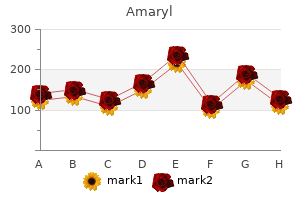
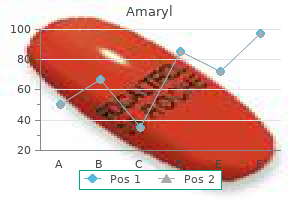
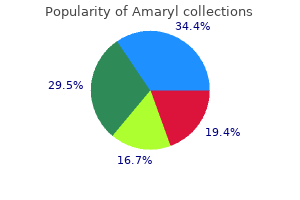
"Cheap 3mg amaryl otc, diabetes medications australia".
By: B. Jack, M.A., M.D., Ph.D.
Vice Chair, Lake Erie College of Osteopathic Medicine
Environmental risk factors associated with pediatric idiopathic pulmonary hemorrhage/hemosiderosis in a Cleveland community metabolic disease 7 letters generic amaryl 1mg without a prescription. Pulmonary hemosiderosis diabetes diet in french discount 4 mg amaryl mastercard, hemorrhagic syndromes and other rare infiltrative disorders diabetes diet type 1 purchase cheap amaryl line. Availability of case definition for acute idiopathic pulmonary hemorrhage in infants [Notice to readers] diabetes xylitol buy amaryl 2mg with mastercard. Idiopathic pulmonary hemosiderosis and related disorders in infancy and childhood. Pathogenesis and management of massive pulmonary hemorrhage in the neonate: case report of a normal survivor. Pulmonary hemorrhage can appear as hemoptysis or blood in the nose or airway with no evidence of upper respiratory or gastrointestinal bleeding. Potential information sources for case-identification and casestatus classification during an investigation of pulmonary hemorrhage are provided (Table 1). A source of bleeding from the nose and oropharynx should be ruled out at the time of admission. Perform to guide diagnosis and therapy for unstable patients with a life-threatening event based on clinical judgment (Source: Jean-Baptiste E. Review course descriptions, · not have evidence of physical abuse; · not have any abnormality identified on admission or follow-up bronchoscopy that would explain the bleeding; and · not have neonatal medical problems that can cause pulmonary hemorrhage. However, the definitions for probable and suspect cases (see the following) will capture the majority of these cases and allow identification of illness among infants who die before examination by a physician. Acute idiopathic pulmonary hemorrhage among infants case-classification scheme Case status categories* Clinically confirmed, 1 Clinically confirmed, 2 Probable, 1 Probable, 2 First criterion Abrupt onset of bleeding from lower airway First criterion met First criterion met First criterion met a. The letter designations, a, b, and c represent approximately equivalent levels within each criterion. The letter designations a, b, and c represent approximately equivalent levels within each category (see also Table 2). Other differential diagnoses associated with pulmonary hemorrhage are listed (Table 5). In addition to the limitations reported for the Cleveland study (5), no risk factors were conclusively linked to disease in the Chicago investigation (4), and only one other cluster (in Detroit) was reported during 19921996 (7). However, the reliable data regarding mortality from pulmonary hemorrhage is only available at the national level. In the national datasets, the majority of cases of pulmonary hemorrhage had diagnoses such as prematurity or immaturity and death occurring within the first 7 days of life. The Cleveland cases occurred among stable, healthy, mature infants who had been discharged from the hospital to their homes after birth and subsequently experienced pulmonary hemorrhage (810). In addition, these national datasets do not determine if infants had identifiable etiologies or complications before their discharge from the hospital or their death. Because the estimated number of hospitalized cases with a primary diagnosis of pulmonary hemorrhage was less than the number of deaths, these national datasets might not be reliable for surveillance for infantile pulmonary hemorrhage. Potential cases will be compared with the recommended case definition by reviewing medical records related to all cases of pulmonary hemorrhage observed since 1979 among children aged <2 years. Both Ohio and Illinois meet the criteria of >100 deaths from pulmonary hemorrhage. Clinical profile of thirty infants with idiopathic pulmonary hemorrhage in Cleveland (Unpublished manuscript). Acute pulmonary hemorrhage/hemosiderosis among infants-Cleveland, January 1993November 1994. Infant pulmonary hemorrhage in a suburban home with water damage and mold (Stachybotrys atra). Acute pulmonary hemorrhage among infants associated with exposure to Stachybotrys atra and other fungi. Overview of investigations into pulmonary hemorrhage among infants in Cleveland, Ohio.
