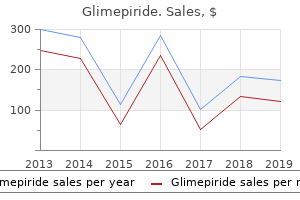
"Buy glimepiride 2mg with mastercard, diabetes insipidus lab values bun".
By: A. Ressel, M.A., M.D., M.P.H.
Professor, UAMS College of Medicine
Blended oxygen and air should be available to help avoid prolonged hyperoxia after the initial resuscitation diabetes insipidus caused by head trauma buy cheap glimepiride 2mg, and it should be used in conjunction with pulse oximetry zentraler diabetes insipidus cheap glimepiride 1mg mastercard, using a probe placed on the right upper ("preductal") extremity diabetes insipidus sweating 1mg glimepiride visa. Studies have demonstrated that a blend of oxygen and air is preferable over either one alone diabetes symptoms pre diabetes risk factors glimepiride 4 mg, but the optimal concentration has not yet been identified; we have chosen to start with 60% oxygen and titrate the concentration based on measured oxygen saturation. We use the saturation targets identified for all babies the first several minutes (see Table 5. If the neonate cries vigorously at birth, we administer blow-by blended oxygen if required on the basis of saturation, and observe the infant for signs of distress. Many of these infants require bag-and-mask ventilation because of apnea or ineffective respiratory drive. In studies comparing these modalities, there were no differences in survival or incidence of chronic lung disease. If the infant is not breathing spontaneously, positive pressure ventilation must be started; provision of adequate support will result in or maintain a normal heart rate. If positive pressure ventilation is used, moderately high-inflating pressures may be necessary for the initial breaths of an infant whose lungs are deficient in surfactant. Within one or two breaths, the peak pressure should be rapidly lowered to minimize lung injury, with the goal of using the smallest tidal volumes and peak pressure possible while still adequately ventilating the infant. These infants usually require continued respiratory support and do benefit from early application of end-expiratory pressure; our practice is to provide this via endotracheal intubation and ventilation shortly after birth. While commonly practiced in many institutions, administration of exogenous surfactant therapy before the first breath has not yet been proved to be more beneficial than administration after initial stabilization of the infant. Exogenous surfactant may be safely administered in the delivery room once correct endotracheal tube position has been confirmed clinically. The pediatrician should assess the response to resuscitation and gauge the need for further interventions. If the infant fails to respond, the team should recheck that all supporting measures are being effectively administered. If, on the other hand, there is no positive response to resuscitation after a reasonable length of time, we consider limiting support to comfort measures alone. As soon as possible, the unit is closed to function as an incubator for continued care. Humidity is maintained at 70% for the first week of life, and 50% to 60% thereafter up to 32 weeks corrected gestation. In addition to reducing insensible fluid losses and thereby simplifying fluid therapy, the use of incubators aids in reducing unnecessary stimulation and noise experienced by the baby. Large fluid losses, balances between fluid intake and blood glucose levels, delicate pulmonary status, and the immaturity and increased sensitivity of several organ systems all require close monitoring. The first several days after birth, but in particular the first 24 to 48 hours, are the most critical for survival. Infants who require significant respiratory, cardiovascular, and/or fluid support are assessed continuously, and their chances for ongoing survival are evaluated as part of this process. If caregivers and the parents determine that death is imminent, continued treatment is futile, or treatment is likely to result in survival of a child with profound neurologic impairment, we recommend the withdrawal of ventilator and other invasive support and redirection of care to comfort measures and support of the family. The lowest possible tidal volume to provide adequate ventilation and oxygenation and a short inspiratory time should be used. Special effort should be made to avoid hyperoxia by targeting oxygen saturations at lower levels than have been traditionally used. A recent report found that a target range of 85% to 89% decreased retinopathy but may be associated with an increase in mortality, compared to a range of 90% to 94%. These alarm limits are designed to allow staff a few seconds General Newborn Condition 161 2. This can be effectively done while still ensuring that a saturation level that remains, for example, at 86% will be addressed by increasing oxygen concentration, even though the value lies within the alarm limits. It is hypothesized that limiting hyperoxia may also reduce the incidence or severity of chronic lung disease. It is important as well to avoid hypocapnia, although the potential benefit of permissive hypercapnia as a ventilatory strategy remains a subject of debate.
