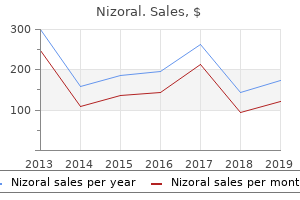
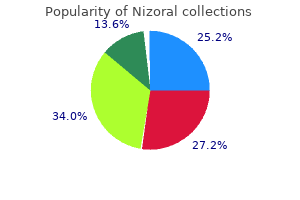
"Purchase nizoral once a day, antifungal drops for ears".
By: W. Spike, MD
Assistant Professor, Duquesne University College of Osteopathic Medicine
Chronic inflammation can lead to airway remodeling kingdom fungi definition biology order nizoral mastercard, which results from a proliferation of extracellular matrix proteins and vascular hyperplasia and may lead to irreversible structural changes and a progressive loss of pulmonary function antifungal veterinary drugs buy nizoral no prescription. Asthma is the most common chronic disease of childhood in industrialized countries fungus gnat nepenthes buy genuine nizoral on line, affecting nearly 7 million children younger than 18 years of age in the United States antifungal hydrogen peroxide 200mg nizoral for sale. One in 5 children went to the emergency department for an asthma-related visit in 2009. Women are more likely than men to have asthma, and boys are more likely than girls to have asthma. These tests are indicated for patients who have dermatographism or extensive dermatitis; who cannot discontinue medications, such as antihistamines, that interfere with skin test results; who are very allergic by history, where anaphylaxis is a possible risk; or who are noncompliant for skin testing. The presence of specific IgE antibodies alone is not sufficient for the diagnosis of allergic diseases. Exacerbating factors include viral infections, exposure to allergens and irritants. Rhinosinusitis, gastroesophageal reflux, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (especially aspirin) can aggravate asthma. Treatment of these conditions may lessen the frequency and severity of the asthma. During acute episodes, tachypnea, tachycardia, cough, wheezing, and a prolonged expiratory phase may be present. Classic wheezing may not be prominent if there is poor air movement from airway obstruction. As the attack progresses, cyanosis, diminished air movement, retractions, agitation, inability to speak, tripod sitting position, diaphoresis, and pulsus paradoxus (decrease in blood pressure of >15 mm Hg with inspiration) may be observed. Physical examination may show evidence of other atopic diseases such as eczema or allergic rhinitis. A chest radiograph should be performed with the first episode of asthma or with recurrent episodes of undiagnosed cough or wheeze to exclude anatomic abnormalities. Repeat chest radiographs are not needed with new episodes unless there is fever (suggesting pneumonia) or localized findings on physical examination. Two novel forms of monitoring asthma and airway inflammation directly include exhaled nitric oxide analysis and quantitative analysis of expectorated sputum for eosinophilia. Spirometry is used to monitor response to treatment, assess degree of reversibility with therapeutic intervention, and measure the severity of an asthma exacerbation. Variability in predicted peak flow reference values make spirometry preferred to peak flow measures in the diagnosis of asthma. For younger children who cannot perform spirometry maneuvers or peak flow, a therapeutic trial of controller medications helps in the diagnosis of asthma. Allergy skin testing should be included in the evaluation of all children with persistent asthma but not during an exacerbation of wheezing. Misdiagnosis delays correcting the underlying cause and exposes children to inappropriate asthma therapy (Table 78-2). Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis is a hypersensitivity type of reaction to antigens of the mold Aspergillus fumigatus. It occurs primarily in patients with steroid-dependent asthma and in patients with cystic fibrosis. Because many children with asthma have coexisting allergies, steps to minimize allergen exposure should be taken (Table 78-3). For all children with asthma, exposures to tobacco and wood smoke and to persons with viral infections should be minimized. Asthma medications can be divided into long-term control medications and quick-relief medications. Long-Term Control Medications Inhaled Corticosteroids Inhaled corticosteroids are the most effective anti-inflammatory medications for the treatment of chronic, persistent asthma and are the preferred therapy when initiating longterm control therapy. Early intervention with inhaled corticosteroids reduces morbidity but does not alter the natural history of asthma.