As newborn screening is expanded to include a large number of other conditions diabetes medications moa generic 1mg amaryl with mastercard, homocystinuria should be routinely detected in newborns diabetes mellitus and periodontal disease order amaryl 1mg otc. The distinguishing feature between homocystinuria caused by deficiency of cystathionine beta synthase and homocystinemia associated with B12 metabolism is the presence of very elevated methionine in the former case diabetes mellitus with peripheral circulatory disorder order generic amaryl line. Low homocysteine values can be seen in patients with sulfite oxidase or molybdenum cofactor deficiency diabete gestazionale buy generic amaryl 1mg line. Sulfocysteine is found in both conditions, while certain urine purines will be elevated in the latter condition. Muscle biopsy - when the clinical picture and plasma lactate measurements suggest a mitochondrial or respiratory chain disorder, a muscle biopsy may be recommended in consultation with the Genetics team. The muscle biopsy is analyzed for histologic or histochemical evidence of mitochondrial disease and may lead to recommendations of more genetic tests for specific mitochondrial diseases. Respiratory chain complex studies are then usually carried out on skeletal muscle or skin fibroblasts. Guidelines for Acute Care of the Neonate, Edition 26, 201819 Section of Neonatology, Department of Pediatrics, Baylor College of Medicine Section 6-Genetics Several websites, including Online Resources Galactosemia Infants with classical galactosemia frequently develop signs and symptoms of galactose toxicity before the results of newborn screening are available, requiring that pediatricians remain vigilant when persistent jaundice, coagulopathy, cataracts, or sepsis-particularly caused by E. Treatment is supportive in addition to substitution of the offending galactose-containing formula with a soy formula. Despite good dietary compliance two thirds of children with classic galactosemia exhibit neurologic sequelae including developmental delay, dysarthria, tremor and, rarely, ataxia. In general, plasma amino acid and urine organic acid analyses usually can be obtained within 24 hours, while an acylcarnitine profile may take 48 to 72 hours. However, treatment can begin before the diagnosis of a specific disorder is established and should not be delayed while awaiting specialized laboratory results. Aggressive correction of acidosis with bicarbonate, infusion of glucose for hypoglycemia, and provision of vitamin cofactors all can be done while a specific diagnosis is pursued. Unlike cases of hyperinsulinism, the glucose requirements should not be greater than those of fasting infants. A nighttime milk drip using a soy based formula and addition of polycose to daytime feeds usually prevents hypoglycemia. If there are no mutations identified, no sweat testing is required but the patient should be carefully watched for the development of any respiratory symptoms. If there are 1 or 2 mutations identified, the patient should be referred for sweat testing. The baby must be a minimum weight of 2 kg, a minimum gestational age of 36 weeks, and a minimum chronological age of 2 weeks to qualify for a sweat test. In addition, a baby may have a false negative result as well if s/he has received multiple blood transfusions. Infants with positive sweat tests and 2 mutations require a Pulmonary Medicine consultation. Modest acidosis and, when present, mild hyperammonemia are the rule, however, urine ketones are typically notably increased. Because of this, excessive fluid resuscitation can be catastrophic in older children. Provision of non-protein calories and insulin can help improve the metabolic abnormalities, and providing a branched-chain amino-acidfree formula allows protein synthesis to proceed, reducing the levels of the toxic branched-chain amino acids. Careful monitoring of amino acid levels in the plasma is required since valine and isoleucine supplementation usually is needed to reduce leucine levels. Depending on the clinical severity, dietary management with a branched chain amino acid free formula or hemodialysis can be used to rapidly reduce leucine levels. Organic Aciduria A newborn who is hyperammonemic and severely acidotic can be assumed to have an organic aciduria. In this setting, intravenous administration of L-carnitine (100 to 300 mg/kg per day divided t. In addition to bicarbonate, providing calories in the form of glucose and insulin can reverse the catabolic state that contributes to metabolic perturbations. Administration of the vitamins thiamine (100 mg), biotin (10 mg), and hydroxycobalamin (1 mg) will address vitamin- responsive 83 Section 6-Genetics Section of Neonatology, Department of Pediatrics, Baylor College of Medicine forms of organic acidurias.
