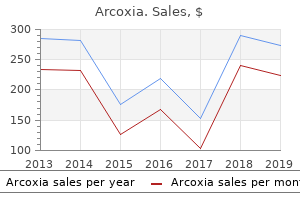
"Order arcoxia 60 mg line, arthritis equipment".
By: U. Mine-Boss, M.A., M.D., Ph.D.
Medical Instructor, University of South Carolina School of Medicine
Then you shall say concerning it: this is a swelling of the coverings of his abdomen arthritis pain tablets cheap arcoxia 90 mg otc, an illness which I will treat rheumatoid arthritis spine buy arcoxia with paypal. You treat it like the sA-Hmm treatment" (Nunn 1996: 165-166); (Ghalioungui 1987: 240241) arthritis research treatment center stockbridge ga discount arcoxia 90mg mastercard. As in the previous case arthritis bracelet buy cheap arcoxia 60mg online, a chronic hygroma, lipoma or fibroma; a not complicated epigastric hernia or umbilical hernia, to be treated with a transcurrent cauterization (Jean 1999: 30). The aAa disease, is again referenced giving instructions for its treatment in a swelling of the brow (maybe an image of the fat pleat in the belly), wp. Nunn considers it to be a classic description of an umbilical or epigastric hernia. If you examine this in his lower abdomen the water of his belly goes up and down, you should say thereon: the Hrw (? You must then hit (the swelling) with the Hmm-instrument56; it (the instrument) must not descend to the msjn. Treat it (the lower abdomen, hypogastrium) like the treatment of the sA-Hmm patient" (Ghalioungui 1987: 242); (Bardinet 1995: 368). A tumour of the lower umbilical abdomen (peritoneal cavity), ascites (Graber-Baillard 1998: 34-35). Pouch formed 55 56 (Ghalioungui 1987: 242) the Hmm, mentioned in Ebers 865, was it a knife or a probe, as it was used for the opening of a tumour (? A swelling of the hypogastrium, having water going up and down, "the heat of the bladder" may be an infection of the bile duct, thus ascites condition present. You should then apply the treatment of wounds on any body part of a man" (Ghalioungui 1987: 243); (Bardinet 1995: 368). The mtw-vessels carry a sfT substance that will produce a pouch itself (Bardinet 1995: 196, 368), the swelling of the mtw channels; Nunn suggests a vascular tumour (hemangioma) (Nunn 1996: 167). The swelling in the belly is caused by a manifestation of the vessel (Ghalioungui 1987: 244). If you examine a swelling of fat in any part of the body of a man, and you find it moving under your fingers and that, because of your hand, it is in parts that stay, you must then say: this is a swelling of fat, aA. You should then perform for it a knife treatment, whereby it is given the treatment of a wound" (Ghalioungui 1987: 244); (Bardinet 1995: 368-369). A lipomatosis tumour, a lipoma (Graber-Baillard 1998: 36), to be treated with an incision (Jean 1999: 30). A swelling of fat in any body part that can be manipulated (Ghalioungui 1987: 244). A ganglionic mass, according to Ghalioungui, diagnosed by Ebbell as a tumour with liquid contents (Ghalioungui 1963: 84), (Ebbell 1937: 124). You should then perform for it a knife treatment, whereby it is treated like the treatment of a wound on any body part of man" (Ghalioungui 1987: 244). An extensive multiple tumour with epidermis coloration (Graber-Baillard 1998: 37-38). There is in it something (vegetable mucilage57) like viscous humor, something comes out after that like wax; it (the swelling) makes a pocket. Another translation is provided in Nunn, he calls matter-pus and operation-knife treatment (Nunn 1996: 76). A localized tumour in a pocket containing waxed water (Graber-Baillard 1998: 38-39). A swelling of pus that has something originating out such as wax, in a pocket, that has to be extracted in full (Ghalioungui 1987: 245). In a tumour with a capsule such as this one, it was strongly recommended (to be extracted) to avoid a relapse. If you examine a swelling of hair, and you find it spherical and soft and its content solid, you must then say: a disease that I treat with the knife treatment. Swelling of hair, Snj, perhaps a dermoid cyst, lined with skin appendages including hair or a sebaceous cyst of the scalp (Nunn 1996:167).
