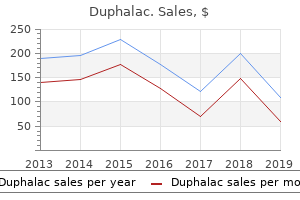
"Cheap duphalac online, medications heart disease".
By: L. Reto, M.B. B.CH., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Co-Director, Kansas City University of Medicine and Biosciences College of Osteopathic Medicine
In vitro susceptibility of Mycobacterium avium complex and Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains to a spiropiperidyl rifamycin medicine 3d printing duphalac 100 ml discount. Efficacy of rifabutin in the treatment of disseminated infection due to Mycobacterium avium complex medications list purchase duphalac on line amex. Reduced serum levels of clarithromycin in patients treated with multidrug regimens including rifampin or rifabutin for Mycobacterium avium intracellulare infection symptoms esophageal cancer buy cheap duphalac 100 ml on line. Varying dosages of rifabutin affect white blood cell and platelet counts in human immunodeficiency virusnegative patients who are receiving multidrug regimens for pulmonary Mycobacterium avium complex disease treatment viral pneumonia purchase 100 ml duphalac with mastercard. Adverse events associated with high-dose rifabutin in macrolide-containing regimens for the treatment of Mycobacterium avium complex lung disease. A randomized, placebo-controlled study of rifabutin added to a regimen of clarithromycin and ethambutol for treatment of disseminated infection with Mycobacterium avium complex. Treatment of Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare complex lung disease with a macrolide, ethambutol, and clofazimine. Immunomodulatory activity and effectiveness of macrolides in chronic airway disease. Aminoglycoside toxicity: daily versus thrice-weekly dosing for treatment of mycobacterial diseases. Ethambutol ocular toxicity during therapy for Mycobacterium avium complex lung disease. American Thoracic Society; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; Infectious Diseases Society of America. Uveitis and pseudojaundice during a regimen of clarithromycin, rifabutin, and ethambutol. Surgical management of resistant mycobacterial tuberculosis and other mycobacterial pulmonary infections. Post-surgical outcome of 57 patients with Mycobacterium xenopi pulmonary infection. Epidemiology and clinical significance of nontuberculous mycobacteria in patients negative for human immunodeficiency virus in Switzerland. Atypical mycobacterial cervical adenitis in normal children: is clarithromycin effective? Treatment of nontuberculous mycobacterial lymphadenitis with clarithromycin plus rifabutin. A prospective, randomized trial examining the efficacy and safety of clarithromycin in combination with ethambutol, rifabutin, or both for the treatment of disseminated Mycobacterium avium complex disease in persons with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Mycobacterium kansasii among patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus in Kansas City. Clinical manifestations and implications of coinfection with Mycobacterium kansasii and human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Mycobacterium kansasii disease in patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus. A randomized trial of clarithromycin as prophylaxis against disseminated Mycobacterium avium complex infection in patients with advanced acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Incidence and molecular typing of Mycobacterium kansasii in a defined geographical area in Catalonia, Spain. Clinical implications of Mycobacterium kansasii species heterogeneity: Swiss National Survey. Evaluation of a modified single-enzyme amplified fragment length polymorphism technique for fingerprinting and differentiating of Mycobacterium kansasii type I isolates. Emergence of Mycobacterium kansasii as the leading mycobacterial pathogen isolated over a 20-year period at a Midwestern Veteran Affairs Hospital. A demographic study of disease due to Mycobacterium kansasii or Mycobacterium intracellulare-avium in Texas. A study of pulmonary disease associated with mycobacteria other than Mycobacterium tuberculosis: identification and characterization of the mycobacteria. Treatment of pulmonary disease due to Mycobacterium kansasii: recent experience with rifampin. Chemotherapy for pulmonary disease due to Mycobacterium kansasii: efficacies of some individual drugs. In vitro activities of norfloxacin and ciprofloxacin against Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Mycobacterium avium complex, Mycobacterium chelonei, Mycobacterium fortuitum, and Mycobacterium kansasii. Pulmonary infection with Mycobacterium kansasii in Wales, 19709: review of treatment and response.