Overexposure of the cranial region to retinoic acid can result in "caudalization fungus gnats natural predators 200mg nizoral free shipping," i fungus fingernail quality nizoral 200 mg. During development fungus killer buy nizoral with amex, the spinal cord and presumptive brainstem develop three layers: (1) a germinal layer or ventricular zone fungal rash on back buy generic nizoral line, (2) an intermediate layer containing neuroblasts and comprising gray matter, and (3) a marginal zone containing myelinated fibers (white matter). Other layers are added in the cerebrum and cerebellum by cell migration along glial scaffolds. The notochord induces the establishment of dorsal-ventral polarity in the neural tube. Ventral portions of the tube will become the basal plate and give rise to motor neurons, whereas the dorsal portions become the alar plates, derivatives of which subserve sensory functions. Meninges are formed by mesoderm surrounding the neural tube with contributions to the arachnoid and pia from neural crest. Folic acid, also known as folate, is a B-vitamin that can be found in some enriched foods and vitamin supplements. Public Health Service recommends that all women who could possibly become pregnant get 400 (or 0. Folic acid is found in some foods, such as enriched breads, pastas, rice, and cereals (some with 100% of the daily requirement). Damage is dependent on gestational age, alcohol dosage, and pattern of maternal alochol abuse. Focal deficiencies in neural crest cell migration may result in lack of innervation to specific organs or parts of organs. In Hirschsprung disease (aganglionic megacolon), failure of neural crest cells to migrate to a portion of the colon results in a localized deficiency in parasympathetic intramural ganglia that may cause a loss of peristalsis and bowel obstruction. Each arch receives its blood supply from a specific aortic arch and its innervation from a specific cranial nerve (special or branchial visceral efferent fibers). The third aortic arch provides most of the adult blood supply to the head and neck. The skeletal muscles of the head and neck primarily arise from the pharyngeal arches and have a unique innervation (special visceral efferent). The face develops from a midline frontonasal prominence and bilateral maxillary and mandibular prominences. Teeth originate from both ectodermal (enamel) and neurectodermal (neural crest: dentin, pulp, cementum, and periodontal ligament) derivatives. Eye the eye is derived from three different germ layers: Neuroectoderm: Vesicular outgrowths of the forebrain differentiate into retina and optic nerve. Surface ectoderm: Contributes to the lens, cornea, and epithelial coverings of the lacrimal glands, eyelids, and conjunctiva. Structures of the outer and middle ear are derived from the first and second pharyngeal arches and the first pharyngeal cleft. Structures of the inner ear are derived from the ectodermal otic placode, not neuroectoderm. Maternal rubella can cause defects in both eye (fourth to sixth weeks of gestation) and ear (seventh to eight weeks). The heart tubes forming on either side of the endodermal tube are brought together by lateral body folding. Looping of the heart tube occurs while the tube is being divided into left and right portions by the interatrial and interventricular septa. In the interatrial septum, the septum primum and septum secundum do not close off the foramen ovale until birth. Failure of the atrioventricular endocardial cushions to fuse can result in septal and valve defects. Neural crest cells contribute to septation of the truncus arteriosus and the formation of the aortic and pulmonary outflows, as well as the aortic arches. Vasculature Vasculogenesis versus Angiogenesis the endothelial lining of most blood vessels forms by coalescence of vascular endothelial progenitors (angioblasts) of mesodermal origin.
Purchase 200 mg nizoral fast delivery. How to make Organic pesticide at home.
Because IgM and IgA do not cross the placenta fungus gnats neem oil nizoral 200mg discount, they are useful in determining congenital infection fungus gnats extension purchase nizoral 200 mg otc. If maternal blood contamination is possible antifungal jock itch spray buy nizoral toronto, repeat the IgM fungus gnats roses purchase cheap nizoral on line, IgA, and IgE testing in a few days. In infants who are IgM and IgA negative, the traditional means of diagnosis is to wait for clearance of transplacental IgG at about 12 months of age. IgA rises rapidly, and it usually disappears by 7 months (uncommonly, more than 1 year). In congenital toxoplasmosis, antibody production varies significantly and is affected by treatment. The Sabin-Feldman dye test (IgG) uses the uptake of methylene blue by Toxoplasma tachyzoites (organisms appear swollen and blue). The tachyzoite membranes lyse in the presence of complement and IgG-specific antibody (organisms appear thin and unstained). There is extensive experience with this test, particularly as an antenatal screen for maternal seroconversion in pregnancy. Persistence of Toxoplasma-specific immunoglobulin (IgM) may indicate active infection. Toxoplasma-specific IgG has been seen, and quantitative IgG levels should be determined as a baseline. They may be single or multiple and are usually limited to intracranial structures. Common locations include periventricular, scattered in the white matter, and the basal ganglia (often caudate). Histology may demonstrate tachyzoites (acute toxoplasmosis) or cysts (acute or chronic toxoplasmosis) in the placenta, tissue, or body fluids. Tissue or mouse culture can be performed to isolate the parasite from peripheral blood buffy coat or the placenta, but may require 1 or 6 weeks, respectively, for results. Congenital infection is frequently subclinical, has symptoms similar to other infections and diseases, and serologic diagnosis may be difficult. Therapy is recommended, regardless of symptoms, to prevent the high incidence of sequelae, resolve acute symptoms, and improve outcomes. Pyrimethamine (1 mg/kg every 12 hours for 2 days, then daily until 2 to 6 months of age, then 3 times weekly until 1 year of age), and sulfadiazine (50 mg/kg every 12 hours until 1 year of age) act synergistically and can result in symptom resolution within the first few weeks of therapy. Other less frequent side effects include gastrointestinal distress, convulsions, and tremor. Folinic acid (10 mg 3 times weekly until 1 week after pyrimethamine is stopped) helps prevent bone marrow suppression, but temporary cessation of therapy with pyrimethamine or dose modification may be required. Side effects of sulfadiazine include bone marrow suppression, crystalluria, hematuria, and hypersensitivity. Alternative medications for atopy or severe intolerance of sulfadiazine include clindamycin, azithromycin, and atovaquone. However, combining these agents with antiretrovirals, such as zidovudine, may increase bone marrow toxicity. Ventricular shunting for ventricular dilation is recommended, although systematic outcome data is unavailable. After treatment with ventricular shunt and medications, some patients experience significant improvement in hydrocephalus with brain cortical expansion and growth. With treatment, chorioretinitis usually resolved within 1 to 2 weeks and did not relapse during therapy. Visual impairment at 5 years of age is a prominent sequela, even with treatment in 85% of patients who had severe disease at birth and 15% of neonates with mild or asymptomatic disease. Acuity may be adequate for reading and daily activities even with large macular scars. Poor acuity has affected school performance and cognitive development for some patients.
