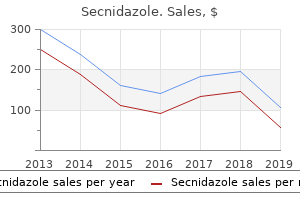
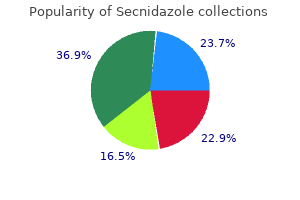
"Order secnidazole 1 gr line, medications 3605".
By: B. Mortis, M.B. B.A.O., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Clinical Director, Marist College
The opiate-induced increase in the calcium flux in podocytes is expected to contribute to podocytopathy treatment solutions purchase secnidazole on line amex, proteinuria symptoms dengue fever buy secnidazole from india, kidney injury and progression of salt-induced hypertension medications kidney patients should avoid generic secnidazole 500mg. Podocytes express FcRn and previous work had proposed that podocytes can act as antigen presenting cells treatment bacterial vaginosis purchase secnidazole 1 gr line. The extensive use of opioids is strongly Podocyte Biology Background: Dysregulation of intrarenal metabolic pathways involved in cholesterol efflux is implicated in lipid-induced podocyte injury in glomerular diseases. Results: After injury, we observed a transient increased expression of podocyte genes in mice and human kidney organoids. Transcriptomics analyses of podocytes isolated from mTmG-Nphs2cre mice during the course of injury revealed a transient increase in the expression of crucial podocyte genes, including Nphs2, Synpo and many others, reflecting a reparative response during the early stages of injury. Mice were anaesthetized, an arterial catheter was placed into the right carotid artery or the aorta and the left kidney was exteriorized. Background: Apoptosis of podocytes has been widely reported in many in vitro studies, but definitive apoptosis has been rarely documented in vivo podocytes. To elucidate this discrepancy, we analyzed dying process in podocytes in vitro and in vivo. Conclusions: these collectively indicate that podocytes dying dependently on caspase 3 are quickly lost by detachment or plasma membrane rupture before completing full apoptotic processes. Ganciclovir was initiated with a subsequent decrease in viral load and sufficient renal recovery to stop hemodialysis. Elucidation of the molecular interplay provides systems-level understanding and mechanistic insights that can lead to new biological hypotheses and therapeutic targets. Degenhardt,1,2 David Unnersjц-Jess,1,2 Sybille Kohler,4 Bernhard Schermer,1,2 Thomas Benzing. Background: Podocyte loss is a hallmark of glomerular diseases leading to glomerulosclerosis and progresssion of kidney disease. Sitting on the outside of the glomerular tuft podocytes have to withstand extensive mechanical stress due to perfusion and filtration. Additionally Bag3 insufficiency renders susceptibility to diabetic nephropathy in a mouse model. These findings point toward Bag3 as a candidate for mechanical stress protection in podocytes. The influence of mechanical clues was examined by stiff matrices and cyclic stretch. Bag3 staining localizes to the slit diaphragm protein nephrin in superresolution microscopy. Importantly the co-chaperone Bag3 shows interaction with essential actin-cytoskeleton regulators like RhoA, Arpc2 and Dynamin2 in co-immunoprecipitation. Knockdown of the Bag3 homologue starvin in drosophila nephrocytes displays a mild filtration disturbance. P209L mutation causes a mild proteinuria in a whole-body overexpression mouse line. Conclusions: the data further emphasize the role of Bag3 and chaperone-assistedselective-autophagy in podocyte mechanoprotection and maintenance of podocyte cytoskeleton architecture. Currently undergoing characterization of podocyte specific Bag3 mouse lines and the use of disease models will further help to understand the role of Bag3 at the kidney filtration barrier. Background: There are few targeted treatments for immune mediated kidney diseases which can result in progressive renal failure. Background: Mutations affecting mitochondrial coenzyme Q (CoQ) biosynthesis lead to kidney failure due to selective loss of essential cells of the kidney filter called podocytes. Curiously, neighboring tubular epithelial cells are spared early in disease, despite their higher mitochondrial content. We combine single nucleus transcriptomics with in vitro metabolomics and transcriptomics analyses to better understand the metabolic perturbations within this disease. We demonstrate broader human disease relevance of these findings by uncovering patterns of Gpx4 and Braf/Mapk pathway gene expression in tissue from patients with several kidney diseases. Results: miR-93 expression is different between male and female mice along disease progression. Conclusions: Gender specific variation in miR-93 expression in glomerular cells might indicate important differences in response to injury in progressive disease. A new 3D co-culture glomerular spheroid model was used to study both signalling pathways and podocyte loss. Functionally, the circulating factor enhanced podocyte motility and podocyte loss.
