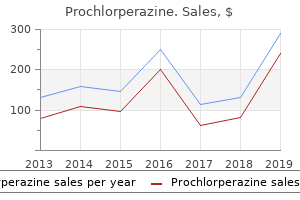
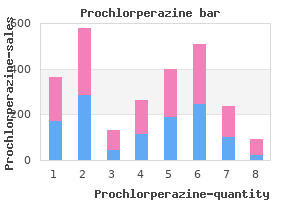
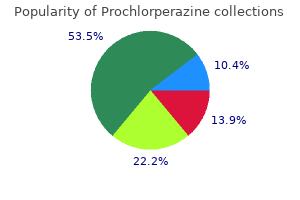
"Discount 5 mg prochlorperazine, medicine keri hilson lyrics".
By: N. Khabir, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., Ph.D.
Clinical Director, Loma Linda University School of Medicine
The foam dosage form is flammable; avoid fire symptoms women heart attack purchase prochlorperazine 5mg without prescription, flame symptoms zoning out purchase prochlorperazine in india, or smoking during or immediately after use treatment yeast 5mg prochlorperazine otc. Nervousness medicine 0829085 purchase prochlorperazine from india, tremor, headache, nausea, tachycardia, arrhythmias, and palpitations may occur. Paradoxical bronchoconstriction may occur with excessive use; if it occurs, discontinue drug immediately. Also not recommended for use in pregnancy because these side effects may occur in the fetus. May decrease the effectiveness of oral contraceptives, increase serum digoxin levels, and increase effects of warfarin. Use with methoxyflurane increases risk for nephrotoxicity and use with isotretinoin is associated with pseudotumor cerebri. Immediate release: Elixir (Elixophyllin): 80 mg/15 mL (473 mL); may contain up to 20% alcohol. Sustained/extended release (see remarks): Tabs: Q12 hr dosing (Theochron and generics): 100, 200, 300, 450 mg Q24 hr dosing (generics): 400, 600 mg Caps (Q24 hr dosing: Theo-24): 100, 200, 300, 400 mg Sustained-release forms should not be chewed or crushed. Drug metabolism varies widely with age, drug formulation, and route of administration. Most common side effects and toxicities are nausea, vomiting, anorexia, abdominal pain, gastroesophageal reflux, nervousness, tachycardia, seizures, and arrhythmias. Liver impairment, cardiac failure, and sustained high fever may increase theophylline levels. Levels are increased with allopurinol, alcohol, ciprofloxacin, cimetidine, clarithromycin, disulfiram, erythromycin, estrogen, isoniazid, propranolol, thiabendazole, and verapamil. Levels are decreased with carbamazepine, isoproterenol, phenobarbital, phenytoin, and rifampin. May cause increased skeletal muscle activity, agitation, and hyperactivity when used with doxapram and increases quinine levels/toxicity. Use ideal body weight in obese patients when calculating dosage because of poor distribution into body fat. Risk factors for increased clearance include: smoking, cystic fibrosis, hyperthyroidism, and high-protein diet. Pigmentary retinopathy may occur with higher doses; a periodic eye exam is recommended. Criteria for dose increase required tolerance of the current dosage level and <50% reduction in seizures. Most common side effects include dizziness, somnolence, depression, confusion, and asthenia. Nervousness, tremor, nausea, abdominal pain, confusion, and difficulty in concentrating may also occur. Cognitive/neuropsychiatric symptoms resulting in nonconvulsive status epilepticus requiring subsequent dose reduction or drug discontinuation have been reported. Suicidal behavior or ideation, bullous dermatitis, and blurred vision have been reported. Bowel obstruction, angle-closure glaucoma, urinary retention, and bronchospasm have been reported. Use as an add on maintenance therapy for asthma along with inhaled corticosteroid.