Inhibitory effect of Andrographis paniculata extract and its active diterpenoids on platelet aggregation metabolic disease 5th order 4 mg glimepiride with visa. Antithrombotic effects of Andrographis paniculata nees in preventing myocardial infarction diabetes diet menu purchase glimepiride 2 mg with visa. Constituents Aniseed fruit contains 2 to 6% of a volatile oil composed mostly of trans-anethole (80 to 95%) who diabetes definition 2011 discount glimepiride online master card, with smaller amounts of estragole (methyl chavicol) diabetic diet on food stamps buy discount glimepiride 2mg on line, -caryophyllene and anise ketone (p-methoxyphenylacetone). Natural coumarins present include scopoletin, umbelliferone, umbelliprenine and bergapten, and there are numerous flavonoids present, including quercetin, apigenin and luteolin. Aniseed appears to have some oestrogenic effects, but the clinical relevance of this is unclear. For information on the interactions of individual flavonoids present in aniseed, see under flavonoids, page 186. Although aniseed contains natural coumarins, the quantity of these constituents is not established, and therefore the propensity of aniseed to interact with other drugs because of their presence is unclear. Consider natural coumarins, page 297, for further discussion of the interactions of natural coumarin-containing herbs. Effects of the naturally occurring alkenylbenzenes eugenol and trans-anethole on drug-metabolizing enzymes in the rat liver. Use and indications Aniseed dried fruit, or oil distilled from the fruit, are used mainly for their antispasmodic, carminative and parasiticide effects. Pharmacokinetics Studies in rats suggested that trans-anethole did not alter 33 34 Aniseed oestrogenic. Importance and management these experimental studies provide limited evidence of the possible oestrogenic activity of aniseed. Because of the nature of the evidence, applying these results in a clinical setting is extremely difficult and, until more is known, it would be unwise to advise anything other than general caution. Estrogenic activity of isolated compounds and essential oils of Pimpinella species from Turkey, evaluated using a recombinant yeast screen. Aniseed + Oestrogens the interaction between aniseed and oestrogens is based on experimental evidence only. Experimental evidence In a yeast oestrogen screen assay, the fruit oil from aniseed was Aristolochia Aristolochia species (Aristolochiaceae) A Synonym(s) and related species the nomenclature of these and related plants has given rise to confusion with other, non-toxic plants. This has been exacerbated by the fact that different Chinese names have been used for each species. Birthwort has been used as a collective name for the Aristolochia species, but it has also been used for one of the species, Aristolochia clematitis L. The Chinese name Mu Tong has been used to refer to some of the Aristolochia species. Aristolochia fangchi has been referred to by the Chinese names Fang Chi, Fang Ji, Guang Fang Ji. Constituents All species contain a range of toxic aristolochic acids and aristolactams. Use and indications Aristolochic acids and aristolactams are nephrotoxic, carcinogenic and cytotoxic. Numerous deaths have resulted from aristolochic acid nephropathy and associated urothelial cancer, caused by ingestion of aristolochia both medicinally and from contamination of food. All plants of the family Aristolochiaceae are banned in Europe and elsewhere, and should be avoided. Constituents the main constituents of the bark are triterpenoid saponins including arjunic acid, arjunolic acid, arjungenin and arjunglycosides, and high levels of flavonoids, such as arjunone, arjunolone, luteolin and quercetin. Polyphenols, particularly gallic acid, ellagic acid and oligomeric proanthocyanidins, are also present. Interactions overview Arjuna appears to have some effects on cardiovascular function, which may lead to interactions with conventional drugs used for similar indications. Arjuna may also affect thyroid function, which could alter the control of both hyperand hypothyroidism.
It was suggested that this adverse event was due to the change in climate rather than the medication diabetic lunch ideas purchase 1 mg glimepiride overnight delivery. Importance and management Clinical evidence is limited to one study that was not specifically designed to assess interactions diabetes type 1 and 2 yahoo purchase glimepiride 2 mg free shipping. The reduction in blood pressure found in animal studies seems unlikely to be clinically relevant managing your diabetes on demand purchase glimepiride 1mg, due to the high doses used diabetes diet sample order glimepiride online. Circosta C, Occhiuto F, Ragusa S, Trovato A, Tumino G, Briguglio F, de-Pasquale A. Importance and management Evidence is limited to a case study, which reports minor adverse effects, and experimental data. The evidence is too sparse to make any firm recommendations, but it may be prudent to consider a possible interaction if a patient taking a coumarin develops otherwise unexplained bruising. The pressed juice (from the aerial parts) contains heterogeneous polysaccharides, inulin-type compounds, arabinogalactan polysaccharides and glycoproteins. Use and indications Echinacea is mainly used for its immunostimulant (immunomodulatory) effects, particularly in the treatment and prevention of the common cold, influenza and other upper respiratory tract infections. It has a long history of medicinal use for infections, both bacterial and viral, especially in skin conditions such as acne and boils, and also in mild septicaemia. E Pharmacokinetics Most work has been carried out using Echinacea purpurea, although other Echinacea species have been studied on selected isoenzymes. Constituents the constituents of the various species are slightly different and this leads to confusion as to the potential for drug interactions. Alkylketones, and the saturated pyrrolizidine alkaloids, tussilagine and isotussilagine, are also present (these are not the unsaturated hepatotoxic type). Polyenes and polyacetylenes, including a range of ketoalkenes and ketopolyacetylenes, have been reported and polysaccharides and glycoproteins are also present. The herb contains similar alkamides, and cichoric acid is the major