"Buy epitol online from canada, medicine x topol 2015".
By: M. Merdarion, M.A.S., M.D.
Vice Chair, Medical University of South Carolina College of Medicine
Socratic questioning-to encourage the client to contemplate medications not to be taken with grapefruit buy epitol 100 mg online, evaluate treatment 7th march generic 100mg epitol with mastercard, and synthesize diverse sources of information; also known as "guided discovery" 6 treatment 10 discount epitol 100 mg otc. Capsule summaries-to maintain focus and a connection to the goals of the therapy 7 treatment ear infection epitol 100mg line. Homework assignments-to serve as a bridge between sessions and to ensure that the client continues to work on problems by collecting information, testing beliefs, and trying new behaviors 8. Feedback in the therapy sessions-to ensure that the client and therapist are communicating Later Sessions Cognitive therapy tends to follow a standard within-session structure to make the maximum use of time, to focus on the most important current problems, to set the tone for a working atmosphere, and to maintain continuity between sessions. Beck structures sessions into eight elements, listed below, which he describes in greater detail (Beck et al. It typically lasts from 12 to 20 weeks, with the client and therapist meeting once per week. However, it can be conducted in less time-for instance, once per week for six to eight sessions. Because cognitive therapy is usually planned for comparatively short treatment times, there has not been much research to study the relative effectiveness of longer term cognitive therapy. However, Lyons and Woods in their metaanalysis of 70 different rational-emotive therapy 67 Chapter 4 studies found that increased effects correlated with longer treatment times (Lyons and Wood, 1991). More research needs to be conducted looking at the effect of treatment duration on the efficacy of these therapies. In a brief version of this therapy, there is less time to understand and restructure all of the cognitions that may be influencing substance abuse. The therapist must use the early sessions to determine the most productive focus of the therapy, given the short timeframe. Restructuring these thought processes may help decrease reasons for substance abuse. If the client is returning to therapy after a period of sobriety that ended in relapse, a focus on the circumstances leading to relapse and other resulting consequences may shape the therapy. A number of specific cognitive therapy techniques may be appropriate for use, depending on the phase of treatment and the issues raised by the client. They also can be used episodically with clients who leave and then return to treatment or during aftercare or continuing care following a more intensive treatment episode. Periods without therapy sessions allow clients time to practice the new skills of identifying and challenging unproductive thinking on their own. However, it is easy to 68 fall back into old, automatic ways of thinking that may require a return to therapy. The therapist can productively build on what was learned in previous sessions, help the client see how she slipped into old patterns, and further reinforce the process of catching oneself in the process of thinking negative automatic thoughts. The therapist must be prepared to move from topic to topic while always adhering to the major theme-that how the client thinks determines how the client feels and acts, including whether the client abuses substances. Cognitive therapy can be quite successful as an option for brief therapy for several other reasons (Carroll, 1996a): It is designed to be a short-term approach suited to the resource capabilities of many delivery systems. It is a flexible, individualized approach that can be adapted to a wide range of clients, settings (both inpatient and outpatient), and formats, including groups. CognitiveBehavioral Theory Early behavioral theories of substance abuse were nonmediational in nature (Donovan and Marlatt, 1993). They focused almost exclusively on overt, observable behaviors, and it was believed that understanding the antecedents and reinforcement contingencies was sufficient to explain behavior and to modify it. Over time, however, these behavioral theories began to incorporate cognitive factors into their conceptualizations of substance abuse disorders. These more recent models are mediational in nature; that is, a greater role is attributed to the interaction among a variety of individual difference variables such as beliefs, values, perceptions, expectations, and attributional processes in mediating the development and Brief CognitiveBehavioral Therapy continuation of substance abuse disorders (Abrams and Niaura, 1987; Mackay and Donovan, 1991; Marlatt et al. This expanded, mediational model has been described as cognitive social learning or cognitivebehavioral theory. Cognitivebehavioral theory represents the integration of principles derived from both behavioral and cognitive theories, and it provides the basis for a more inclusive and comprehensive approach to treating substance abuse disorders.
