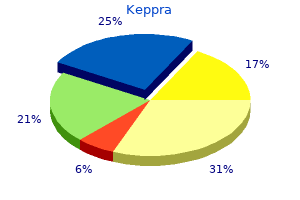
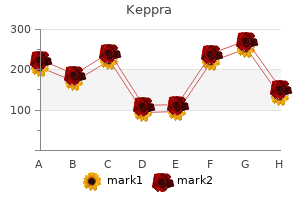
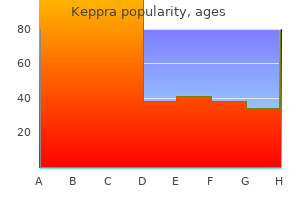
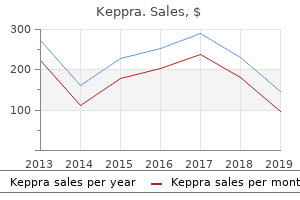
"Order discount keppra online, medications of the same type are known as".
By: R. Goran, M.B. B.A.O., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Assistant Professor, New York Institute of Technology College of Osteopathic Medicine at Arkansas State University
These assays are highly specific but cannot differentiate acute infection from chronic infection symptoms wheat allergy discount keppra 500mg on line. Reservoir symptoms your period is coming buy keppra in india, source medicine 035 order 500 mg keppra with visa, and transmission of infection Hepatitis C is exclusively a human disease medications every 8 hours discount keppra 250 mg otc. Patients who are infected with the virus are the important reservoir of infection. Blood or blood products and also organs of infected patients are the major sources of infection. The use of intravenous drugs is most important risk factor responsible for around 50% of both acute and chronic infections. Sexual transmission: Sexual transmission is believed to be responsible for approximately 20% of cases of hepatitis C. Hepatitis C virus genotyping is a recent method, which is frequently helpful for predicting the likelihood of response and duration of treatment. The genotyping is performed either by direct sequence analysis or restriction fragment length polymorphism. Other therapeutic options include the use of protease inhibitors, ribozymes, and viral vaccines. Chapter 66 Hepatitis D Virus Hepatitis D virus is the smallest of known human pathogens that causes infections in humans. Chronic coinfection often leads to a rapidly progressive subacute or chronic hepatitis, resulting in more rapid progression to cirrhosis. It is observed more commonly among patients with history of intravenous drug users. Hepatitis D virus, like hepatitis B virus, is a blood pathogen and is transmitted mostly by blood and vaginal secretions. It is most commonly transmitted by nonpercutaneous routes, especially by close intimate contact in endemic areas of Mediterranean countries. Infection appears to be more commonly transmitted through contaminated blood and blood products in nonendemic areas of northern Europe and North America. Intravenous drug use and multiple blood transfusions are the important risk factors for parenteral transmission of the disease. The incubation period varies from 21 to 45 days but may be shorter in cases of superinfection. Nearly 1% of the patients with coinfections progress to develop fulminant hepatitis resulting in more rapid progression to cirrhosis. Antiviral therapy with interferon is also ineffective in patients with chronic infections. It causes fulminant disease in pregnant women, especially in last trimester of pregnancy and has a high fatality rate of 1520%. During 19861988, one such large outbreak was reported in north-east China affecting nearly 10,000 people. Tropical climate, poor sanitation, and poor personal hygiene all contribute to the epidemic of the disease in developing countries. Hepatitis E virus is transmitted primarily by fecaloral route due to fecal contamination of water in endemic areas. The flavivirus-like isolates were first demonstrated in Tamarin monkeys inoculated with blood from a surgeon with acute hepatitis in 1995. Hepatitis G virus is a blood-borne virus, which is transmitted by transfusion of contaminated blood or blood products. Administration of immunoglobulin does not prevent development of clinical disease. The family Retroviridae, depending on (a) the diseases they cause, (b) tissue tropism and host range, (c) morphology of virions, and (d) genetic complexity are classified into three subfamilies, as follows: Oncovirinae: the Oncovirinae or oncoviruses include only the retroviruses that can transform target cells. The viruses depending on their core and capsid, as demonstrated in electron microscopy, are classified further into types A, B, C, or D. Lentivirinae: the lentivirinae or lentiviruses are slow (lent: slow) viruses associated with neurological and immunosuppressive diseases in humans as well as in animals.
