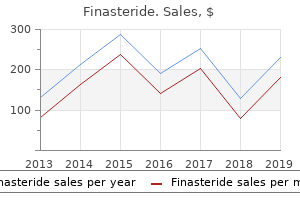
"Discount 1mg finasteride overnight delivery, hair loss cure when".
By: Y. Vasco, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., Ph.D.
Clinical Director, Jacobs School of Medicine and Biomedical Sciences, University at Buffalo
Hypoplasia: Underdevelopment or incomplete development of an organ or tissue in the body hair loss juicing order finasteride 5 mg on-line. This condition can contribute to reproductive issues hair loss 30 year old woman purchase finasteride 1mg with visa, including irregular periods and difficulty becoming pregnant hair loss cure toronto purchase cheap finasteride on-line. Impaired glucose tolerance: People with impaired glucose tolerance have trouble breaking down the sugars found in their diets hair loss 5 months postpartum discount finasteride 5 mg without prescription, but they do not yet have diabetes. For example, health problems associated with bone marrow transplant that develop months or years after the procedure. Leukemia: Leukemia is a group of bone marrow diseases involving an uncontrolled increase in white blood cells (leukocytes). Lymphocyte: Type of white blood cell that fights infection by producing antibodies and other protective substances. Macrophage: A white blood cell that helps to destroy invading microorganisms and is involved in the immune response. This syndrome encompasses a group of health conditions that develop when a certain type of blood cells (known as the myeloid class of blood cells) are not present in sufficient numbers in the bone marrow. Short segments of ribonucleic acid that bind to and turn off specific products of the genetic code. Neutropenia: A health condition characterized by abnormally low levels of neutrophils in the blood. This United States-based program operates the Be the Match Registry of volunteer bone marrow, hematopoietic cell, and umbilical cord blood donors. Opportunistic infection: this type of infection is common in immunecompromised patients who are unable to fight off microbes that do not normally cause disease in humans. Oxidative stress: Occurs when the levels of oxygen and its breakdown products, reactive oxygen species, are too high in cells. Pap test: A gynecological test used to detect cervical cancer and precancerous lesions. A condition that occurs when blood vessels in the liver called sinusoids become excessively dilated and form large blood-filled spaces, like cysts, that are scattered throughout the liver. Disc-like fragments of cells that circulate in the bloodstream and help promote clotting at the site of a cut or injury. Pluripotent stem cells: Cells capable of developing into almost any type of cell in the body. Stem cells can be found in embryos, in umbilical cord blood, and in the blood and bone marrow of adults. Polypharmacy: the administration of many different medicines during the treatment for the same disease. Pouce flottant: A so-called "floating" thumb that lacks bones and is composed of skin and soft tissue. Radius: Of the two long bones in the forearm, the radius is the shorter and thicker one. Recessive: A mutation is said to be recessive if an individual must inherit two copies of the mutant gene, to have the disease. Short bowel syndrome: this condition occurs when nutrients from food are not properly absorbed because a large segment of the small intestine is nonfunctional or has been surgically removed. Stem cells: Cells that can develop into one of many types of specialized cells in the body. Stem cell gene therapy: A novel treatment that combines gene therapy and stem cell therapy in an effort to correct a faulty gene in the stem cells of the recipient. Stem cells are obtained from the patient, grown and "corrected" in a laboratory, and then returned to the patient. T cells: White blood cells that play a key role in the immune response by searching out and destroying material that is considered "foreign. An abnormal passage between the esophagus and the trachea, or windpipe, that may result in food from the esophagus crossing into the airways or air entering the esophagus. Transferrin saturation: the amount of iron carried by the transferrin protein in the blood. Triphalangeal thumb: A thumb that has an extra bone (called a phalanx) that can vary in size and shape. Unsaturated iron binding capacity test: A test that reveals the amount of transferrin that is not being used to transport iron.
