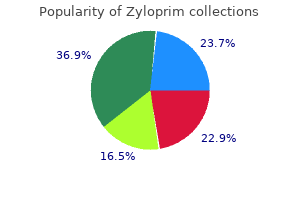
"Order genuine zyloprim online, treatment variable".
By: S. Grim, MD
Assistant Professor, Michigan State University College of Osteopathic Medicine
The subtle sphere (or the "soul symptoms your having a girl order zyloprim now," as Christians mystics use that term) is the beginning of the transpersonal realms; as such symptoms vs signs zyloprim 100mg sale, it is supramental treatment quotes images zyloprim 300 mg with amex, transegoic medicine reactions generic zyloprim 100 mg free shipping, and transverbal. But in order to reach that sphere, one must (as in all transformations) "die" to the lower sphere (in this case, the mental-egoic). As the person with an Oedipus complex remains unconsciously attached to the body and its pleasure principle, so the person with an Apollo complex remains unconsciously attached to the mind and its reality principle. As it was, I was fortunate to make some progress, to be able eventually to rise above the 377 fluctuations of mental contractions and discover, however initially, a realm incomparably more profound, more real, more saturated with being, more open to clarity. Many of the problems that we face in our personal lives, and in our life with "others" have to do with an overly dogged attachment to our limited self, our personal concerns, our boundaries, our needs, our particular culture, worldviews, ideas, and ways of being to the exclusion of the concerns all others. We suffer in our rigid individualism, often alone and feeling fearful and beset on all sides by "others," not to mention the impermanent, limited time and power we have to express our individuality in this short life. Mystics the world over suggest that ultimately, we have forgotten something, or that in this life there is an even larger reality beyond individuality, division, boundaries, time, and space which knows no limits whatsoever, and yet is the very fabric of our being, the very awareness looking out of these eyes, listening with these ears at this very moment, and every moment from beginingless time. We seek for Spirit in the world of time, but Spirit is timeless, and cannot there be found. We seek for Spirit in the world of space; but Spirit is spaceless, and cannot there be found. We seek for Spirit in this or that object, shiny and alluring and full of fame or fortune; but Spirit is not an object, and it cannot be seen or grasped in the world of commodities and commotion. The One is the Goodness from which all things flow: It is the Origin and Source of all manifestation, at all times, in all places. All things, high or low, sacred or profane, yesterday or tomorrow, issue forth from the divine Fountainhead, the Source of All, the Origin of all. The One as Goodness is the first cause of all causes; it is the alpha point of all worlds; and as such, all worlds express the Goodness, the compassion, the love and superabundance of the Divine. The Absolute is the Nondual Ground of both the One and the Many: It is equally and both Good and Goodness, One and Many, Ascent and Descent, Alpha and Omega, Wisdom and Compassion. Both Ascending and Descending paths express profound truths- neither of their truths is denied (in fact, both are strongly asserted). But neither path alone expressed the whole Truth, and neither path alone 36 Wilber, Ken. Reality is not just summit (Omega) and not just source (Alpha), but is Suchness- the timeless and ever-present Ground which is equally and fully present in and as every single being, high or low, ascending or descending. This is the absolutely transpersonal, transcendent experience and recognition of total Unity that we ultimately seek. And those who find it best, develop a full and healthy enough personal self to build on, and eventually release, in that space of transcendent witnessing that Spirit is the Ground and Goal and Substance of all things. This is the domain of mystics in all world religious traditions, from Christian mystics to Sufi, Kabbalist, Hindu, and Buddhist mystics. With Big Mind, no one is higher or lower, in or out, worthy or unworthy; there is no limit to time, space, or being. Moreover, the skills that you used to get "up there" play into whether or not you have the oxygen, the skills, the time, the energy to come back down off the mountain and reengage with the world as-it-is, moment to moment. Getting off the mountain, for most climbers of Everest, is actually the most challenging and perilous part of the climb. The Return of the Hero after he has already gotten what he went for, can be frought with danger itself of many varieties. The full round, the norm of the monomyth, requires that the hero shall now begin the labor of bringing the runes of wisdom, the Golden Fleece, or his sleeping princess, back into the kingdom of humanity, where the boon may redound to the renewing of the community, the nation, the planet or the ten thousand worlds. Even the Buddha, after his triumph, doubted whether the message of realization could be communicated, and saints are reported to have passed away while in the supernal ecstasy. Numerous indeed are the heroes fabled to have taken up residence forever in the blessed isle of the unaging Goddess of Immortal Being. Yet there is even more than Bliss, more than Oneness, more than merely summitting the mountain. The descent, the reentry, the translation of what you have witnessed, experienced, and realized (from prepresonal to personal to transpersonal, from self-needs to self-actualization to selftranscendence) as a permanent acquisition needs to be made plain to the world of the many.