caffeic acid derivative present. Cytochrome P450 inhibitory action of Echinacea preparations differs widely and co-varies with alkylamide content. Interactions overview Theoretically, echinacea may antagonise the effects of immunosuppressants. The use of echinacea has been studied with a number of drugs that are used as probe substrates for cytochrome P450 activity or P-glycoprotein. With the possible exceptions of midazolam and caffeine, no clinically relevant interactions have been identified. Echinacea seems to present a low risk for interactions occurring as a result of these mechanisms. E Echinacea 169 Echinacea + Caffeine Echinacea appears to have a variable effect on the pharmacokinetics of caffeine. Clinical evidence In a pharmacokinetic study, 12 healthy subjects were given an 8-day course of Echinacea purpurea root 400 mg four times daily, with a single 200-mg oral dose of caffeine on day 6. There was a large variation between subjects, with some having a 50% increase in caffeine clearance, and some a 90% decrease. However, some patients did experience a decrease in caffeine clearance, which suggests that, rarely, caffeine levels may be raised. Some patients may therefore experience some increase in the adverse effects of caffeine, such as headache, tremor and restlessness, particularly if they have a a high caffeine intake. Should this occur, advise the patient to either stop taking echinacea and/or reduce their caffeine intake. Importance and management the available evidence seems to reliably suggest that in most patients echinacea does not affect the pharmacokinetics of dextromethorphan. However, dextromethorphan is generally considered to have a wide therapeutic range and the dose is not individually titrated. E Echinacea + Digoxin Echinacea does not appear to have a clinically relevant effect on the pharmacokinetics of digoxin. Clinical evidence In a study, 18 healthy subjects were given an extract containing Echinacea purpurea 195 mg and Echinacea angustifolia 72 mg three times daily for 14 days with a single 250-microgram dose of digoxin before and after the course of echinacea. No significant effects on the pharmacokinetics of digoxin were reported for echinacea, suggesting that echinacea does not have any significant effects on P-glycoprotein. Importance and management the available evidence suggests that echinacea does not significantly Echinacea + Dextromethorphan Echinacea does not appear to have a clinically relevant effect on the pharmacokinetics of dextromethorphan. Clinical evidence In a study, 12 healthy subjects were given Echinacea purpurea root 400 mg four times daily for 8 days with a single 30-mg dose of dextromethorphan on day 6.
A skeletal abnormality resulting in short stature with associated poor weight gain (D) diabetes insipidus thiazide buy glimepiride 4 mg otc. Malabsorption diabet xesteliyin mualicesi buy glimepiride 4mg on-line, or the inability to completely absorb ingested calories and nutrients (E) diabetes prevention diet uk cheap glimepiride 2mg mastercard. Endocrinologic abnormalities diabetes symptoms veins cheap glimepiride 3mg online, such as growth hormone deficiency or hypothyroidism 2. In addition to a head circumference > 95%, his coronal and sagittal sutures are split 1 cm and his fontanelle is bulging. The infant was fed with formula until 6 months, at which time she was switched to baby foods and whole milk. Which one of the following is correct regarding lead screening and lead intoxication Low lead levels on screening indicate that a child is at no risk for the neurologic sequelae of lead exposure. Ingestion of paint from a home built in 1990 would place a child at risk for lead poisoning. At a prenatal visit, the expectant parents of a first-born male child ask you to summarize the benefits, risks, and contraindications to performing a circumcision on their son. Circumcision has been demonstrated definitively to decrease the risk of urinary tract infection. Because of the young age at which circumcision is performed, analgesia is generally not required, thus decreasing the risks of the procedure when performed in the newborn period. If their child is not circumcised in the newborn period, he may require circumcision at 9 months of age if he is subsequently diagnosed with phimosis. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends routine circumcision for medical benefit. The use of both fluoride drops and fluoride toothpaste simultaneously, which has caused fluorosis (B). A 1-year-old child living in an apartment with old chipping paint is suspected of being at high risk for lead intoxication. Which of the following findings on a routine health maintenance visit would support this diagnosis On a routine health maintenance visit, a 9-month-old infant is noted to have normal growth and development, and an unremarkable physical examination. Which of the following should be included in your counseling of the parents at this time Vitamin D supplementation should be initiated if the patient has minimal exposure to sunlight. The patient should be encouraged to begin using a walker to stimulate gross motor development. You receive a telephone call from the parents of a 10-month-old infant, who are concerned that their baby does not yet have any teeth. Immunization is indicated, and both live and non-live vaccine options are available. For each patient, select the appropriate type of immunization indicated at this time, if any. A 2-year-old child living in a region of the country at high risk for hepatitis A exposure presents for a routine health maintenance visit. A 5-year-old child with otherwise up-to-date immunization status presents with no known history of chicken pox exposure and no record of having received the varicella vaccine. The diagnosis of plagiocephaly is made at a 4-month routine health maintenance visit. Which of the following would be the most appropriate course of action at this time Obtain skull radiographs to better delineate which cranial sutures may have fused prematurely. Reassure the parents that this is likely positional plagiocephaly, and recommend stretching exercises, repositioning the head during sleep, and increased time in the prone position when awake.
Generic glimepiride 3mg without a prescription. Dinaz Aerobic Exercise for Diabetes.