Though memory is affected hair loss young men purchase finasteride us, language hair loss in men young buy 5mg finasteride fast delivery, praxis and visuo-spatial skills are relatively spared hair loss cure-7 cheap finasteride 1 mg on line, at least initially hair loss 10 months after baby generic 5 mg finasteride with visa. Neuropsychological evaluation Distributed and localized cognitive function may be assessed clinically using the various components of the examination outlined briefly in this chapter. This 30-point test includes questions which assess orientation, attention, memory, language and visuo-spatial function. However, this overall test score is insensitive to early dementia, particularly if premorbid intellectual ability was superior, and to circumscribed cognitive deficits, especially those involving non-dominant hemisphere and frontal lobe function. Many patients with cognitive deficits require more detailed psychometric evaluation by a neuropsychologist. Dementia Dementia may be defined as acquired global impairment of intellectual function, usually progressive, and occurring in a setting of clear consciousness. More precisely, a demented patient has significant impairment of two or more areas of cognition (one of which must be memory, the other domains being language, praxis, visuo-spatial skills, personality, social behaviour or abstract thought) in the absence of delirium and of psychiatric disease, such as depression or schizophrenia, which may mimic dementia. Cortical and subcortical dementia A useful subdivision of dementias is between those where the cerebral cortex is the primary site of disease and those with major involvement of subcortical structures (though some disorders present a mixed picture). In cortical dementias, patients have impaired memory, language, praxis and/or visuo-spatial function. Subcortical dementias are more characterized by slowing of cognitive function (bradyphrenia) and by personality and mood disturbances. Patients appear apathetic and Key points Cognitive function may be subclassified as distributed or localized (to a particular part of the brain) the hallmark of delirium is impaired attention and concentration Persistent memory failure may occur in isolation (amnesic syndrome) or in association with other cognitive deficits (dementia) Dysphasia is impairment of language function due to brain damage the non-dominant hemisphere is largely responsible for visuo-spatial skills 16 Chapter 4 Vision and other cranial nerves the human brain is highly adapted for processing visual information. The topical diagnosis of dysfunction in the anterior visual pathways and ocular motility disorders depends upon careful neuro-ophthalmological examination involving the upper cranial nerves. The olfactory pathways may give rise to positive, as well as negative, clinical features, in their most extreme form olfactory hallucinations, as occur in epilepsy of temporal lobe origin (Chapter 10). I: Olfactory nerve In a routine cranial nerve examination, it is sufficient simply to ask whether the patient has been aware of any deterioration in sense of smell. If the history indicates the need for more detailed assessment, each nostril should be tested individually with bottles containing various aromatic oils. It is more important for the patient to be able to detect different odours than to name them accurately. Care must be taken to distinguish between substances stimulating the olfactory nerves, and more pungent, irritant chemicals. Patients who have lost their sense of smell (anosmia) will still respond to ammonia, via this alternative pathway. This is best examined with a Snellen chart, the patient reading the lines of letters from a distance 17 Chapter 4 Vision and other cranial nerves 6 metres 1 metre Figure 4. Each eye is tested individually, and refractive errors are corrected either with lenses or by looking through a pinhole. Acuity is expressed as a fraction, the numerator being the distance between patient and chart, and the denominator being given by the line of letters of smallest size the patient can read accurately. Near vision charts, which involve reading print of varying size, are primarily useful in assessing the need for near correction but are a valuable additional test, particularly in patients with visual field defects who may find it difficult to locate the letters on a distance chart. Visual acuity is impaired early in diseases of the optic nerve and in retinal conditions involving the macula. A red pin is useful for assessing small areas of defective vision (scotomas), caused by retinal disease or optic neuropathy. Relative scotomas can be detected when the target does not disappear completely but the colour is lost. Lesions posterior to the optic chiasm are often detectable with much larger stimuli. Nerve fibres in the visual pathways retain a crude spatial relationship to each other, reflecting their origin in the retina. This fact and the partial decussation of the pathways at the optic chiasm produce characteristic patterns of visual field disturbance, which greatly aid in lesion localization.
Junctional Flexibility Adds Diversity the enormous diversity generated by means of V hair loss treatments that really work order genuine finasteride online, D hair loss radiation order finasteride online now, and J combinations is further augmented by a phenomenon called junctional flexibility hair loss in men from stress generic 1mg finasteride amex. As described above hair loss cure 3 bolt cheap 1mg finasteride amex, recombination involves both the joining of recombination signal sequences to form a signal joint and the joining of coding sequences to form a coding joint (see Figure 5-7). Although the signal sequences are always joined precisely, joining of the coding sequences is often imprecise. In one study, for example, joining of the V 21 and J 1 coding sequences was analyzed in several pre-B cell lines. Sequence analysis of the signal and coding joints revealed the contrast in junctional precision (Figure 5-12). As illustrated previously, junctional flexibility leads to many nonproductive rearrangements, but it also generates productive combinations that encode alternative amino acids at each coding joint (see Figure 5-9), thereby increasing antibody diversity. The immunoglobulin loci of other individuals might contain slightly different numbers of particular types of gene segments. The genome contains additional segments that are incapable of rearrangement or contain stop codons or both. In the mouse case, the figures contained in the table are only best estimates, because the locus has not been completely sequenced. Because of the diversity contributed by junctional flexibility, P-region nucleotide addition, N-region nucleotide addition, and somatic mutation, the actual potential exceeds these estimates by several orders of magnitude. The nucleotide sequences flanking the coding joints between V 21 and J 1 and the corresponding signal joint sequences were determined in four pre-B cell lines. The sequence constancy in the signal joints contrasts with the sequence variability in the coding joints. This second cleavage sometimes occurs at a position that leaves a short single strand at the end of the coding sequence. The subsequent addition of complementary nucleotides to this strand (P-addition) by repair enzymes generates a palindromic sequence in the coding joint, and so these nucleotides are called P-nucleotides (Figure 5-13a). Variation in the position at which the hairpin is cut thus leads to variation in the sequence of the coding joint. Evidence that TdThis responsible for the addition of these N-nucleotides has come from transfection studies in fibroblasts. However, when the fibroblasts were also transfected with the gene encoding TdT, then V-D-J rearrangement was accompanied by addition of N-nucleotides at the coding joints. The additional heavychain diversity generated by N-region nucleotide addition is quite large because N regions appear to consist of wholly random sequences. Somatic Hypermutation Adds Diversity in Already-Rearranged Gene Segments All the antibody diversity described so far stems from mechanisms that operate during formation of specific variable regions by gene rearrangement. Additional antibody diversity is generated in rearranged variable-region gene units by a process called somatic hypermutation. Normally, somatic hypermutation occurs only within germinal centers (see Chapter 11), structures that form in secondary lymphoid organs within a week or so of immunization with an antigen that activates a T-cell-dependent B-cell response. Somatic hypermutation occurs at a frequency approaching 10 3 per base pair per generation. This rate is at least a hundred thousand-fold higher (hence the name hypermutation) than the spontaneous mutation rate, about 10 8/bp/generation, in other genes. Most of the mutations are nucleotide substitutions rather than deletions or insertions. Somatic hypermutation introduces these substitutions in a largely, but not completely, random fashion. Following exposure to antigen, those B cells with higher-affinity receptors will be preferentially selected for survival. This result of this N-Addition Adds Considerable Diversity by Addition of Nucleotides Variable-region coding joints in rearranged heavy-chain genes have been shown to contain short amino acid sequences that are not encoded by the germ-line V, D, or J gene segments. During subsequent repair, complementary nucleotides are added, called P-nucleotides, to produce palin- dromic sequences (indicated by brackets).