Grade of Recommendation: B Debi et al10 conducted a prospective randomized controlled trial evaluating the efficacy of topical steroid application to reduce pain following lumbar discectomy arthritis diet advice discount arcoxia 120mg mastercard. The authors concluded that local application of steroid to the decompressed nerve root produced short-term benefit but no long-term effect arthritis medication after gastric bypass cheap arcoxia master card. This study provides Level I therapeutic evidence that application of steroids on a collagen sponge to the decompressed nerve root results in short-term (14 day) improvement in back pain arthritis medication celebrex cheap arcoxia 60mg, but not leg pain rheumatoid arthritis tendonitis arcoxia 120mg cheap, which may not be clinically relevant. Of these 167 patients, 82 were treated with discectomy alone and 85 received an additional steroid plus fentanyl sponge. There were no differences between patient groups with regard to functional outcome measures in medium and long term this clinical guideline should not be construed as including all proper methods of care or excluding or other acceptable methods of care reasonably directed to obtaining the same results. There was a trend towards improvement in leg weakness and radiculopathy scores in the gel group only at the 30-day follow-up. When a post hoc analysis was performed in patients with significant leg pain scores and weakness preoperatively, there was a statistically significant difference in several scores at 30 days. Some select patients with significant leg pain scores and preoperative weakness may experience some short-term (30 day) benefits. Due to the significant (50%) loss to follow-up in this small study, it is impossible to draw any conclusions regarding the one-year results of the study. Outcomes were assessed at six months using the Hopkins scale, along with the degree of There is insufficient evidence to make a recommendation for or against the application of a fat graft following open discectomy for patients with lumbar disc herniation with radiculopathy whose symptoms warrant surgery. Grade of Recommendation: I (Insufficient Evidence) Jensen et al12 performed a prospective randomized controlled trial to evaluate whether a free fat graft at the time of open lumbar discectomy affects clinical outcome or scar formation. Of the 99 patients included in the study, 50 received a free at graft and 49 did not. Patients treated with fat graft had less dural scar but no difference in radicular scarring. This study provides Level I therapeutic evidence that adding a fat graft following open discectomy does not improve clinical outcome. Gambardella et al13 conducted a prospective randomized controlled trial evaluating the effect of an adipose tissue graft on postoperative scarring and clinical outcomes. Of the 74 patients included in the study, 37 received an adipose graft and 37 did not. Clinical and radiologic outcomes were superior in patients treated with the adipose graft. The authors concluded that adipose tissue autograft has a positive effect in preventing postoperative scarring and failed back syndrome. Scarring was associated with increased pain, and at reoperation, there was more scarring in the control group. Evaluation of varied surgical approaches used in the management of 170 far-lateral lumbar disc herniations: indications and results. Lateral transmuscular or combined interlaminar/paraisthmic approach to lateral lumbar disc herniation? Prospective triple-blind randomized study with reference to clinical factors and enhanced computed tomographic scan 1 year after operation. Tubular diskectomy vs conventional microdiskectomy for sciatica: a randomized controlled trial. Two-year outcome after lumbar microdiscectomy versus microscopic sequestrectomy: part 2: radiographic evaluation and correlation with clinical outcome. Differential treatment of nerve root compression pain caused by lumbar disc herniation applying nucleoplasty. People with lumbar disc herniation and associated radiculopathy benefit more from microdiscectomy than advice in the short term, although there is no difference in the long term. Foraminal and far lateral lumbar disc herniations: surgical alternatives and outcome measures. Automated percutaneous lumbar discectomy for the contained herniated lumbar disc: a systematic assessment of evidence. Perioperative epidural steroids for lumbar spine surgery in degenerative spinal disease: A review. Experience with limited versus extensive disc removal in patients undergoing microsurgical operations for ruptured lumbar discs. Peridural scar and its relation to clinical outcome: A randomised study on surgically treated lumbar disc herniation patients. Percutaneous lumbar laser disc decompression: a systematic review of current evidence.
T1: Solitary tumor without vascular invasion; T2: Solitary tumor with vascular invasion or multiple tumors; T3: Tumor perforating the visceral peritoneum or involving the local extra hepatic structures by direct invasion arthritis red feet discount arcoxia online amex. Intrahepatic Bile Ducts 203 In order to view this proof accurately arthritis pain kirkland buy cheap arcoxia on line, the Overprint Preview Option must be set to Always in Acrobat Professional or Adobe Reader rheumatoid arthritis diet blog buy discount arcoxia 90 mg online. These include the following: Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma Mass forming tumor growth pattern Periductal infiltrating tumor growth pattern Mixed mass forming and periductal infiltrating growth pattern Mixed Hepatocellular this staging classification does not apply to primary sarcomas of the liver stroma or to liver metastases from other sites arthritis in feet pics order genuine arcoxia on-line. The histopathologic subtype and, in the case of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, the tumor growth pattern both should be recorded, since they may provide prognostic information. Surgical treatment of 32 patients with peripheral intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Macroscopic types of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: clinicopathologic features and surgical outcomes. Predictive factors for long-term survival in patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Analysis of the relationships between clinicopathologic factors and survival time in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Combined hepatocellular and cholangiocarcinoma: proposed criteria according to cytokeratin expression and analysis of clinicopathologic features. A comparison of trends in the incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in the United States. Results of surgical treatment for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and clinicopathological factors influencing survival. A new staging system for mass-forming intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: analysis of preoperative and postoperative variables. Increasing incidence and mortality of primary intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in the United States. Spanish experience in liver transplantation for hilar and peripheral cholangiocarcinoma. Rising incidence of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in the United States: a true increase? Risk factors for intrahepatic and extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a hospital-based case-control study. Value of lymph node dissection during resection of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Impact of classification of hilar cholangiocarcinomas (Klatskin tumors) on the incidence of intra- and extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in the United States. The liver is a common site of involvement; thus, liver invasion impacts the primary tumor (T) classification. Other surrounding structures, such as the duodenum and transverse colon, are at risk of direct tumor extension. Invasion of hilar structures (common bile duct, hepatic artery, portal vein) usually renders these tumors locally unresectable. Development of jaundice suggests hilar involvement and is associated with unresectablility and poor prognosis. Cholelithiasis is associated with carcinoma of the gallbladder in the majority of cases. Many of these cancers are found incidentally following cholecystectomy, either at operation or on final histologic analysis of the specimen. Tumors encountered this way may have a better prognosis when amenable to definitive surgical resection either at the time of cholecystectomy or at a subsequent operation. As many as 50% of resected gallbladder cancers undergo definitive resection at a second operation, with the gallbladder having been removed previously for presumed benign disease. Cystic duct involvement merits consideration of formal bile duct resection at the time of the definitive operation to achieve negative margin status. Peritoneal involvement is common, and diagnostic laparoscopy at the time of surgery is usually advised.