Overview of psoriasis and guidelines of care for the treatment of psoriasis with biologics medicine hollywood undead generic prochlorperazine 5 mg with mastercard. Guidelines of care for the management of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: Section 2 treatment 12mm kidney stone purchase discount prochlorperazine online. Guidelines of care for the management and treatment of psoriasis with topical therapies medications known to cause hair loss purchase prochlorperazine 5mg overnight delivery. American Optometric Association Clinical Practice Guideline: Care of the Patient with Anterior Uveitis treatment ind buy generic prochlorperazine line. The Health Plan makes no representations and accepts no liability with respect to the content of any external information used or relied upon in developing this clinical policy. The purpose of this clinical policy is to provide a guide to medical necessity, which is a component of the guidelines used to assist in making coverage decisions and administering benefits. This clinical policy may be subject to applicable legal and regulatory requirements relating to provider notification. Providers are expected to exercise professional medical judgment in providing the most appropriate care, and are solely responsible for the medical advice and treatment of members. Unauthorized copying, use, and distribution of this clinical policy or any information contained herein are strictly prohibited. Providers, members and their representatives are bound to the terms and conditions expressed herein through the terms of their contracts. Centene and Centene Corporation are registered trademarks exclusively owned by Centene Corporation. Specifically, Core Element 2 states that "all hospitals shall adopt or adapt to their local context the National Antibiotic Guidelines" to optimize antimicrobial use and help improve the quality of patient care and patient safety. Adaptations of available guidelines and treatment recommendations were made taking into consideration the latest national Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance Program resistance rates, list of approved drugs in the National Formulary, quality of the evidence, balance of potential benefits and harm, cost-effectiveness, availability of diagnostic tests, feasibility and resource implications. Interim recommendations were viii discussed en banc and a consensus was usually reached. Brief descriptions of disease categories with their etiologic agents, corresponding antibiotic regimens (dose, route, frequency and duration) for pediatric and adult patients, relevant comments and key references are presented. A section on surgical prophylaxis, although not treatment-focused, has been added since antibiotic misuse to prevent surgical site infections also needs urgent attention. Bacterial load (inoculum size), virulence, regrowth pattern and susceptibility pattern of the pathogen. Prior antimicrobial therapy: exert selection pressure for micro-organisms resistant to the antibiotic previously given to outgrow the rest of the microflora, invade and cause infection. However, when inappropriately used, antibiotic combination can lead to deleterious effects. Provide broad-spectrum empiric therapy in the initial therapy of critically ill patients and neutropenic patients with severe life-threatening infections. Sound clinical judgment/assessment remains the most important method to determine the efficacy of the treatment. Complete reliance on chemotherapy with omission of surgical drainage and other non-pharmacologic therapy when necessary. Inadequacy of knowledge of diagnostic procedures and management of infectious diseases. In cases of suspected catheter-related infection, or skin or softtissue infection, pneumonia, or hemodynamic instability consider adding Vancomycin 40-60mg/kg/d q6h (Max: 2-4g/day) If with abdominal symptoms (pain or blood per rectum) or suspected C. Intravenous antibiotics should be given as soon as sepsis or septic shock is recognized and within the 1st hour. Assess for risk (low or high risk) of complication for severe disease at presentation of fever. Continue treatment until patient is afebrile and absolute neutrophil count is >500 cells (some >1000 cells).
Quality prochlorperazine 5 mg. GIANT TONSILS WITH WHITE PUS (Strep Throat? / Mono?) | Dr. Paul.
Another great demand will be for widespread vaccination to contain disease spread for such diseases as smallpox and anthrax treatment definition statistics cheap prochlorperazine 5mg on-line. If the disease is one for which specific therapy such as antibiotics is indicated (for example medicine park cabins discount prochlorperazine 5mg amex, tularemia) medicine jewelry purchase 5 mg prochlorperazine free shipping, instructions for obtaining and administering the drug should be disseminated treatment zygomycetes 5mg prochlorperazine amex. With a disease like yellow fever, with high mortality and for which no specific therapy is available, instructions for general supportive care that might be provided by nonmedical personnel should be disseminated. An exception to this pattern might be seen following an attack with a biological toxin. However, if the agent is transmissible from human to human, they should be placed in quarantine during this period. It may be necessary for one physician, with a small number of ancillary personnel, including nurses, medical technicians, and nonmedical personnel, to care for several hundred patients. Information should be disseminated about the normal course of the disease, the specific signs or symptoms of adverse prognostic significance, the situations requiring individual medical attention or advice, and the procedures for obtaining essential medical supplies. This arrangement would allow a limited number of professional personnel to care for the maximum number of patients. For more information regarding management and treatment of biologically contaminated casualties, refer to Appendix D. The common term used to describe people in this situation is psychological effects or worried well. The actual cause is usually psychological, rather than medical, among psychological effects people. Psychological problems commonly associated with personnel having psychological effects include- Clinical depression. During the sarin gas release in the Tokyo subway system in 1995, the hospitals were presented with over 5,500 possible casualties. Only 1,000 were casualties related to the attack and only 12 deaths were related to this catastrophe. The total number of those who presented themselves to the hospital with complaints of postexposure symptoms exceeded the number who did require medical treatment caused by exposure. Medical personnel and behavioral health treatment providers must be prepared to provide some level of treatment for individuals showing acute or transient emotional and behavioral signs and symptoms. While the acutely ill patients have priority of treatment, attention must also be paid to the personnel with psychological effects. If a contaminated patient dies while being treated in a medical system, medical personnel will ensure the contaminated remains are isolated and handed over to mortuary affairs personnel as soon as possible. The handling, transport, and disposition of biologically contaminated human remains on the battlefield or after removal from the medical system are not a medical responsibility, but a logistics function; however, medical expertise should be sought. Moreover, contaminated human remains pouches should be clearly labeled/marked with a tag noting the type of biological hazard present (if known) and placed in a designated holding area. In the event of leakage of bodily fluids, the remains should not be removed but placed in a second human remains pouch. Then the outer pouch should be labeled/marked in the same manner as the initial human remains pouch. General principles governing medical disposition of contaminated human remains at a patient decontamination site or casualty collection point include- Contaminated human remains are segregated from other casualties. A temporary morgue area may be set up for holding human remains while awaiting transportation to a mortuary affairs contaminated remains mitigation system. Contaminated human remains, as determined by the senior medical authority, are not evacuated with other casualties, nor are they routinely evacuated on medical vehicles. Those charged with the responsibility for handling, transporting, and determining disposition of biologically contaminated human remains must be cognizant of and utilize all means to minimize the risk of potential secondary transmission hazards. If the geographic combatant commander authorizes temporary interment, contaminated human remains must be interred according to current theater or Service procedures until a determination is made regarding further disposition of the contaminated human remains. To minimize risk of transmission hazard, the following considerations should be taken: Although the process has not been tested or approved, current evidence indicates that human remains contaminated with spore-forming bacteria can be reliably sterilized only by gamma-ray irradiation or by electron beam. However, alternative decontamination schemes may be employed which could reduce spore burdens to levels acceptable with regard to later transmission risk. All autopsies involve exposure to blood, a risk of being splashed or splattered, and a risk of percutaneous injury. All autopsies generate fine aerosols which can create airborne particles that contain infectious pathogens not normally transmitted by the airborne route. For more information refer to Technical Guide 195A, Safety and Health Guidance for Mortuary Affairs Operations: Infectious Materials.