Demographics hair loss cure march 2013 discount 1 mg finasteride visa, Eligibility Verification hair loss cure jock discount finasteride 5 mg with visa, Medical History hair loss 3 months after stress generic finasteride 5 mg mastercard, Historical and Concomitant Medications Patient demographics will be recorded on the demography source documents hair loss medication side effects order finasteride 1mg with visa. The Investigator or designated staff will review inclusion/exclusion criteria to verify eligibility. For subjects enrolling into the retreatment cohort, demographic information and detailed medical history will not be re-collected. Physical Exam A complete physical examination will be performed by the investigator according to Table 6-1. Weight will be measured in kilograms and recorded in the Vital Signs source documents. Blood pressure and pulse should be measured on patients after at least 3 minutes in the sitting position. Vital signs will be taken 10 minutes prior to and 10 minutes immediately after each infusion and then every 15 minutes for at least one hour and then every hour for the next two hours until these signs are satisfactory and stable. Up and about more than 50% of waking hours Capable of only limited self-care, confined to bed or chair more than 50% of waking hours Completely disabled. Local Laboratory Evaluations Pre-entry, screening and other laboratory assessments will be performed accordingly to Table 61. The Investigator will evaluate the clinical significance of each applicable laboratory value outside of the reference range. This decision shall be based upon the nature and degree of the observed abnormality. The Investigator may choose to repeat any abnormal result once, in order to rule out laboratory error. Serum Immunoglobulin Levels Peripheral blood will be sampled at screening and accordingly to Table 6-1, for analysis of serum immunoglobulin. Pregnancy Testing Women of child-bearing potential, defined as all women physiologically capable of becoming pregnant, must use effective contraception (see Section 4. Additionally, if menses is delayed for more than 7 days, the patient should be instructed to conduct a urine pregnancy to rule out any possibility of pregnancy. Patients should be instructed to inform site of any positive urine pregnancy results not conducted at the clinic. Repeat serum pregnancy testing will be performed for confirmation of a positive urine pregnancy test. Research Assessments to Assess Engraftment, Persistence and Bioactivity the following assessments will be collected according to Tables 6-1 and 6-2 and will be analyzed as described below. For cytokine analyses peripheral blood and marrow samples will be collected in red top (no additive) tubes. An additional larger blood draw (~100cc) on Day 28 will be drawn and archived for future research purposes. Quality of Life (QoL) Quality of life questionnaires will be administered at screening and again at Months 3 and 6. If site staff is administering to the patient, the questions should be described to elicit patient experiences, opinions and observations on how their disease is affecting them. Complete Enrollment Form (including patient past medical history, laboratory, radiological reports, physical exam, concomitant medications and any other source documentation to support patient meets eligibility criteria and has completed all required screening assessments) 2. After a subject has passed all screening procedures and is ready to be enrolled, the subject is enrolled using the same Subject No. If the subject fails screening for any reason, the reason will be entered into the Screening Disposition page. For patients that do not have a historical apheresis available, a 4-6 blood volume apheresis procedure will be carried out at the apheresis center during the screening procedures. If this is the case, the patient therefore would not have to repeat the baseline apheresis on this study. Apheresis Visit Procedure this material is the property of the University of Pennsylvania. In addition, chemotherapy can potentiate the ability of T cells to kill tumor cells116, 117. If the patient is positive for influenza, oseltamivir phosphate (Tamiflu) or equivalent should be administered (see Tamiflu package insert for dosing information). If clinical symptoms develop, the infusion will be delayed until resolution of these symptoms.
Generic 5 mg finasteride with mastercard. Hrithik Roshan क्यों गंजे नहीं हुए ? How to Stop Genetic Hair Fall or DHT like Hrithik Roshan ?.