It is one of the main branches of the trigeminal nerve treatment 4 high blood pressure purchase duphalac 100ml without prescription, that leaves the skull through the foramen ovale medications help dog sleep night purchase duphalac cheap online. What is the main connection between the sphenopalatinal fossa and the nasal cavity? What should be administered in case of an idiopathic convulsion accompanied unconsciousness? Observing a serious necrotizing inflammation in the oral cavity treatment 0f osteoporosis order 100ml duphalac fast delivery, what can be the cause of the underlying systemic disease? How long should be the Syncumar administered in case of the first deep venous thrombosis medications venlafaxine er 75mg 100ml duphalac sale, if there is no detectable thrombophylia? Which of the following signs does not belong to the consequences of the peptic ulcer? Which disease can be indicated by a thoracic pain, intensifying at breathing and coughing, evidenced from the history of the patient? It is the first step in the medication, in case of a moderate anaphylactic reaction (urticaria, flush): A. What is the first task in case of detecting an acute respiratory distress, following an obstruction in the upper respiratory tract, if the patient is unconscious? In case of which of the listed medications has to be avoided the simultaneous administration of epinephrine? Which of the following drugs can cause xerostomia as a characteristic side effect? Which of the listed side effects ought not be calculated up in case of employing nitrites and nitrates? Which of the following drugs make the patient susceptible to an orthostatic collapse? Which of the listed penicillin derivates is effective against the Gram negative bacteria? It is an ionic pump occurring both in the plasma membrane and in the intracellular organels. Hypoglycaemia Hyperglycaemia Certain amino acids Growth hormones Catecholamines Which Ig-subclass has a pentamer structure? How is the double-layer epithelial sheath called, which is formed at the unification of the outer and the inner enamel epithelium? Secreting- and maturating- ameloblasts Activating and resting ameloblasts inhibition and activation ameloblasts fusion and dissociation ameloblasts 15/36 E. How many percent can be absorbed systematically from the topically applied fluoride? Into the urine Into the defecation Into the saliva Into the sweat Into the breast milk How much content does the 1 pp fluoride volume mean? What is the safe and tolerable dose of the fluoride calculated per body weight kilogramms? These anatomic features have access to the anterior and posterior ethmoid air cells of paranasal sinuses: 1. Which of the following blood vessel branches have a role in the blood supply of the palatinal tonsills? These are the primary lymph nodes of the lymphatic vessels running from the tip of the tongue 1. These are cranial nerves related to the taste sensation, the nuclei of which are taste sensory centers: 1. Which dura mater sinuses do carry the venous blood toward the internal jugular vein? What is to be done in case of dental treatment of a patient with angina pectoris in the history? Occurrence of infective endocarditis has particularly high risk in the following patients: 1.
The multilayered stratified squamous epithelium of the grooves shows lighter spots treatment kidney stones cheap duphalac 100 ml visa. Digestive System 2 376 Lingual Papillae-Foliate Papillae Human foliate papillae are well developed only in children 5 medications post mi buy duphalac 100 ml. However treatment jaundice cheap generic duphalac canada, rabbits possess dense fields of foliate papillae at the posterior lateral edges of the tongue treatment associates buy generic duphalac pills. Two small groups of glands 3 are present in the subepithelial connective tissue 4. They are located in close proximity to the striated skeletal muscle fibers 5 of the tongue. Then, having traversed the tightly structured aponeurosis, they spread into the mucous membrane. The vessel terminals form a densely woven network, which ends in a capillary web area. The clustered mucous glands are not restricted to the tunica mucosa but extend deeper between the muscle fiber bundles. Connective tissue septa (trabeculae) (stained blue) and sectioned striated muscle fibers 1 are present between the glandular lobes. The nuclei (stained red) in the basal cell region and the cytoplasm with its honeycomb structure (cf. Digestive System 379 Parotid Gland the parotid gland (glandula parotidea, or short parotis) is the largest human salivary gland. The entire length of the secretory duct is always contained in the glandular lobe. A long intercalated duct 3 traverses the center of the image from top left to bottom right. A sectioned salivary or striated duct 2 is visible in the lower right half of the image. The oval nuclei of the pseudostratified columnar epithelial cells are located in the central or basal cell regions. It is caused by involutions of the basal plasmalemma and densely packed mitochondria between the membrane pleats (cf. A longitudinally section of an intercalated duct 3 is visible in the right part of the figure, another duct is crosssectioned 4 (cf. The supranuclear or apical cell region of the serous acinar cells is filled with secretory granules (stained blue). There are fibrocytes and capillaries in the loose connective tissue between acini. Digestive System 3 382 Submandibular Gland the submandibular gland is a mixed (seromucous) gland. The figure displays several lobes that are separated by connective tissue septa (trabeculae). The larger ducts, the blood and lymph vessels and the vegetative nerves traverse the loose interlobular connective tissue 1. The fibrous connective tissue between the lobes continues inside the lobes as reticular connective tissue. The lobe in the upper layer contains several mucous terminal portions with serous demilunes 2 (cf. The branched ducts in the submandibular gland are particularly long and elaborate 3. As observed for the parotid glands, the serous secretory cells can be stained with acidophilic dyes. The tubular cells from purely mucous glands are distinct because they are stained lighter than the serous cells. The flat nuclei of mucous gland cells appear dense and reside in the basal or basolateral cell regions (cf. Again, note the salivary serous gland cells (demilunes) at the end of the mucous gland tubules. The combination of dyes in this preparation does not stain the interlobular connective tissue.