The somatopleuric mesoderm (answer c) makes important contributions to the skin (dermis) and nonmuscle portions of the limbs fungus in hair purchase genuine nizoral online. The hypoblast (answer e) is the thin layer of cells ventral to the epiblast; it is displaced by the epiblast cells fungal respiratory infections quality nizoral 200mg, which form endoderm fungus yellow toenail best 200mg nizoral. The intermediate mesoderm is the origin of the urogenital systems and the adrenal cortex (answer a) antifungal quizlet buy nizoral canada. The humerus (answer c) forms from somatopleuric mesoderm, but the muscles attached to it are of somite origin. The masseter (answer e) is a muscle of mastication formed from the first branchial arch and innervated by branchial visceral efferent (special visceral efferent) fibers from the nucleus ambiguus compared with the general somatic efferent innervation of the biceps and other muscles, not of branchial arch origin. The cortex, peripheral areas of gray matter, is formed through the migration of cells from the mantle zone to the marginal zone. Segmentation of the cranial neural tube forms the brain vesicles listed in the table below. Primary Brain Vesicle Prosencephalon (forebrain) Mesencephalon (midbrain) Rhombencephalon (hindbrain) Secondary Brain Vesicle Telencephalon Diencephalon Mesencephalon Metencephalon Myelencephalon Adult Brain Derivative Cerebral cortex, corpus striatum Hypothalamus, thalamus Superior and inferior colliculi Pons and cerebellum Medulla 25. During embryonic folding, the dorsal part of the yolk sac is incorporated into the embryo as the primitive gut. The primordial germ cells subsequently migrate along the dorsal mesentery of the hindgut (answer a) and into the gonadal (genital) ridge by week 6 (answer b). The primary sex cords grow into the mesenchyme underlying the ridge, and the primordial germ cells become incorporated into the primary sex cords (answer d). The chorion (answer e) is the outermost fetal membrane and is composed of extraembryonic somatic mesoderm, cytotrophoblast, and the syncytiotrophoblast. It is divided into the chorion frondosum, where the villi form and proliferate, and the smooth chorion, also known as the chorion laevae. Embryology: Early and General Answers 93 (Modified, with permission, from Sweeney L. The yolk sac produces predominantly hematocytoblasts (stem cells) and primitive erythroblasts. The endoderm of the yolk sac is incorporated into the embryo as part of the primitive gut during embryonic folding and is home to the primordial germ cells before they migrate to the hindgut. The transfer of nutrients is an important function of the yolk sac early in development, but once the uteroplacental circulation is established, the placenta takes over that role (answer b). The cells of the amnion (answer d) form the amniotic fluid with eventual addition of urine from the developing kidneys. The diagram above illustrates the location of the yolk sac and other embryonic structures. Fertilization of one oocyte by two sperm (answer c) cannot occur because of the Ca2+-dependent block to polyspermy (see question 6). That egg cortical reaction affects the zona pellucida in two ways: (1) hydrolysis of carbohydrate prevents sperm binding and (2) proteolytic activity hardens it. Ectoderm is continuous with the amniotic membrane, endoderm with the lining of the yolk sac (answer c), and embryonic mesoderm with the extraembryonic mesoderm (answer d). The chorion (answer a) consists of two parts, smooth (laeve) and villous (frondosum; see figure in feedback to question 25. Fusion of the endocardial heart tube and incorporation of the yolk sac into the primitive gut also occurs as a result of lateral folding. Craniocaudal folding (answer b) establishes the definitive head and tail regions of the embryo. Fusion is already complete at the time that looping of the heart tube occurs (answer c). Gastrulation (answer d) establishes the three germ layers (trilaminar disk), and neurulation establishes the neural groove with two neural folds. The region labeled with the arrow in the accompanying electron micrograph of the plasma membrane is responsible for which of the following functions Creation of a barrier to water-soluble molecules Specific cellular receptors for ligands Catalyzing membrane-associated activities Transport of small ions Connections to the cytoskeleton 97 Copyright 2007 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. His mother reports that she had numerous upper respiratory infections and chronic diarrhea as a young child.