Biopsy diagnosis: Supraclavicular lymph node symptoms nausea fatigue purchase secnidazole 1 gr line, metastatic signet ring cell adenocarcinoma symptoms torn meniscus purchase discount secnidazole online, most likely from stomach *b symptoms 4dp5dt order cheap secnidazole line. Metastatic site: Upper lobe bronchus medicine ball abs purchase secnidazole now, metastatic signet ring cell adenocarcinoma * Codes for this case as recorded in registry. If a diagnosis of "malignant Brenner tumor" were reported, however, its correct code would be 9000/3; similarly a diagnosis of "Brenner tumor, borderline malignancy" would be correctly coded 9000/1. They are available for use when appropriate; for example, 9000/2 would be used for "Brenner tumor in situ" if such an entity were to be identified. It should be noted that some of the possible combinations probably do not exist or have not been recognized and defined; a "benign sarcoma" would contradict current concepts and usage. It should be emphasized here that the matrix system was designed to give the pathologist the final say on whether a tumor is considered to be benign, malignant, in situ, or uncertain whether malignant or benign. The behavior code assigned here is what most pathologists believe is the usual behavior. Recently some pathologists have felt, in the absence of a demonstrable tumor, it should be considered "in situ". In this event they should describe the tumor as "in situ" and code it accordingly. Assign the highest grade or differentiation code described in the diagnostic statement. It would be incorrect to code this diagnosis to the morphology code 8070/39, which does not indicate grade. It should be noted that words such as "anaplastic", "well differentiated", and "undifferentiated" are used as integral parts of approximately 15 histologic terms for neoplasms (in addition to those used to describe lymphomas). Examples are: "malignant teratoma, anaplastic" (9082/34), "retinoblastoma, differentiated" (9511/31), and "follicular adenocarcinoma, well differentiated" (8331/31). Coders should use the appropriate morphology code together with the proper grading code, as indicated in the examples. This same 6th digit column may also be used to denote cell lineage for leukemias and lymphomas (Table 22). However, some registries may wish to retain the additional digit to identify cases in which the diagnosis is supported by immunophenotypic data. Words used to designate degrees of differentiation are listed in a separate column. Differentiation describes how much or how little a tumor resembles the normal tissue from which it arose. When a diagnosis indicates two different degrees of grading or differentiation, the higher number should be used as the grading code. Thus "moderately differentiated squamous cell carcinoma with poorly differentiated areas" should be given the grading code "3". Use the topography code provided when a topographic site is not stated in the diagnosis. To facilitate the coding of such terms, a topography code has been added in parentheses in both the numeric list of morphology and the alphabetic index, when appropriate. Occasionally the topography code appears in the 3-digit heading and then applies to all terms included under that heading. An underscore ( ) following the decimal point indicates the existence of subsite codes. Coders should refer to the numerical list or the alphabetic index for specific subsite codes. The topography code attached to a morphology term may be used when the topographic site is not given in the diagnosis. Many morphology terms do not have topography codes assigned because the tumors frequently arise in more than one organ or topographic site. It may be that the site given in a diagnosis is different from the site indicated by the site-associated topography code. However, if the term "infiltrating duct carcinoma" is used for a primary carcinoma arising in the pancreas, coders should ignore the suggested breast topography code and assign the correct code, C25. Remember that the site-associated topography codes attached to morphology terms designate the usual site of origin of particular neoplasms. An unusual, but possible, example would be the diagnosis "osteo-sarcoma of kidney", for which the kidney topography code (C64. For example, "bile duct carcinoma" (8160/3) is a specific histologic type, frequently found in both the intrahepatic bile ducts of the liver (C22.