Although no information is available on the doses ingested medications breastfeeding buy prochlorperazine with paypal, the doses are likely to be high treatment integrity buy prochlorperazine with american express, in light of the high mortality rate symptoms neck pain cheap prochlorperazine 5mg with mastercard. When the same woman symptoms zoloft withdrawal purchase cheap prochlorperazine on-line, 6 months later, ingested a total of 35 mg over 2 weeks, she reported only nausea. There was no sign of hepatoxicity, suggesting that hepatotoxicity of AfB1 may be lower in well nourished persons than in experimental animals (Peraica et al. Aflatoxins have been suggested as an etiological factor in encephalopathy and fatty degeneration of viscera, similar to Reye syndrome (Peraica et al. The clinical picture includes enlarged, pale, fatty liver and kidneys and severe cerebral edema, but use of aspirin or phenothiazines is also suspected to be involved in the etiology (Peraica et al. As in animals, adverse effects of aflatoxins on the embryo and the developing fetus (such as regression of testis, impairment of spermatogenesis and premature loss of germ cells) have been reported in humans (Gupta, 2011). These findings were correlated with the presence of higher concentrations of aflatoxins in the semen of infertile men (40% of cases compared to 8% of controls). Aflatoxins were also reported to lower fertility and significantly increased mortality of embryos in humans (Gupta, 2011), but information on effect levels in humans was not located. Rats are more sensitive than mice, and Fischer rats the most sensitive strain (Gupta, 2011). Following acute exposure, the clinical signs include gastrointestinal dysfunctions, decreased feed intake and efficiency, weight loss, jaundice, drop in milk production, nervous signs, bleeding and death (Agag, 2004). The susceptibility of individual animals to aflatoxicosis varies considerably depending on dose, duration of exposure, species, age, sex, and nutrition (Agag, 2004). In the rat, the main lesions following the administration of AfB1 at high doses were seen in the liver, while kidney and adrenals also show damage (Talebi et al. These studies reported mainly on mortality, and a limited number reported on systemic effects following exposure. Deaths occurred when male Fischer 344 rats were fed a diet containing a mixture of AfB1 (1 ppm and 0. However, when Sprague Dawley rats were fed a diet containing aflatoxins (AfB1 was present at a level of 0. The available studies indicate that AfB1 impairs the reproductive performance of females, resulting in adverse effects on sexual maturation, growth and maturation of the follicles, levels of hormones, gestation and growth of the fetus (Gupta, 2011). Male reproductive toxicity studies with aflatoxins in vivo and in vitro have reported testicular degeneration and decreased sperm production (Gupta, 2011). In a related study, decreased conception rate and litter size, and increases in fetal resorption and implantation loss were seen in rats gavaged with AfB1 at 7. In mice, oral administration of 4 mg/kg AfB1 on day 8 or 9 of pregnancy resulted in fetal anomalies including exencephaly (brain is located outside of the skull), open eyes and protrusion of intestines in fetuses exposed on day 8. Alternatively, the observations on day 8 may reflect factors other than AfB1 exposure. Malformations have also been observed following parenteral dosing at 32 mg/kg and higher. Based on the limited data available, a single dose of 4 mg/kg AfB1 may cause developmental toxicity, although, as noted, this study is of poor quality. However, no threshold for 78 immunotoxicity has been defined for any species (Williams et al. The primary immunosuppressive effect of aflatoxins is on cell-mediated immunity, particularly delayed-type hypersensitivity. No such effects were observed in C57B1/6 mice given the same dose of AfB1 or in rabbits fed 24 ppm aflatoxin in feed. Aflatoxins were also reported to reduce antibody titers to some infectious bacteria in rabbits (Williams et al. Aflatoxin has also been shown to reduce phagocytic activity in rabbit alveolar macrophages and to inhibit phagocytic cell function in normal peripheral blood monocytes in vitro (Williams et al. These studies include single dose, acute/short-term, repeated dose, and chronic exposure studies 79 in which the experimental animals were fed diet naturally or artificially contaminated with AfB1, mixtures of aflatoxins or AfM1.