The parietal layer of lateral plate mesoderm then forms the dermis of the skin in the body wall and limbs xerostomia medications side effects order zyloprim master card, the bones and connective tissue of the limbs medicine januvia buy discount zyloprim 100 mg line, and the sternum symptoms thyroid purchase generic zyloprim online. In addition treatment locator buy cheap zyloprim online, sclerotome and muscle precursor cells that migrate into the parietal layer of lateral plate mesoderm form the costal cartilages, limb muscles, and most of the body wall muscles (see Chapter 11). The visceral layer of lateral plate mesoderm, together with embryonic endoderm, forms the wall of the gut tube. Mesoderm cells of the parietal layer surrounding the intraembryonic cavity form thin membranes, the mesothelial membranes, or serous membranes, which will line the peritoneal, pleural, and pericardial cavities and secrete serous fluid. Mesoderm cells of the visceral layer form a thin serous membrane around each organ (see Chapter 7). Blood vessels form in two ways: vasculogenesis, whereby vessels arise from blood islands. The first blood islands appear in mesoderm surrounding the wall of the yolk sac at 3 weeks of development and slightly later in lateral plate mesoderm and other regions. These islands arise from mesoderm cells that are induced to form hemangioblasts, a common precursor for vessel and blood cell formation. Although the first blood cells arise in blood islands in the wall of the yolk sac, this population is transitory. These cells colonize the liver, which becomes the major hematopoietic organ of the embryo and Amniotic cavity Ectoderm Mesonephros Dorsal mesentery Visceral mesoderm layer Parietal mesoderm layer Wall of gut Serous membrane (peritoneum) Body wall Parietal mesoderm layer Intraembryonic cavity Endoderm of yolk sac A B Figure 6. Cross section through a 21-day embryo in the region of the mesonephros showing parietal and visceral mesoderm layers. The intraembryonic cavities communicate with the extraembryonic cavity (chorionic cavity). Villus Amnionic cavity Amnion Blood vessel Heart Pericardial cavity Allantois Connecting stalk Chorion Blood vessel Yolk sac Blood island presomite embryo of approximately 19 days. This germ layer covers the ventral surface of the embryo and forms the roof of the yolk sac. With development and growth of the brain vesicles, however, the embryonic disc begins to bulge into the amniotic cavity. Lengthening of the neural tube now causes the embryo to curve into the fetal position as the head and tail regions (folds) move ventrally. Simultaneously, two lateral body wall folds form and also move ventrally to close the ventral body wall. As the head and tail and two lateral folds move ventrally, they pull the amnion down with them, such that the embryo lies within the amniotic cavity. The ventral body wall closes completely except for the umbilical region where the connecting stalk and yolk sac duct remain attached. Failure of the lateral body folds to close the body wall results in ventral body wall defects (see Chapter 7). As a result of cephalocaudal growth and closure of the lateral body wall folds a continuously larger portion of the endodermal germ layer is incorporated into the body of the embryo to form the gut tube. The midgut communicates with the yolk sac by way of a broad stalk, the vitelline (yolk sac) duct. This duct is wide initially, but with further growth of the embryo, it becomes narrow and much longer. This membrane separates the stomadeum, the primitive oral cavity derived from ectoderm, from the pharynx, a part of the foregut derived from endoderm. In the fourth week, the oropharngeal membrane ruptures, establishing an open connection between the oral cavity and the primitive gut. This membrane separates the upper part of the anal canal, derived from endoderm, from the lower part, called the proctodeum, which is formed by an invaginating pit lined by ectoderm. The membrane breaks Hindgut Foregut Amniotic Endoderm cavity Cloacal Heart membrane tube Ectoderm Connecting stalk Angiogenic cell cluster Allantois Pericardial cavity Oropharyngeal membrane A Oropharyngeal membrane Cloacal membrane B Lung bud Liver bud Midgut Heart tube Remnant of the oropharyngeal membrane Vitelline duct Allantois C D Yolk sac Figure 6.