It is the result of increased capillary growth as the body attempts to supply more oxygen to distal body cells diabetes in dogs and weight loss purchase amaryl canada. Pain related to sore throat or mouth lesions may prevent the child from drinking properly diabetes mellitus vital signs buy amaryl 3 mg overnight delivery. Tachypnea and increased work of breathing interfere with the ability to safely ingest fluids diabetes symptoms neck discoloration order amaryl online pills. Evaluate breath sounds over the anterior and posterior chest diabetes diet coke generic 1mg amaryl otc, as well as in the axillary areas. The intensity and pitch should be equal throughout the lungs; document diminished breath sounds. In the absence of concurrent lower respiratory illness, the breath sounds should be clear throughout all lung fields. During normal respira- tion, the inspiratory phase is usually softer and longer than the expiratory phase. Bronchiolitis, asthma, pulmonary edema, and an intrathoracic foreign body can cause prolonged expiratory phases. When the upper airway is congested (as in a severe cold), the noise produced in the upper airway might be transmitted throughout the lung fields. When upper airway congestion is transmitted to the lung fields, the congestedsounding noise heard over the trachea is the same type of noise heard over the lungs but is much louder and more intense. To ascertain if these sounds are truly adventitious lung sounds or if they are transmitted from the upper airway, auscultate again after the child coughs or his or her nose has been suctioned. Another way to discern the difference is to compare auscultatory findings over the trachea to the lung fields to determine if the abnormal sound is truly from within the lung or is actually a sound transmitted from the upper airway. Wheezing, a high-pitched sound that usually occurs on expiration, results from obstruction in the lower trachea or bronchioles. Wheezing that clears with coughing is most likely a result of secretions in the lower trachea. Wheezing resulting from obstruction of the bronchioles, as in bronchiolitis, asthma, chronic lung disease, or cystic fibrosis, that does not clear with coughing. Rales (crackling sounds) result when the alveoli become fluid-filled, such as in pneumonia. Note the location of the adventitious sounds as well as the timing (on inspiration, expiration, or both). Flat or dull sounds might be percussed over partially consolidated lung tissue, as in pneumonia. Increased tactile fremitus might occur in a case of pneumonia or pleural effusion. Poor perfusion might be reflected in weaker peripheral pulses (radial, pedal) when compared to central pulses. The tests can assist the physician in diagnosing the disorder and/or be used as guidelines in determining ongoing treatment. Laboratory or non-nursing personnel obtain some of the tests, while the nurse might obtain others. In either instance the nurse should be familiar with how the tests are obtained, what they are used for, and normal versus abnormal results. This knowledge will also be necessary when providing patient and family education related to the testing. Some children react to the skin test almost immediately; others take several minutes. Arterial blood gases Usually reserved for severe illness, the intubated child, or suspected carbon dioxide retention Hold pressure for several minutes after a peripheral arterial stick to avoid bleeding. Note if the child is crying excessively during the blood draw, as this affects the carbon dioxide level. If a parent or familiar adult can accompany the child, often the child is less afraid. If the child is unable or unwilling to hold still for the x-ray, restraint may be necessary. To obtain a nasopharyngeal specimen instill 1 to 3 mL of sterile normal saline into one nostril, aspirate the contents using a small sterile bulb syringe, place the contents in sterile container, and immediately send them to the lab. Indication Identification of masses, abscesses Nursing Implications Requires the child to lay still. Nasogastric tube is inserted and saline is instilled and suctioned out of the stomach for the specimen.