These realities should be kept in mind when designing arthritis pain suddenly worse order arcoxia cheap online, and choosing to fund arthritis magazine generic arcoxia 90mg overnight delivery, such trials arthritis in neck pain relief purchase genuine arcoxia online. Those responsible for cancer control programmes 102 should strongly encourage the development of trials that test technologies and applications that could be feasibly implemented in a variety of settings arthritis pain lower back cheap arcoxia 120mg with mastercard, including less developed countries. However, effective approaches for bringing these benefits to patients in the community have not yet been developed for many settings. Various models for the delivery of palliative care, especially for the patient at home, need to be developed and investigated. In the context of a national cancer control programme, a surveillance programme should provide data on a continuing basis on incidence, prevalence, mortality, diagnostic methods, stage distribution, treatment patterns, and survival. It can also provide information about important risk factors and the prevalence of exposure to those factors in the population. Surveillance, therefore, plays a crucial role in formulating the cancer control plan, as well as in monitoring its success. Benefit comes only from careful analysis of the collected data, and it is therefore essential to allocate adequate resources for that purpose when a surveillance system is planned. A comprehensive national cancer control programme requires a system of surveillance of cancer, its determinants, and outcomes. Over the past 50 years, the concept of cancer surveillance has evolved, centred upon the population-based cancer registry as a core component of the cancer control strategy (Greenwald, Sondik, Young, 1986; Armstrong, 1992). The roles of cancer surveillance are: to assess the current magnitude of the cancer burden and its likely future evolution; to provide a basis for research on cancer causes and prevention; to provide information on prevalence and trends in risk factors; to monitor the effects of prevention, early detection/screening, treatment, and palliative care. Incidence Incidence of disease is clearly an important measure of burden, since it describes the new cases that will require medical attention. It is the key 105 Surveillance in Cancer Control measure when considering prevention. Measurement of incidence requires the identification of all new cases of disease in a defined population through some kind of case-finding mechanism, with record-linkage to ensure that persons are not confused with events. Cancer registries may present incidence according to histological subtype of cancer, or stage of disease at diagnosis. Mortality Mortality rates have been more widely used, since these have been available for a much longer period, and usually for large (national) populations. They are used in evaluations comparing disease rates between different populations, and over time to study differences in disease risk. They also provide a measure of disease outcome for evaluating, for example, the effectiveness of programmes of prevention, early detection and treatment of cancer. Essentially, these quantify the spectrum of morbidity in terms of its duration and severity between onset of a disease and death or recovery. Survival Survival from cancer is the measure most often used to evaluate cancer treatment. Computation of survival depends upon follow-up of diagnosed cancer patients, and the calculation of the proportion surviving after different intervals of time. Overall survival in the population reflects many factors-the stage of disease (influenced by early diagnosis or screening) and the availability of, access to , and effectiveness of treatment. Stage-specific survival provides a more relevant indicator of effectiveness of therapy (although accuracy with which stage of disease is measured varies between populations, and over time). Prevalence can be estimated directly by some cancer registries from their files of registered cases who have not died. Alternatively, prevalence can be estimated from the incidence of disease and survival curves, either for short-term survivors (for example, up to 5 or 10 years) or, if incidence and survival data are available for long periods, including long-term survivors also. This is because of the serious nature of most cancers, which means that, except in a few societies without access to medical care, patients will almost always present for diagnosis and treatment. This has permitted the development and use of cancer registries, particularly population-based registries, which relate the incident cancer cases to a defined population-at-risk (Jensen et al. The population-based cancer registry collects data on every person with cancer in a defined population, usually comprising people resident in a welldefined geographical region. The cooperation of the medical profession and health care services is vital to the success of cancer registration. The population-based cancer registry provides incidence rates, and the emphasis is on epidemiology and public health. The emphasis of a cancer registry should be on the quality of the data collected, rather than on the quantity.
Order arcoxia with a mastercard. Managing Arthritis in Dogs with JM Joint Mobility Dog Food.