Continuous proliferation of epithelial cells at the base of the shaft pushes the hair upward medications to avoid during pregnancy order zyloprim american express, and by the end of the third month medicine 74 effective 300 mg zyloprim, the first hairs appear on the surface in the region of the eyebrow and upper lip symptoms graves disease discount 300mg zyloprim with amex. The first hair that appears medicine 014 purchase zyloprim 300 mg with visa, lanugo hair, is shed at about the time of birth and is later replaced by coarser hairs arising from new hair follicles. The epithelial wall of the hair follicle usually shows a small bud penetrating the surrounding mesoderm. Cells from the central region of the gland degenerate, forming a fat-like substance (sebum) secreted into the hair follicle, and from there, it reaches the skin. Epidermis Sebaceous gland Smooth muscle fibers Hair bud Dermal root sheath A Hair shaft Epithelial hair sheath Hair papilla Blood vessel B C Figure 21. Proliferation of mammary ridge Epidermis Mesenchyme Position of accessory nipples A Epithelial pit Mammary line Lactiferous duct B C 344 Part 1I Systems-Based Embryology 20 weeks, the fetus is covered by downy hair, lanugo hair, which is shed at the time of birth. Sebaceous glands, sweat glands, and mammary glands all develop from epidermal proliferations. Supernumerary nipples (polythelia) and breasts (polymastia) are relatively common. A woman appears to have accessory nipples in her axilla and on her abdomen bilaterally. What is the embryological basis for these additional nipples, and why do they occur in these locations During the process of induction, one group of cells or tissues (the inducer) causes another group (the responder) to change its fate. The responding cells must have the competence to respond, which is conferred by a competency factor. For example, even subtle alterations of the ligand and/or its receptor can alter signaling because of the high degree of specificity between these proteins. Also, if any of the proteins in the signaling cascade downstream from receptor activation have been altered, then normal signaling may be disrupted. Fortunately, there is redundancy built into the system that can circumvent alterations in the pathways. The most common cause for abnormal chromosome number is nondisjunction during either meiosis or mitosis. If fertilization occurs between a gamete lacking a chromosome and a normal one, monosomy results; if it occurs between a gamete with two copies and a normal one, trisomy results. Trisomy 21 (Down syndrome), the most common numerical abnormality resulting in birth defects (intellectual disability, abnormal facies, heart malformations), is usually caused by nondisjunction in the mother and occurs most frequently in children born to women older than 35 years of age, reflecting the fact that the risk of meiotic nondisjunction increases with increasing maternal age. Other trisomies that result in syndromes of abnormal development involve chromosomes 8, 9, 13, and 18. Monosomies involving autosomal chromosomes are fatal, but monosomy of the X chromosome (Turner syndrome) is compatible with life. This condition is usually (80%) a result of nondisjunction during meiosis of paternal chromosomes and is characterized by infertility, short stature, webbing of the neck, and other defects. Karyotyping of embryonic cells obtained by amniocentesis or chorionic villus biopsy (see Clinical Correlates in Chapter 9) can detect chromosome abnormalities prenatally. Chromosomes sometimes break, and the pieces may create partial monosomies or trisomies or become attached (translocated) to other chromosomes. Translocation of part of chromosome 21 onto chromosome 14, for example, accounts for approximately 4% of cases of Down syndrome. The risk of chromosomal abnormalities is increased by maternal and paternal age over 35 years. Mosaicism occurs when an individual has two or more cell lines that are derived from a single zygote but that have different genetic characteristics. The different cell lines may arise by mutation or by mitotic nondisjunction during cleavage, as in some cases of Down syndrome. The role of the corpus luteum is to produce hormones essential for preparing the uterus for pregnancy and then for maintaining that pregnancy until the placenta becomes fully 347 348 Answers to Problems functional (approximately the beginning of the fourth month). Initially, progesterone is the primary hormone produced, and it causes the uterus to enter the progestational (secretory) phase. The corpus luteum originates from the theca interna (derived from ovarian stromal cells) and from granulosa cells that remain in the ovary after ovulation.
Syndromes
- Complete physical exam
- Arthritis of the knee
- Be asked to do a lot of deep breathing to help prevent pneumonia and infection. Deep breathing exercises also help inflate the lung that was operated on. Your chest tube(s) will remain in place until your lung has fully inflated.