An earlier version of this paper was presented at a meeting of the authors of this volume symptoms 2dpo cheap keppra online visa, in Ferney-Voltaire medications causing thrombocytopenia purchase keppra 250mg visa, France medications zanaflex discount keppra 250mg otc, in November 2013 symptoms pneumonia buy generic keppra 500mg. Black, Zulfiqar Bhutta, Jerry Keusch, and Carol Levin, as well as from Elizabeth Brouwer and Zachary Olson. Health Gains and Financial Risk Protection Afforded by Treatment and Prevention of Diarrhea and Pneumonia in Ethiopia 359 Constenla, D. World Health Report 2010: Health Systems Financing, the Path to Universal Coverage. First and fore- most, we would like to thank our 33 volume editors who provided the intellectual vision for their volumes based on years of professional work in their respective fields, and then dedicated long hours to reviewing each chapter, providing leadership and guidance to authors, and framing and writing the summary chapters. We also thank our chapter authors who collectively volunteered their time and expertise to writing over 160 comprehensive, evidence-based chapters. We owe immense gratitude to the institutional sponsor of this effort: the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation. The Foundation provided sole financial support of the Disease Control Priorities Network. Many thanks to Program Officers Kathy Cahill, Philip Setel, Carol Medlin, and (currently) Damian Walker for their thoughtful interactions, guidance, and encouragement over the life of the project. We are tremendously grateful for the wisdom and guidance provided by our advisory committee to the editors. Patrick Kelley, Gillian Buckley, Megan Ginivan, and Rachel Pittluck managed this effort and provided critical and substantive input. The World Bank External and Corporate Relations Publishing and Knowledge division provided exceptional guidance and support throughout the demanding production and design process. We would particularly like to thank Carlos Rossel, the publisher; Mary Fisk, Nancy Lammers, Rumit Pancholi, and Deborah Naylor for their diligence and expertise. Additionally, we thank Jose de Buerba, Mario Trubiano, Yulia Ivanova, and Chiamaka Osuagwu of the World Bank for providing professional counsel on communications and marketing strategies. Stйphane Verguet added invaluable guidance in applying and improving the extended cost-effectiveness analysis method. Shane Murphy, Zachary Olson, Elizabeth Brouwer, Kristen Danforth, David Watkins, Jennifer Nguyen, and Jennifer Grasso provided exceptional research assistance and analytic assistance. The efforts of these individuals were absolutely critical to producing this series, and we are thankful for their commitment. He is conducting epidemiologic research on the interaction of infectious diseases and nutrition, clinical and community-based trials of new vaccines to prevent childhood infectious diseases, and trials of nutritional interventions to reduce infectious disease morbidity and mortality, as well as improve growth and development. He is also assisting with implementation of disease control and nutrition programs in developing countries and conducting evaluations of their effectiveness and mortality impact. He is currently a Professor of International Health at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. She was previously Director, Reproductive Health and Research, World Health Organization. She is the Founding Director of the International Centre of Reproductive Health, Ghent University, Belgium, with sister organizations in Kenya and Mozambique. Neff Walker Neff Walker is a Senior Scientist in the Institute for International Programs, Department of International Health, Bloomberg School of Public Health, Johns Hopkins University. In both positions a primary focus of his work was the development Ramanan Laxminarayan Ramanan Laxminarayan is Vice President for Research and Policy at the Public Health Foundation of India, and he directs the Center for Disease Dynamics, Economics & Policy in Washington, D. His research deals with the integration of epidemiological models of infectious diseases and drug resistance into the economic analysis of public health problems. He was one of the key architects of the Affordable Medicines Facility for malaria, a novel financing mechanism to improve access and delay resistance to antimalarial drugs. In 2012, he created the Immunization Technical Support Unit in India, which has been credited with improving immunization coverage in the country. Jamison is a Senior Fellow in Global Health Sciences at the University of California, San Francisco, and an Emeritus Professor of Global Health at the University of Washington.
In cases of patient sensitivity to penicillin treatment junctional tachycardia order keppra in india, alternate therapy with erythromycin or tetracyclines may also be effective (see Figure 15 treatment 1st degree av block buy keppra no prescription. In spite of an inexpensive and highly effective cure treatment narcolepsy generic keppra 250mg line, there are still over 8000 new cases of syphilis in the United States each year (Figure 15 treatment xanax withdrawal purchase keppra with american express. Treponema pallidum by direct immunofluorescence Primary syphilis presenting as painless chancres of the penis Figure 15. Lyme disease is currently the most common arthropod-transmitted disease in the United States, averaging at least 10,000 cases per year. Clinical significance the first stage of Lyme disease begins 3 to 32 days after a tick bite, when a characteristic red, circular lesion with a clear center (erythema chronicum migrans) appears at the site of the bite (Figure 15. Weeks to months after the onset, the second stage of the disease begins, with symptoms such as arthritis, arthralgia, cardiac complications, and neurologic complications such as meningitis. Lyme disease is rarely fatal, but can result in a poor quality of life if untreated. IgM antibodies, which are directed against flagellar antigens, appear early after the onset of the disease, whereas IgG antibodies appear later. These antibodies offer protective immunity to reinfection, but the immunity is lost if the disease is treated early and successfully. Although caused by different spirochetes, the general similarities in the progression of Lyme disease and syphilis are striking. Serologic tests have been used to diagnose Lyme disease, but the number of false-positives can outnumber the true-positives. The most definitive test today is the