Nikolopoulou symptoms 8 days after iui discount secnidazole,1 medications vs grapefruit order secnidazole once a day,2 Megan Griffith medicine man lyrics cheap secnidazole 500 mg otc,1 medications pain pills buy online secnidazole,2 Marina Loucaidou,1 Michelle Willicombe,1,2 Candice A. Reported recurrence rates are higher in centres that perform surveillance biopsies. Of those whose biopsies did not show recurrence, the mean time to the most recent biopsy was 2. In the 4 patients with clinically significant proteinuria rituximab was used to treat with a complete or partial response in all patients (mean time 22. There are no significant differences in rejection, graft loss, death or death with functioning graft between those with recurrence and those without recurrence in our cohort. Department of Nephrology, School of Medicine, Kanazawa Medical University, Uchinada, Japan. Introduction: Polycythemia has been recognized as a common occurrence in certain renal diseases such as cystic diseases of the kidney, renal cancer, tuberous sclerosis and hydronephrosis. However, polycythemia in association with membranous nephropathy has rarely been reported. It is yet to be seen if polycythemia resolves with remission of membranous nephropathy. We postulated that hypoxia induced by decreased renal perfusion is the main trigger for polycythemia. However, it is puzzling as to why more patients with membranous nephropathy are not polycythemic. This leads us to believe that there might be some unique processes leading to polycythemia in membranous nephropathy, as in this patient, which might need further investigation. Polycythemia would further enhance the risk of thromboembolism in such patients whose risk of hypercoagulability is already high in setting of severe hypoalbuminemia. Hence, prophylactic anticoagulation should strongly be considered in these patients. Introduction: Although proteinuria in pregnancy is common and usually due to preeclampsia, nephrotic range proteinuria especially early in pregnancy, warrants investigation and treatment. Case Description: A previously well 20 year old G1P0, presented at 9 weeks gestation with 3 weeks of oedema and shortness of breath. There was no active bleeding on endoscopy and she had no further episodes in pregnancy. She was managed by the renal and joint renal-obstetric clinic throughout pregnancy. In our patient who presented early in pregnancy with marked oedema and heavy proteinuria a kidney biopsy was performed. Kidney biopsy should be performed when the benefit of obtaining a diagnosis outweighs the risks of the procedure. However, there is a risk of maternal complications including gestational diabetes and weight gain. Introduction: Membranous nephropathy secondary to neoplastic processes is a recognized phenomenon, and it may be the first finding that leads to the diagnosis of the underlying malignancy. Subsequently, he presented in December 2019 with anasarca, acute kidney injury and nephrotic syndrome (proteinuria greater than 9 g per day). In February 2020, he presented with worsening anasarca and a myasthenic flare, for which he was treated with steroids, five sessions of plasma exchange and rituximab. Discussion: When a patient is diagnosed with secondary membranous nephropathy without an identifiable cause, it is recommended to perform general screening for cancers. Introduction: Cystinuria, a rare inherited metabolic disorder characterized by defective proximal tubule cystine transport, manifests predominantly in childhood or young adulthood with renal colic and recurrent nephrolithiasis, often requiring urologic intervention. Insoluble cystine in the urine precipitates into hexagonal crystals that can coalesce into larger, recurrent calculi, with associated higher risk of chronic kidney disease. Prevention of stone formation is the primary goal, using conservative nonpharmacologic approaches and if unsuccessful then pharmacologic. He was referred to Metabolic Stone Clinic to discuss alternative treatment options. In 2012, an increase in proteinuria promped repeat biopsy resulting in a diagnosis of membranous glomerulonephritis. Intravenous cyclosphosphamide was started, steroids were tapered, and Humira was discontinued. In September of 2019, 4 weekly doses of Rituximab 375 mg/m2 followed by 1 gram doses at 4 month intervals were administered.