The most reliable test to diagnose insulinoma is a fast up to 72 h with serum glucose treatment leukemia order duphalac 100ml on-line, Cpeptide medications 230 order duphalac 100ml with mastercard, and insulin measurements every 48 h medicine 100 years ago buy duphalac 100ml with mastercard. If at any point the patient becomes symptomatic or glucose levels are persistently <2 1950s medications order discount duphalac on-line. Some 7080% of patients develop hypoglycemia during the first 24 h and 98% by 48 h. In nonobese normal subjects, serum insulin levels should decrease to <43 pmol/L (<6 µU/mL) 591 when blood glucose decreases to 2. In addition to having an insulin level >6 µU/mL when blood glucose is 40 mg/dL, some investigators also require an elevated C-peptide and serum proinsulin level, an insulin/glucose ratio >0. Surreptitious use of insulin or hypoglycemic agents may be difficult to distinguish from insulinomas. The combination of proinsulin levels (normal in exogenous insulin/hypoglycemic agent users), Cpeptide levels (low in exogenous insulin users), antibodies to insulin (positive in exogenous insulin users), and measurement of sulfonylurea levels in serum or plasma will allow the correct diagnosis to be made. In these patients the assessment of proinsulin and C-peptide levels at the time of hypoglycemia are particularly helpful for establishing the correct diagnosis. Before surgery, the hypoglycemia can be controlled by frequent small meals and the use of diazoxide (150800 mg/d). Diazoxide is a benzothiadiazide whose hyperglycemic effect is attributed to inhibition of insulin release. Other agents effective in some patients to control the hypoglycemia include verapamil and diphenylhydantoin. Long-acting somatostatin analogues such as octreotide are acutely effective in 40% of patients. However, octreotide needs to be used with care because it inhibits growth hormone secretion and can alter plasma glucagon levels; therefore, in some patients it can worsen the hypoglycemia. For the 515% of patients with malignant insulinomas, the drugs just listed or somatostatin analogues are used initially. If they are not effective, various anti-tumor treatments such as hepatic arterial embolization, chemoembolization, or chemotherapy have been used (see later). The tumor is clinically heralded by a characteristic dermatitis (migratory necrolytic erythema) (6790%), accompanied by glucose intolerance (4090%), weight loss (6696%), anemia (3385%), diarrhea (1529%), and thromboembolism (1124%). The rash starts usually as an annular erythema at intertriginous and periorificial sites, especially in the groin or buttock. It subsequently becomes raised and bullae form; when the bullae rupture, eroded areas form. A characteristic laboratory finding is hypoaminoacidemia, which occurs in 26100% of patients. From 5082% have evidence of metastatic spread at presentation, usually to the liver. Diagnosis the diagnosis is confirmed by demonstrating an increased plasma glucagon level (normal is <150 ng/L). Plasma glucagon levels are >1000 ng/L in 90%, between 500 and 1000 ng/L in 7%, and <500 ng/L in 3%. Other diseases causing increased plasma glucagon levels include renal insufficiency, acute pancreatitis, hypercorticism, hepatic insufficiency, prolonged fasting, or familial hyperglucagonemia. With the exception of cirrhosis, these disorders do not increase plasma glucagon to >500 ng/L. There is no general distinction in the literature between a tumor that contains somatostatin-like immunoreactivity (somatostatinoma) and does (1145%), or does not (5589%) produce a clinical syndrome (somatostatinoma syndrome) by secreting somatostatin. In one review of 173 cases of somatostatinomas, only 11% were associated with the somatostatinoma syndrome. Somatostatinomas occur primarily in the pancreas and small intestine, and the frequency of the symptoms differs in each. Each of the usual symptoms is more frequent in pancreatic than intestinal somatostatinomas: diabetes mellitus (95% vs 21%), gallbladder disease (94% vs 43%), diarrhea (92% vs 38%), steatorrhea (83% vs 12%), hypochlorhydria (86% vs 12%), and weight loss (90% vs 69%). Somatostatinomas occur in the pancreas in 5674% of cases, with the primary location in the pancreatic head. It is a potent inhibitor of many processes including release of almost all hormones, acid secretion, intestinal and pancreatic secretion, and intestinal absorption. Most of the clinical manifestations are directly related to these inhibitory actions. Diagnosis In most cases somatostatinomas have been found by accident either at the time of cholecystectomy or during endoscopy.
Duphalac 100ml on line. Glandular Fever Symptoms.