polymerase chain reaction assay, which is rapid, sensitive, and specific (see p. Treatment and prevention B Epidemic louseborne In condition of poor hygiene Amoxicillin and doxycycline are useful treatments in the early stages of the disease (see Figure 15. Prevention of infection also includes use of insect repellents, and wearing clothing that sufficiently protects the body from tick bites. The organism is responsible for the disease relapsing fever, which is characterized by several cycles of apparent recovery, each followed by a relapse. This ability accounts for the relapsing nature of the disease because with each relapse a new antigenic variant arises. Pathogenesis A distinction is often made between endemic and epidemic relapsing fever. An endemic disease such as Lyme disease, which occurs in most areas of the world, is tickborne (B. Fatalities from the endemic disease are rare; however, during epidemics in crowded, unsanitary, louse-infested environments, fatalities can be as high as thirty percent if untreated. Temperature 106 104 102 100 98 myalgia myalgia myalgia Borrelia in blood smears: Yes No Yes Time No Yes Antibiotic treatment for 10 days Figure 15. Clinical significance the first symptoms of relapsing fever appear three to ten days after exposure to an infected arthropod (Figure 15. These symptoms include an abrupt onset of high fever, accompanied by severe headache, muscle pain, and general malaise. During this febrile period, which lasts three to five days, abundant spirochetes are present in the blood. Apparent recovery is experienced for a period of four to ten days, but is followed by a recurrence of the initial symptoms. In fatal cases, the spirochete invades many organs of the body (heart, spleen, liver, kidney), with death generally due to myocarditis. Diagnosis and treatment Diagnosis is usually based on the appearance of Giemsa- or Wrightstainable, loosely coiled spirochetes in the blood during the febrile stage of the disease. Tetracyclines, erythromycin, and penicillin have proven effective treatments (Figure 15. However, the relapsing nature of the disease makes it difficult to distinguish spontaneous remissions from response to therapy. No vaccines are available, and prevention is best accomplished by protecting against lice. The organism is a slender (lepto = slender), tightly coiled, culturable spirochete with a single, thin, axial filament, and hooked ends (Figure 15. Many serogroups and serotypes (serovars) are recognized and specific to distinct geographic locales. Electron micrograph of one end of a negatively stained Leptospira interrogans showing the axial fibril.
Lymph nodes measure 125 mm in diameter and are surrounded by a connective tissue capsule medications zolpidem order keppra on line amex. The reticulum or framework of the lymph node is composed of phagocytes and specialized types of reticular or dendritic cells (Color Photo 10) treatment associates buy 250 mg keppra fast delivery. Cortex: the cortex and the deep cortex treatment meaning purchase keppra overnight delivery, also known as paracortical area medications causing hyponatremia buy 250 mg keppra amex, are densely populated by lymphocytes. Roughly spherical areas containing densely packed lymphocytes, termed primary lymphoid follicles or nodules, are found in the cortex. The primary follicles are very densely packed with small lymphocytes, not actively involved in an immune response. The larger, less dense follicles, termed secondary follicles, are found in the cortex of a lymph node draining an area in which an infection has taken place. The secondary follicles contain clear germinal centers where B lymphocytes actively divide as a result of antigenic stimulation. T lymphocytes are found predominantly in the deep cortex or paracortical area; for this reason, the paracortical area is designated as T-dependent. Interdigitating cells are also present in this area, where they present antigen to T lymphocytes. These cords are elongated branching bands of the lymphocytes, plasma cells, and macrophages. Following the period of division, there is a rigorous selection process in which more than 90% of these B cells die by apoptosis or cell death. The initial activation of B cells is also thought to take place within the T-cell-rich paracortex. These organs serve as the sites for interaction of mature lymphocytes with antigens. Lymph nodes the lymph nodes are extremely numerous and disseminated all over the body. They play a very important and dynamic role in They act as filter for the lymph, the fluid, and cellular content of the lymphocytic circulatory system. They also provide sites for mingling of lymphocytes, monocytes, and dendritic cells for initiation of immune responses. Most antigen-activated B cells divide and differentiate into antibody-producing plasma cells in lymphoid follicles, but only a few B cells in the antigen-activated population find their way into germinal centers. Those that do, undergo one or more rounds of cell division during which the genes that encode their antibodies mutate at an unusually high rate. It is a large, ovoid secondary lymphoid organ situated high in the left abdominal cavity. The spleen parenchyma is heterogeneous and is composed of the white and the red pulp. Instead, blood-borne antigens and lymphocytes are carried into the spleen through the splenic artery. The narrow central arterioles, which are derived from the splenic artery after multiple branchings, are surrounded by lymphoid tissue (periarteriolar lymphatic sheath). In the white pulp, T lymphocytes are found in the lymphatic sheath immediately surrounding the arteriole. B lymphocytes are primarily found in perifollicular area, germinal center, and mantle layer, which lie more peripherally relative to the arterioles. Chapter 16 Key Points Functions of the spleen: the spleen plays a major role in: Mounting immune responses to antigens in the blood stream. The circulating antigens are trapped by the macrophages present in the marginal zone. These macrophages then process the antigen, migrate deeper into the white pulp, and initiate the immune response by interacting with T and B lymphocytes. Filtering or clearing of (a) infectious organisms; (b) aged or defectively formed elements. The main filtering function is performed by the macrophages lining up the splenic cords. Lymphatic Circulatory System Leukocytes and their products use two circulatory systems: cardiovascular system and the lymphatic circulatory system.
Buy keppra overnight. signs and symptoms of depression.