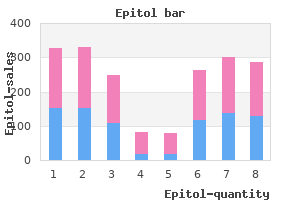
Many of these interventions also benefit maternal health and prevent stillbirths (Bhutta et al symptoms 8 weeks purchase cheap epitol. More research is urgently needed for preterm birth prevention symptoms kidney order genuine epitol online, which is a longer-term investment but would have widespread impact on mortality medications ms treatment purchase epitol 100 mg line, childhood disability and healthcare expenditure medications not to crush order epitol 100mg visa. For care of premature babies, the emphasis is on scaling up implementations more rapidly as soon as possible, so that the maximum number of premature babies and their mothers benefit. In this way, hundreds of thousands of lives could be saved with the application of current knowledge. Multiple studies in high-income contexts have attempted to prevent preterm birth, yet have failed to identify high-impact interventions in the preconception and antenatal periods. Many interventions have been evaluated, and some have been identified as beneficial though limited in public health impact, such as progesterone therapy, which has only been studied in certain high-risk populations. Reducing the rate of elective cesarean births or inductions without medical indication before the recommended 39 completed weeks of gestation may have an important impact on prevention overall, but has yet to be broadly implemented (National Collaborating Centre for Womenґs and Childrenґs Health, 2011). Unfortunately, to date, few studies have assessed preterm birth outcomes in these countries with accurate measures of gestational age (Lawn et al. The greatest potential for prevention of preterm birth, therefore, lies in strategic, sufficiently funded research of interventions that have strong potential to reduce the risk of preterm birth. The re a re some signif ic ant se c onda r y p reve ntion interventions that reduce the impact of preterm birth. Antenatal corticosteroid injections given to women in preterm labor are highly effective at preventing respiratory distress syndrome in premature babies, but remain underused in many low- and some middle-income countries. There is, thus, a need for delivery research that can help understand context-specific reasons for the continued low coverage in these countries and identify ways to adapt known effective strategies for use in low-resource settings. Tocolytic medicines rarely stop preterm labor, but may help delay labor for hours or days, allowing the baby additional precious time to develop before birth. Care of premature babies is primarily an action gap As evidenced by the large survival gap between babies born in high-income countries and those born in lowPhoto: Chhandak Pradhan/Save the Children and middle-income countries, effective interventions exist to reduce death and disabilit y in premature babies, yet this care does not reach the poorest and most disadvantaged populations where the burden is highest (Chapter 5). There is a "know-do gap" or a gap between what is known to work and what is done in practice. More than 60% of all premature babies are born in South Asia and sub-Saharan Africa (Chapter 2), with just over half now being born in facilities. Most preterm births Hence, for preterm birth prevention, there is a large solution gap. In high-income settings, if all existing interventions, including smoking cessation, reached universal coverage, they would avert a small proportion of preterm births. However, low- and middle-income countries with the highest burden of preterm births also carry the greatest burden of higher-risk conditions that are preventable or treatable. I n a few c o u n t r i e s, case management of neo natal sepsis is being scaled up using community-based health workers. If scaled up and made universally available, especially in high-burden countries, community and facility interventions would have an immediate, significant effect on reducing the 1. This care would also address other causes of neonatal deaths, stillbirth and maternal death and reduce the risks of associated lifelong disability for survivors. Translating knowledge into action through existing health systems platforms will require a focus on systems issues, especially human resources and, notably, nursing skills for obstetric and newborn care. Also, increasing commodities for family planning, obstetric and newborn care are key opportunities for accelerating progress. For sustainable effect, interventions to prevent preterm bir th in the preconception and antenatal periods and to reduce death and disabilit y in premature b a b i e s mu s t b e inte g r a the d within the existing health system. The continuum of care is a core organizing principle for health systems emphasizing Photo: Chris Taylor/Save the Children linkages between healthcare packages across time and through various service delivery strategies (Chapter 1). An effective continuum of care addresses the health needs of the adolescent, woman, mother, newborn and child throughout the life cycle, wherever care is provided, whether it be at the home, primary care level or district and regional hospitals. Integrated service delivery packages within the continuum of care have many advantages: costeffectiveness is enhanced; available human resources are maximized; and services are more family-friendly, reducing the need for multiple visits (Ekman et al. Most impor tantly, they can help prevent stillbir ths, improve prevention and care of premature babies and save the lives of women, newborns and children (Friberg et al. Interventions with the highest impact on the prevention of preterm birth and care of the premature baby can be 82 the Global Action Report on Preterm Birth Figure 6.
