"Generic 50mg tenormin amex, 2014 2014".
By: O. Pyran, M.A., M.D., M.P.H.
Clinical Director, University of North Carolina School of Medicine
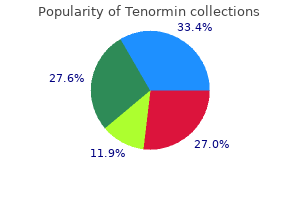
Following statements are true: [P] Hemicholinium inhibits the acetylcholine synthesis [Q] Parathion is a short duration anticholineterase [R] Botulinum toxin inhibits acetylcholine release [S] Physostigmine is used in treatment of myasthenia gravis (a) Q and R (c) R and S (b) P and R (d) P and Q 6 heart attack recovery diet buy tenormin 50mg cheap. Following are the antagonist of nicotinic receptor (1)2: [P] Cytosine [Q] Epibatidine [R] Atracurium [S] Vecuronium 13 can prehypertension kill you order cheap tenormin online. In the treatment of myasthenia gravis heart attack death buy 50 mg tenormin visa, the best agent for distinguishing between myashenic crisis and cholinergic crisis blood pressure chart 40 year old male cheap 100 mg tenormin with visa, given intravenously, is (a) Pyridostigmine (b) Edrophonium (c) Physostigmine (d) Neostigmine 2. Epinephrine is added to local anaesthetics (a) To cause haemeostasis (b) To prolong the action of local anaesthetics (c) To stimulate wound healing (d) All of the above 16. Neostigmine may cause all of the followings except (a) Block accommodation reflex (b) Reversible inhibition of acetyl cholinesterase (c) Constipation (d) Bronchoconstriction 17. Following statements are true for b2 receptor [P] It produces glycogenolysis effect [Q] It produces lipolysis effect [R] It relaxes uterus [S] It produces constriction effect on bronchi (a) Q and S (c) P and R (b) Q and R (d) P and Q [R] Ephedrine (a) P and Q (c) Q and S [S] Amphetamine (b) Q and R (d) R and S 22. Pilocarpineis classified as (a) Cholinesterase inhibitor (b) Sympathomimetic (c) Cholinomimetic (d) Cholinolytics 23. Propranolol is contraindicated in patients with (a) Angina pectoris (b) Supraventricular arrhythmias (c) Glaucoma (d) Hypertension 24. Mechanism of action of organic phosphate parathion is (a) Phosphorylation of the cationic site of cholinesterases (b) Phosphorylation of the esteratic site of cholinesterases (c) Acetylation of the esteratic site of cholinesterases (d) Acetylation of the cationic site of cholinesterases 25. Following statements are true for ritodrine [P] It is b2 agonist [Q] It produces arrhythmia as side effect [R] It is b1 agonist [S] It is used for nasal decongestion (a) P and Q (c) P and R (b) Q and R (d) Q and S 26. Neostigmine effectively antagonizes skeletal muscle relaxation produced by (a) Tubocurarine (c) Pancuronium (b) Gallamine (d) All of the above 19. Following statement is true for labetalol [P] It is and b antagonist [Q] It produces tachycardia as side effect [R] It is non-selective b antagonist [S] It is used in hypertension in pregnancy (a) Q and R (c) P and S (b) P and Q (d) R and S 20. All of the following statements related to neostigmine are correct except (a) Neostigmine is a quaternary ammonium compound (b) Neostigmine is medium duration of action (c) Neostigmine has direct effect on neuromuscular junctions (d) All of the above 28. Antidote of atropine is (a) Neostigmine (b) Pralidoxime (c) Physostigmine (d) None of above autonomiC n ervous s ystem 2. Sweating is inhibited by (a) Atropine (b) Phenothiazines (c) Scopolamines (d) All of the above 32. Beta agonist used in bronchial asthma exert action by (a) Blocking B1 receptor (b) Blocking B2 receptor (c) Stimulating B1 receptor (d) Stimulating B2 receptor 33. Which of the following agent irreversibly bound with acetyl cholinesterase (a) Dispropyl flurophosphate (b) Ecothiopate (c) Both a and b (d) None of the above 34. Alcuronium is a semisynthetic derivative with similar properties of (b) Pancuronium (a) Gallamine (d) D-tubocurarine (c) Succinylcholine 35. Antidote of organo phosphorous poisoning is (b) Pralidoxime (a) Physostigmine (d) Tubocurarine (c) Neostigmine 37. Action of D-tubocurarine is (a) Competitive blockade of musscarinic receptors (b) Competitive blockade of nicotinic receptors (c) Irreversible blockade of muscarinic receptor (d) None of above 38. Gingival hyperplasia is an oral condition possible in using (b) Phenytoin (a) Phenobarbital (d) Valproic acid (c) Pentobarbital 39. Tachyphylaxis is an unwanted effect of (a) Methohexamine (b) Methylphenidate (d) Methamphetamine (c) Ephedrine 42. Activation of alpha-2 receptors in the pancreatic islets causes (a) Suppression of insulin secretion (b) Stimulation of insulin release (c) Suppression of glucagon secretion (d) None of above 43. Darifenacin is a (a) M1 antagonist (c) M3 agonist (b) M2 