The elderly cannot stand up as quickly and tend to walk somewhat unsteadily medications on airline flights purchase secnidazole now, with stooped posture and broader steps medicine effects buy secnidazole overnight delivery, leading to an elevated risk of falling medications prescribed for adhd discount secnidazole 1gr without a prescription. The gait cycle (time between two successive contacts of the heel of one foot with the ground = 2 steps) is characterized by the gait rhythm (number of steps per unit time) symptoms nausea fatigue order secnidazole 500mg without a prescription, the step length (actually the length of an entire cycle, i. Gait Disturbances Stance phase Swing phase Right leg supports Gait cycle Right leg advances Steppage gait Knee instability (quadriceps paresis, leg dorsally angulated) Posture and gait in youth (left) and old age (right) Ataxic gait Spastic gait (right hemiparesis) Spastic gait (spastic paraparesis) Hypokinetic-rigid gait (left, Parkinson disease; right, start delay/gait apraxia) Psychogenic gait disturbances (histrionic movements) Rohkamm, Color Atlas of Neurology © 2004 Thieme All rights reserved. Motor Function 61 Tremor Tremor, the most common movement disturbance, is an involuntary, rhythmic, oscillating movement of nearly constant amplitude. Different types of tremor may be classified by the circumstances in which they are activated or inhibited and by their location, frequency, and amplitude (Table 3, p. Rest tremor occurs in the absence of voluntary movement and is aggravated by emotional stress (excitement, time pressure) and mental activity. The tremor subsides when the limbs are moved, but begins again when they return to the resting position. Postural tremor occurs during maintenance of a posture, especially when the arms are held outstretched, and disappears when the limbs are relaxed and supported. Kinetic tremor occurs during active voluntary movement; it may be worst at the beginning (initial tremor), in the middle (transitory tremor), or at the end of movement (terminal tremor). Intention tremor, the type that is worst as the movement nears its goal, is characteristic of cerebellar and brain stem lesions. The frequency of tremor in each individual case is relatively invariant and may be measured with a stopwatch or by electromyography. Different types of tremor have characteristic frequencies, listed in the table below, but there is a good deal of overlap, so that differential diagnosis cannot be based on frequency alone. The tremor of Parkinson disease is due to rhythmic neuronal discharges in the basal ganglia (internal segment of globus pallidus, subthalamic nucleus) and thalamus (ventrolateral nucleus), which are the ultimate result of degeneration of the dopaminergic cells of the substantia nigra that project to the striatum (p. Essential tremor is thought to be due to excessive oscillation in olivocerebellar circuits, which then reaches the motor cortex by way of a thalamic relay. Intention tremor is caused by lesions of the cerebellar nuclei (dentate, globose, and emboliform nuclei) or their projection fibers to the contralateral thalamus (ventrolateral nucleus, p. In any variety of tremor, the abnormal oscillations are relayed from the motor cortex through the corticospinal tracts (p. Motor Function 62 Rohkamm, Color Atlas of Neurology © 2004 Thieme All rights reserved. Tremor Dangling arm Rest tremor Kinetic tremor Action tremor Tremor types Physiological tremor Essential tremor Parkinsonian tremor Orthostatic tremor Cerebellar tremor Holmes tremor Neuropathy-related tremor Substance-induced tremor* Palatal tremor Voice tremor Writing tremor Psychogenic tremor Intention tremor (end tremor) *Due to coffee, tea, alcohol, medications (stimulants, neuroleptics, antidepressants, anticonvulsants, cyclosporine A), neurotoxins (heavy metals, insecticides, herbicides, solvents) 63 Rohkamm, Color Atlas of Neurology © 2004 Thieme All rights reserved. Motor Function Dystonia "Dystonia" is a general term for involuntary movement disorders involving sustained muscle contraction according to a stereotypic pattern, usually resulting in spasmodic or torsional movement and abnormal posture. They may arise only during skilled activities such as writing or playing a musical instrument (action dystonia). Incomplete relief can be obtained by the avoidance of triggering activities and by the use of antagonistic maneuvers. Dystonia may be classified by its distribution as focal (affects only one region of the body), segmental (two adjacent regions), multifocal (two or more nonadjacent regions), generalized, or lateralized (hemidystonia), and by its etiology as either primary (idiopathic) or secondary (symptomatic). Secondary dystonia is usually caused by a disorder of copper, lipid, or amino acid metabolism, or by a mitochondrial disorder (p. Arm and Leg Dystonia these are most often produced by specific, usually complex, activities (task-specific dystonia). Toe or foot dystonia ("striatial foot") is seen in patients with Parkinson disease and dopa-responsive dystonia. In spastic dysphonia, the voice usually sounds strained and forced, and is interrupted by constant pauses (adductor type); less commonly, it becomes breathy or whispered (abductor type). Dopa-responsive dystonia (Segawa syndrome) arises in childhood and mainly impairs gait (p. Paroxysmal, autosomal dominant inherited forms of dystonia are characterized by recurrent dystonic attacks of variable length (seconds to hours). The attacks may be either kinesiogenic (provoked by rapid movements), in which case they usually involve choreoathetosis, or nonkinesiogenic (provoked by caffeine, alcohol, or fatigue). Spasmodic contraction of the orbicularis oculi muscle causes excessive blinking and involuntary eye closure. It can often be accompanied by ocular foreign-body sensation and be ameliorated by distracting maneuvers, and is worse at rest or in bright light. There may be involuntary clonic eye closure, tonic narrowing of the palpebral fissure, or difficulty opening the eyes (eye-opening apraxia, p.