For Sandra medicine 44 159 purchase epitol 100mg visa, this experience may be seen as an opportunity for practicing love and forgiveness symptoms 2 days before period buy epitol us, moving out from behind rigid self-separateness treatment of gout discount epitol 100mg on line, facing fears treatment head lice purchase epitol cheap online, and transforming her selfdefinition. This means that the "now" is the only place where awareness, responsibility, and change can occur. Therefore, the process of therapy is to help the client make contact with the present moment. Rather than seeking detailed intellectual analysis, the Gestalt therapist looks to create a "safe emergency" in the therapeutic encounter. This may be accomplished in a fairly short amount of time by explicitly asking clients to pay attention. The therapist may point out how the client could be avoiding the present moment through inauthentic "games" or ways of relating such as "talking about" feelings rather than experiencing them directly. These may all serve the goal of helping clients move into the immediacy of their experience rather than remaining distant from it through intellectualization or substance abuse. The term contact in Gestalt refers to meeting oneself and what is other than oneself. Without appropriate contact and contact boundaries there is no real meeting of the world. Instead, one remains either engulfed by the world on one hand or, on the other hand, distant from the world and people. Substance abuse interrupts the flow of what Perls called "organismic self-regulation. The substance Gestalt Therapy Gestalt theory holds that the analysis of parts can never provide an understanding of the whole. In a therapeutic setting, this approach opposes the notion that human beings can be understood entirely through a rational, mechanistic, scientific process. Gestalt therapists seek to help their clients gain awareness of themselves and the world. Discomfort arises from leaving elements and experiences of the psyche incomplete- primarily past relationships and intrapsychic conflicts that are unresolved, which Perls calls "unfinished business" (Perls, 1969). Substance abuse may also be understood as "introjection" in which the client attempts to "swallow whole" or "drink in" his environment without contact and discrimination. This type of client bypasses and blocks other experiences that might enable contact and the development of discrimination. Perls maintains that such a client seeks immediate confluence without preparatory contact. This pattern of interaction extends to other relationships (besides the substance) as well. They, too, must be able to make and sustain contact with the client and with their own reactions. The therapist may simply help her become aware of basic sights, sounds, somatic reactions, feelings, and thoughts as well as what her attention drifts to . The immediate contact between therapist and client is a component of the "now" where these sensations are explored directly. The therapist might notice and ask about her style of eye contact, or her fidgeting body, or stream of thoughts. The therapist might invite her to name and explore the sensation that the thought of death, for example, brings; perhaps this involves a sense of a void, or feeling cold and dark, or a feeling of engulfment. She then may be asked to become these sensations-for example, the therapist may ask her to be "the void" and encourage her to speak as if she were that void. This may then open possibilities for a dialog with the void through acting out the opposite polarity: separateness and choice. This might involve using an empty chair technique in which the client would literally move into the chair of the "void," speak as if she were that, and then move into an opposite chair and respond in a dialog. A therapist could also explore her introjection through questions such as, "How is this void different or the same as from the feeling of alcohol or in relationships with your children or husband? Sandra seems to have a great deal of "unfinished business" that involves unexpressed feelings. Experimentation with these sensations may begin to free her to express and meet these feelings more directly. Each person has a unique identity that can only be known through relationships with others. The meaning of life and of existence is never fixed; rather, it constantly changes.
In summary 9 medications that can cause heartburn trusted epitol 100mg, histopathologic alterations in the mouth medicine you cannot take with grapefruit order genuine epitol, larynx symptoms of kidney stones buy discount epitol, tracheobronchial tree and pulmonary parenchyma treatment tinnitus purchase epitol pills in toronto, associated with smoking, have been documented in man. The alterations in the bronchi support the hypothesis that cigarette smoking is a cause of human chroni,c bronchitis. Whereas definite pathologic changes in the lung parenrhvma of man also are clearly associated with cigarette smoking, the abnormalities observed in the lung parenchyma cannot be related with certainty to recognized disease entities at the present time. Rhinitis, angina, and laryngitis, also observed frequently in cigarette smokers, are reversible on cessation of smoking. These observations have become clinical tradition, yet surprisingly little documentation of predictable changes in these tissues as a consequence of smoking is available (129). Thus, evidence of progressive non-neoplastic disease in the upper respiratory tract, induced by smoking, is lacking. Only in studies of "stomatitis nicotina" and of epithelial changes in the larynx has there been adequate pathological substantiation of the clinical opinion that alterations are induced by smoking. Asthma, as here defined may occur in vascular diseases, but in these instances the airway obstruc. Support for this association comes largely from the presence of skin test reactions to tobacco products and passive transfer tests (168, 169). In the "Tokyo-Yokohama Asthma" studies, a severe asthma-like disease, presumed to be caused by air pollution, affected cigarette smokers predominantly (155 J. The absence of smoking data on unaffected members of the same population leaves the question of an additive effect of cigarette smoking unanswered. One study suggests that non-smokers may have a slightly greater prevalence of asthma than smokers; the possibility of bias due to self-selection of the base population could not, however, be excluded in this