of chest radiographic patterns in pulmonary tuberculosis by degree of human immunodeficiency virus-related immunosuppression.