- Problems with bone marrow such as lymphoma, leukemia, multiple myeloma, or aplastic anemia
- Fatigue
- Slow heart rate
- CT scan of the head
- Genetic diseases and chromosomal abnormalities, including Marfan syndrome, Down syndrome, Apert syndrome, Basal cell nevus syndrome
Peritoneal ligaments are double layers of peritoneum (mesenteries) that pass from one organ to another or from an organ to the body wall medicine 360 order zyloprim online from canada. Mesenteries and ligaments provide pathways for vessels symptoms 4dp5dt fet purchase zyloprim with paypal, nerves medications safe while breastfeeding generic zyloprim 100 mg otc, and lymphatics to and from abdominal viscera symptoms 1dpo effective zyloprim 300mg. Initially the foregut, midgut, and hindgut are in broad contact with the mesenchyme of the posterior abdominal wall. By the fifth week, however, the connecting tissue bridge has Bare area of liver Diaphragm Falciform ligament Dorsal mesogastrium Celiac artery Dorsal mesoduodenum Vitelline duct Superior mesenteric artery Mesentery proper Allantois Inferior mesenteric artery Cloaca Umbilical artery Dorsal mesocolon Figure 15. The liver is connected to the ventral abdominal wall and to the stomach by the falciform ligament and lesser omentum, respectively. The superior mesenteric artery runs through the mesentery proper and continues toward the yolk sac as the vitelline artery. Chapter 15 Pharyngeal pouches Pharyngeal gut Tracheobronchial diverticulum Esophagus Stomodeum Liver Gallbladder Vitelline duct Allantois Proctodeum Cloaca Stomach Pancreas Primitive intestinal loop Hindgut Heart bulge Urinary bladder Cloacal membrane Digestive System 211 Esophagus A B Figure 15. In the region of the stomach, it forms the dorsal mesogastrium or greater omentum; in the region of the duodenum, it forms the dorsal mesoduodenum; and in the region of the colon, it forms the dorsal mesocolon. Ventral mesentery, which exists only in the region of the terminal part of the esophagus, the stomach, and the upper part of the duodenum. Growth of the liver into the mesenchyme of the septum transversum divides the ventral mesentery into (a) the lesser omentum, extending from the lower portion of the esophagus, the stomach, and the upper portion of the duodenum to the liver and (b) the falciform ligament, extending from the liver to the ventral body wall. The tracheoesophageal septum gradually partitions this diverticulum from the dorsal part of the foregut. In this manner, the foregut Foregut Tracheoesophageal septum Pharynx Trachea Respiratory diverticulum Lung buds A B C Esophagus Figure 15. Trachea Bifurcation Proximal blindend part of esophagus Tracheoesophageal fistula Communication of esophagus with trachea Bronchi A Distal part of esophagus B C D E Chapter 15 Longitudinal rotation axis Digestive System 213 Lesser curvature Stomach Duodenum A B Esophagus C Greater curvature Anteroposterior axis Lesser curvature D Pylorus Greater curvature E Greater curvature Figure 15. Hence, the left vagus nerve, initially innervating the left side of the stomach, now innervates the anterior wall; similarly, the right nerve innervates the posterior wall. During this rotation, the original posterior wall of the stomach grows faster than the anterior portion, forming the greater and lesser curvatures. The cephalic and caudal ends of the stomach originally lie in the midline, but during further growth, the stomach rotates around an anteroposterior axis, such that the caudal or pyloric part moves to the right and upward, and the cephalic or cardiac portion moves to the left and slightly downward. The stomach thus assumes its final position, its axis running from above left to below right. Since the stomach is attached to the dorsal body wall by the dorsal mesogastrium and to the ventral body wall by the ventral mesogastrium. Rotation about the longitudinal axis pulls the dorsal mesogastrium to the left, creating a space behind the stomach called the omental bursa (lesser peritoneal sac). As this process continues in the fifth week of development, the spleen primordium appears as a mesodermal proliferation between the two leaves of the dorsal mesogastrium. With continued rotation of the stomach, the dorsal mesogastrium lengthens, and the portion between the spleen and dorsal midline swings to the left and fuses with the peritoneum of the posterior abdominal wall. The posterior leaf of the dorsal mesogastrium and the peritoneum along this line of fusion degenerate. The spleen, which remains intraperitoneal, is then connected to the body wall in the region of the left kidney by the lienorenal ligament and to the stomach by the gastrolienal ligament. Lengthening and fusion of the dorsal mesogastrium to the posterior body wall also determine the final position of the pancreas. Initially, the organ grows into the dorsal mesoduodenum, but eventually its tail extends into the dorsal mesogastrium. Transverse section through a 4-week embryo showing intercellular clefts appearing in the dorsal mesogastrium. The clefts have fused, and the omental bursa is formed as an extension of the right side of the intraembryonic cavity behind the stomach. Lesser omentum Liver Lesser Omental omentum bursa Liver Dorsal mesogastrium Dorsal pancreas Falciform ligament Stomach Spleen Lienorenal ligament A Umbilical vein Falciform ligament B Gastrolienal ligament Figure 15.
Generic zyloprim 100mg otc. Cold and flu Causes And SymptomsInfluenza VirusCauses of Cold And FluCold And Flu Influenza Virus.