Supplemental oxygen diabetes symptoms ring around neck 2mg amaryl otc, nasal and/or nasopharyngeal suctioning diabetes daily purchase generic amaryl canada, oral or intravenous hydration diabetes in spanish best buy amaryl, and inhaled bronchodilator therapy are used diabetic diet recipe purchase genuine amaryl. The infant with tachypnea, significant retractions, poor oral intake, or lethargy can deteriorate quickly, to the point of requiring ventilatory support, and thus warrants hospital admission. Provide 100% oxygen in the least invasive manner that is most acceptable to the child. Do not under any circumstance attempt to visualize the throat: reflex laryngospasm may occur, precipitating immediate airway occlusion. If the child with epiglottitis experiences complete airway occlusion, an emergency tracheostomy may be necessary. Epiglottitis is characterized by dysphagia, drooling, anxiety, irritability, and significant respiratory distress. The small airways become variably obstructed; this allows adequate inspiratory volume but prevents full expiration. The severity of disease is related inversely to the age of the child, with the most severe cases occurring between 1 and 3 months of age (Weisman & Figure 19. Auscultation Auscultate the lungs, noting adventitious sounds and determining the quality of aeration of the lung fields. Earlier in the illness, wheezes might be heard scattered throughout the lung fields. Children with less severe disease might require only antipyretics, adequate hydration, and close observation. They can often be successfully managed at home, provided the primary caregiver is reliable and comfortable with close observation. In addition to the nursing diagnoses and related interventions discussed in the Nursing Care Plan for respiratory disorders, interventions common to bronchiolitis follow. Aerosolized ribavirin is recommended only for the highest-risk, most severely ill patients (Lauts, 2005). The infant might appear listless and disinterested in feeding, surroundings, or parents. Position the child with the head of the bed elevated to facilitate an open airway. These children often require frequent assessment and suctioning to maintain a patent airway (Lauts, 2005). Nasal bulb suctioning may be sufficient to clear the airway in some infants, while others will require nasopharyngeal suctioning with a suction catheter. The routine use of sterile normal saline is not indicated in all children, as its use has been demonstrated to result in decreased oxygen saturations for up to 2 minutes after suctioning is complete (Ridling et al. Adjust the pressure ranges for suctioning infants and children between 60 and 100 mm Hg, 40 and 60 mm Hg for premature infants. Attention to hand washing is necessary, as droplets might enter the eyes, nose, or mouth via the hands. Providing Family Education Educate parents to recognize signs of worsening distress. Tell parents to call their physician or nurse practitioner if the breathing is rapid or becomes more difficult or if the child cannot eat secondary to tachypnea. Children who are less than 1 year of age or who are at higher risk (those who were born prematurely or who have chronic heart or lung conditions) might have a longer course of illness. Instruct parents that cough can persist for several days to weeks after resolution of the disease, but infants usually act well otherwise. Promoting Adequate Gas Exchange Infants and children with bronchiolitis might deteriorate quickly as the disease progresses. Assessment should include work of breathing, respiratory rate, and oxygen saturation. The percentage of inspired oxygen (FiO2) should be adjusted as needed to maintain oxygen saturation within the desired range. Positioning the infant with the head of the bed elevated may also improve gas exchange. Frequent assessment is necessary for the hospitalized child with bronchiolitis (Cooper et al.
Buy generic amaryl on-line. diabetes symptoms in women Diabetes kills diabetes symptoms in women.