antagonist (d) M3 antagonist 44. Drug of choice in the treatment of cardiogenic shock is/are (b) Epinephrine (a) Isoproterenol (c) Dopamine (d) All of the above 46. Pilocarpine is best used in (a) Congential glaucoma (b) Open angle glaucoma (c) Secondary glaucoma (d) All of the above 48. For glycogenolysis in liver one of the following adrenoreceptor is responsible: (a) Alpha-1 receptor (b) Alpha-2 receptor (c) Beta-1 receptor (d) Beta-2 receptor 2. Serious unwanted effect of epinephrine is (a) Respiratory difficulty (b) Palpitation (c) Cerebral heamorrhage (d) Tremor 52. Drug of choice in motion sickness is (a) Atropine (b) Scopolamine (c) Carbamazepine (d) Metoclopromide 53. In belladonna poisoning convulsions can be controlled by (b) Phenytoin (a) Paraldehyde (c) Diazepam (d) Carbamazepine 54. Major adverse effect of clonidine is (a) Bradycardia (b) Tachycardia (c) Sexual dysfunction (d) Dry mouth 56. Prolactin = milk synthesizing hormone induce the synthesis of milk and after parturition induces milk secretion.
Syndromes
- Avoid all alcohol
- Intestines
- Are you afraid or worried about something?
- Avoid giving complex directions.
- Difficulty lifting up the foot and toes and making toe-out movements
- Making words longer (I am Boooobbby Jones.)
- Large tongue, sometimes protruding
- Angle-closure glaucoma is an emergency. This is very different from open-angle glaucoma, which painlessly and slowly damages vision.
- Rapid heartbeat
A girl 216 below 14 years of age in Kenya is not legally deemed to be able to give consent blood pressure medication helps acne purchase tenormin 100 mg. Clinical Features these will range from none or mild to very severe injuries that may be life threatening pulse pressure hemorrhage buy 50 mg tenormin with mastercard. The medical personnel must approach the rape victim with great understanding blood pressure medication karvea buy cheap tenormin 50 mg, respect and concern for her well being hypertension questions and answers cheap tenormin 100 mg amex. Careful history and medical record is important because this will be required in court. If the patient has eaten, drunk, bathed or douched, this may affect the outcome of laboratory test. History must be taken to evaluate the risk of acquisition of sexually transmitted disease and pregnancy. During physical examination, document location, nature and extent of external trauma to face, neck, breast, trunk, limbs, the genitalia, vagina and cervical trauma must also be documented. It should include age, marital status, occupation, education, ethnic origin, area of residence, drinking, smoking and any substance abuse habits, past obstetric and gynaecological history. Record of each pregnancy in chronological order should include date, place, maturity, labour, delivery, weight, sex and fate of the infant and any puerperal morbidity. Patients should be told how to recognize and report promptly any deviation from normal so that prompt treatment may be initiated. Principles of management include: - Identification of high risk patient cases - Prophylaxis and prenatal counselling - to prevent some high risk patients - Early start of antenatal care - Close medical supervision during pregnancy - Special tests and examinations to evaluate foetal development and well being as well as maternal well-being - Timely intervention for therapy and delivery. Mild anaemia Hb 8-10 mg, moderate Hb 6-7 gm, severe Hb 4-5 gm, very severe below Hb 4 gm. Most cases are due to Iron deficiency: Dietary deficiency, blood loss from hookworm infestations. Folate deficiency due to inadequate intake especially in urban areas, also due to haemolysis of malaria. Iron deficiency and folk acid deficiency often occur together causing "Dimorphic Anaemia". Clinical Features General weakness, dizziness, pallor, oedema, in haemolytic anaemia; jaundice, hepatosplenomegaly occur in haemolytic anaemia. The foetal and maternal status will depend on extent of bleeding, duration and aetiology. For mothers who have been in labour recession of the foetal presenting part and disappearance of foetal heart sounds suggest rupture of the uterus. Once rupture of the uterus has been ruled out then treatment for abruptio placentae should be instituted. Placenta Praevia the management of placenta praevia depends on gestation, extent of bleeding and clinical findings. The decision follows after evaluation, complete examination of maternal and foetal status. Palpitations, body oedema, cough, easy fatigability, evidence of heart enlargement, murmurs, thrills, left parasternal heave, raised jugular venous pressure.