Solid tumor with humoral mediation of hypercalcemia (lung treatment ketoacidosis purchase secnidazole australia, kidney symptoms 4dp5dt fet generic 1 gr secnidazole with amex, squamous cell carcinoma) B medicine 503 buy secnidazole with amex. Clinical Features Most pts with mild to moderate hyperparathyroidism are asymptomatic 6mp medications cheap secnidazole, even when the disease involves the kidneys and the skeletal system. Pts frequently have hypercalciuria and polyuria, and calcium can be deposited in the renal parenchyma (nephrocalcinosis) or form calcium oxalate stones. The characteristic skeletal lesion is osteopenia or osteoporosis; rarely, the more severe disorder osteitis fibrosa cystica occurs as a manifestation of long-standing, more severe hyperparathyroidism. Hypercalcemia may be intermittent or sustained, and serum phosphate is usually low but may be normal. Total serum calcium should be corrected when serum albumin is abnormal [addition of 0. Table 187-3 shows general recommendations that apply to therapy of severe hypercalcemia [levels of >3. In pts with severe primary hyperparathyroidism, surgical parathyroidectomy should be performed promptly. Asymptomatic disease may not require surgery; usual surgical indications include age <50, nephrolithiasis, creatinine clearance <60 mL/min, reduction in bone mass (T score <2. Postoperative management requires close monitoring of calcium and phosphorus, as transient hypocalcemia is common. Adequate hydration and parenteral bisphosphonates can be used to reduce calcium levels. Long-term control of hypercalcemia is difficult unless the underlying cause can be eliminated. Symptoms include peripheral and perioral paresthesia, muscle spasms, carpopedal spasm, tetany, laryngeal spasm, seizure, and respiratory arrest. The above-mentioned correction (see "Hypercalcemia") can be used to assess whether the serum calcium concentration is abnormal when serum proteins are low. Alkalosis increases calcium binding to proteins, and in this setting direct measurements of ionized calcium should be used. The most common forms of chronic severe hypocalcemia are autoimmune hypoparathyroidism and postoperative hypoparathyroidism following neck surgery. Chronic renal insufficiency is associated with mild hypocalcemia compensated for by secondary hyperparathyroidism. Management of chronic hypocalcemia requires a high oral calcium intake, usually with vitamin D supplementation (Chap. Restoration of magnesium stores may be required to reverse hypocalcemia in the setting of severe hypomagnesemia. Etiology the causes of hypophosphatemia include: decreased intestinal absorption (vitamin D deficiency, phosphorus-binding antacids, malabsorption); urinary losses (hyperparathyroidism, hyperglycemic states, X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets, oncogenic osteomalacia, alcoholism, or certain toxins); and shifts of phosphorus from extracellular to intracellular compartments (administration of insulin in diabetic ketoacidosis or by hyperalimentation or refeeding in a malnourished pt). The total body phosphate depletion cannot be predicted from the serum phosphate level; careful monitoring of therapy is therefore required. Hypocalcemia should be corrected first, and the dose reduced 50% in hypercalcemia. Serum calcium and phosphate levels should be measured every 612 h; a serum calcium Ч phosphate product of >50 must be avoided. The clinical consequences of severe hyperphosphatemia are hypocalcemia and calcium phosphate deposition in tissues. Depending on the location of tissue calcifications, serious chronic or acute complications may ensue. Therapy consists of treating the underlying disorder and limiting dietary phosphorus intake and absorption. Oral aluminum phosphate binders or sevelamer may be used, and hemodialysis should be considered in severe cases. Etiology Hypomagnesemia generally results from a derangement in renal or intestinal handling of magnesium and is classified as primary (hereditary) or secondary (acquired).
Discount 1 gr secnidazole mastercard. Treating a lamb for pneumonia.