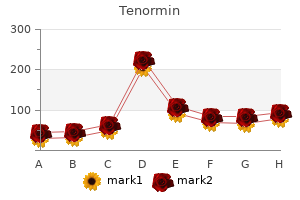
One of the following belongs to Umbelliferae family (b) Taxus (a) Cardamom (d) Dill (c) Sandal wood oil 76 hypertension organization order tenormin with amex. Characteristic of clove stalks which is a clove adulterant is (a) It contain only 5% of oil (b) Oil is removed from clove (c) Dark brown arrhythmia recognition order tenormin 50mg, ovate and ripened fruits of clove (d) Expanded flowers of clove trees 77 arrhythmia unborn baby purchase tenormin american express. Dill is derived from biological sources (a) Anethum graveolens (b) Eugenia caryophyllus (c) Carum carvi (d) Allium sativum 54 arteria lusoria tenormin 100mg with amex. The bitter taste of fennel is due to presence of (a) Anethole (b) Fenchone (c) Both (a) and (b) (d) None 56. Linamarin is biogenetically derived from (a) Tryptophan (b) Phenylalanine (c) Tyrosine (d) Valine 58. All drugs come under Umbelliferae family except (b) Dill (a) Caraway (c) Cummin (d) Lemmon oil 59. All drugs come under Lauraceae family except (b) Cassia cinnamon (a) Camphor (c) Cinnamon (d) Sandalwood 61. Garlic comes under family (b) Zingiberaceae (a) Rutaceae (c) Liliaceae (d) Labitae 64. Anethum graveolens is a biological source of (b) Clove (a) Dill (d) Fennel (c) Cummin 65. Ocimum sanctum is a biological source of (b) Thyme (a) Tulsi (d) None of the above (c) Ajowan 66. Microscopically characteristic of caraway is (a) Microrosette calcium oxalate (b) Acicular calcium oxalate crystal (c) Prismatic calcium oxalate crystal (d) Absent of calcium oxalate crystal 80. Microscopical characteristic of fennel is all of the following except (a) Anomocytic stomata are present (b) Rosette calcium oxalate are present (c) Aleurone grains are present (d) Starch grains are present 81. Chenopodium contain (a) Not less than 65% of ascaridol (b) Not less than 5% of ascaridol (c) Not less than 10% of ascaridol (d) Not less than 6. Triterpene class of terpenoid contains number of isoprene units (b) 6 (a) 9 (c) 3 (d) 1 83. Terpenoid present in eucalyptus is (b) Geraniol (a) Eugenol (c) Cineol (d) Zingiberone 84. Alcoholic type of volatile oil is present in (a) Peppermint (b) Turpentine (d) Clove (c) Sandalwood oil 85. Chenopodium contains type of volatile oil (a) Alcoholic (b) Phenolic (c) Ester (d) Oxide 86. The sedative chemical constituent of calamus is (b) Valtrate (a) Asarone (c) Eugenol (d) None 87. Cochineal contains: (a) Carminic acid (c) Citric acid (b) Caffeine (d) None of the above 91. Anethole is present in (a) Foeniculam vulgaris (b) Anethum sowa (c) Anethum graveolens (d) Carum carvi 93. Annato and Crocus can be classified as (a) Tetraterpenoids (b) Triterpenoids (c) Monolerpenoids (d) Diterpenoids 94. The drug which does not contain ketone volatile oil is (b) Caraway (a) Dill (d) Cumin (c) Sandalwood oil 96. The percentage of abietic acid in colophony is (a) 90% (b) 60% (c) 40% (d) 25% 99. Azadirachtin is a strong (a) Analgesic (b) Antioxidant (d) Hypnotic (c) Antifeedant 100. Vitamin A is (a) Acyclic diterpene (b) Monocyclic diterpene (c) Bicyclic diterpene (d) Tricyclic diterpene 102. Vanillin, the active constituent of vanilla can be synthesized from (b) Carvone (a) Eugenol (d) Vinblastin (c) Vincristine 103. Main constituent of wintergreen oil is (b) Pinene (a) Linalool (c) Geranial (d) Methyl salicylate 89. Main chemical constituent of chenopodium oil is (a) CitronellaI (b) Geranial (c) Ascaridiole (d) Menthol 90. Chemically isoprene is (a) 2-methyl-but- 3-ene (b) 1,3-butadiene (c) 2-methyl 1,3-butadiene (d) 1-methyl 1,3-butadiene 107. Leiberman-Burchard test is used for the identification of (a) Sterols (b) Triterpenes (d) Both (a) and (b) (c) Alkaloids 109.
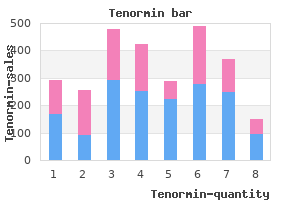
Here we review the various classes of transcriptional regulatory elements (core promoters arteria radialis order tenormin cheap, proximal promoters heart attack vs stroke discount tenormin online visa, distal enhancers hypertension over 55 purchase tenormin 100 mg with visa, silencers arrhythmia palpitations tenormin 100 mg low price, insulators/boundary elements, and locus control regions) and the molecular machinery (general transcription factors, activators, and coactivators) that interacts with the regulatory elements to mediate precisely controlled patterns of gene expression. The biological importance of transcriptional regulation is highlighted by examples of how alterations in these transcriptional components can lead to disease. Finally, we discuss the methods currently used to identify transcriptional regulatory elements, and the ability of these methods to be scaled up for the purpose of annotating the entire human genome. Key questions now relate to understanding how these genes and their products function, as well as how their spatial and temporal expression patterns are established at both the cellular and organismal level. To understand the molecular mechanisms that govern specific expression patterns on a global scale, it is important to identify the transcriptional regulatory elements associated with each predicted gene. Moreover, the ability to identify such elements is an important step toward understanding how gene expression is altered in pathological conditions. Thus, one of the main emerging challenges for genomics research is to identify all functional elements in the genome, including those that regulate gene expression. The availability of the complete human genome sequence, in combination with genome-wide expression data, will facilitate the comprehensive identification of these transcriptional regulatory elements. In addition, these resources serve as a starting point for studying transcription regulation of human genes on a global scale, and provide information regarding the establishment of spatial and temporal gene expression patterns and the mechanisms required for their establishment. Here we review the various classes of transcriptional regulatory elements and the current understanding of how they function. We begin with an overview of the eukaryotic transcription process and the molecular machinery that drives it. We then focus on the role of transcriptional regulatory elements in gene expression and highlight diseases that result from their alteration. Finally, we review the methods currently used to identify transcriptional regulatory elements, both experimentally and through bioinformatics approaches. Most regulation, however, is believed to occur at the level of transcription initiation. The structure of human gene promoters can be quite complex, typically consisting of multiple transcriptional regulatory elements. The presence of multiple regulatory elements within promoters confers combinatorial control of regulation, which exponentially increases the potential number of unique expression patterns. An understanding of how the combinatorial organization of a promoter encodes regulatory information first requires an overview of the proteins that constitute the transcriptional machinery. The promoter, which is composed of a core promoter and proximal promoter elements, typically spans less than 1 kb pairs. Distal (upstream) regulatory elements, which can include enhancers, silencers, insulators, and locus control regions, can be located up to 1 Mb pairs from the promoter. Transcriptional activity is greatly stimulated by a second class of factors, termed activators. Many activators form heterodimers and/or homodimers, and thus their binding sites are generally composed of two half-sites. Notably, the precise subunit composition of an activator can also dictate its binding specificity and regulatory action (37). The best-studied examples are nuclear hormone receptors, a large class of ligand-dependent activators. Various studies have shown that the relative orientation of the half-sites, as well as the spacing between them, play a major role in directing the regulatory action of the bound nuclear hormone receptor dimer (37). Finally, activators have also been proposed to function by recruiting activities that modify chromatin structure (47, 106). The activity of an activator may be modulated by the third group of factors required for eukaryotic transcription: coactivators (reviewed in 115, 168). A notable property of activators is that they can stimulate transcription synergistically, a phenomenon in which the regulatory effect of multiple factors working together is greater than the sum of the activities driven by each factor individually. This effect can arise from cooperation between multiple copies of the same factor (29), or can be "promiscuous" and result from cooperation between different factors (114) (see also the "Enhanceosomes" sidebar). Significantly, there are limits to the promiscuity of activator cooperativity, and it has been shown that the core promoter can play a role in controlling regulatory signals from upstream elements (132). Transcriptional synergy presumably arises from postbinding interactions, as it can be observed even under conditions of saturated activator binding. Although the phenomenon of transcriptional synergy has long been recognized, the mechanism underlying it has remained elusive (72).
Generic 50 mg tenormin with visa. How to cure High Blood Pressure naturally in Hindi.