study (84). Apart from the exceptions noted above, it is clear that cigarette smoking is of no importance as a cause of asthma. A hypothetical contraindication to cigarette smoking can be postulated for asthmatics on the basis of the physiologic alterations induced in the tracheobronchial tree by tobacco Nonetheless, substantiation of worsening from cigarette smoking smoke. A cause-and-effect relationship between cigarette smoking and asthma, as defined above, is not supported by evidence available. Studies adequate for examination of this association are available for only viral illness,and two categories of infectious diseases, upper respiratory on transmission of common colds failed tuberculosis I 30 I. Experiments to demonstrate increased susceptibility in volunteers with a history of cigarette smoking (50 J. Jloreover, common colds were detected among 5,500 employees over a P-year period with approximately the same frequency in In a study of illness in a group of families smokers and non-smokers (110). The possibility that the relationship is not a direct one needs further careful examination. Certain social factors, important to epidemiological assessment in tuberculosis, have not been considered in detail in these studies. Of particular interest in this regard is a study (29) in which both cigarette and alcohol consumption were found to be in excess in tuberculosis patients as compared to the matched controls. The number of cigarettes consumed in the two groups was the same, however, at each level of alcohol intake. Matching by cigarette consumption failed to weaken the association between alcohol consumption and tuberculosis (29). Thus, the relationship between tuberculosis and smoking in this study was only an indirect one: the association was found to occur between smoking and alcohol consumption and between alcohol consumption and tuberculosis, rather than between smoking and tuberculosis. Thus the association between smoking and the infectious diseases is confined at present to a single cause-of-death category: Influenza and pneumonia contribute to the excess deaths in cigarette smokers, but the data are insufficient to evaluate this observation. In the limited number of studies available, cigarette smoking has not been shown to contribute to the incidence or severity of either naturally acquired or experimentally induced upper respiratory viral infections. In 1955, cancer of the lung was certified as the underlying cause of death in 27,133 persons and chronic bronchopulmonary diseases in 11,480 persons. A tabulation of all diagnoses, both contributing as well as underlying causes of death, however, showed that cancer of the lung was entered upon a total of 28,123 death certificates, whereas the chronic bronchopulmonary diseases were certified as contributing to 32,051 deaths (47). The possibility that mortality data, as presently recorded, may underestimate the role of chronic bronchopulmonary diseases through incorrect listing by the physician as contributory rather than the principal cause has also been suggested (115). Social security records in 1960 show that chronic bronchopulmonary diseases, particularly emphysema, ranked high among the conditions for which disability benefits were allowed to male workers 50 years of age or older in the United States (186). Chronic bronchitis and emphysema are the chronic bronchopulmonary diseases of greatest public health importance in the United States. The scope of the subsequent remarks is limited thereand fore to the possible relationship of smoking to chronic bronchitis 27; Since dexriptions of both were published long before ciga.
Diabetes mellitus treatment kidney cancer order 100mg epitol amex, fasting blood glucose concentration schedule 8 medicines buy epitol 100mg free shipping, and risk of vascular disease: a collaborative metaanalysis of 102 prospective studies treatment 2 prostate cancer purchase epitol amex. Complications and cardiovascular risk factors in insulin-dependent diabetes- findings in an Irish clinic and in other European centres symptoms 7 days past ovulation 100mg epitol with amex. Cardiovascular risk prediction in adults with type 1 diabetes: the Fremantle Diabetes Study. Sexspecific-differences in cardiometabolic risk in type 1 diabetes: a cross-sectional study. Characterization of patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus in southern Brazil: chronic complications and associated factors. Vascular complications in young Asian Indian patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Micro and macrovascular complications of diabetes mellitus in Cameroon: risk factors and effect of diabetic check-up - a monocentric observational study. Glucose abnormalities and heart failure predict poor prognosis in the population-based Reykjavнk Study. Comparison of comorbidities in patients with pre-diabetes to those with diabetes mellitus type 2. Uric acid is not an independent predictor of cardiovascular mortality in type 2 diabetes: a population-based study. Prevalence, management and control of diabetes mellitus and associated risk factors in primary health care in Portugal. Albuminuria, cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in diabetic and non-diabetic subjects in a rural general practice. Effect of diagnosis-time and initial treatment on the onset of type 2 diabetes mellitus complications: a population-based representative cross-sectional study in Hungary. The prevalence of macrovascular complications among diabetic patients in the United Arab Emirates. Associations of blood glucose and prevalent diabetes with risk of cardiovascular disease in 500,000 adult Chinese: the China Kadoorie Biobank. Mortality from heart disease in a cohort of 23,000 patients with insulin-treated diabetes. Cause-specific mortality trends in a large populationbased cohort with long-standing childhood-onset type 1 diabetes. The joint effects of different types of glucose-lowering treatment and duration of diabetes on total and cardiovascular mortality among subjects with type 2 diabetes. Risk of cardiovascular and all-cause mortality: impact of impaired health-related functioning and diabetes. Associations between diabetes, leanness, and the risk of death in the Japanese general population: the Jichi Medical School Cohort Study. Interaction of body mass index and diabetes as modifiers of cardiovascular mortality in a cohort study. Cause-specific mortality in insulin-treated diabetic patients: a 20-year follow-up. Ethnic disparities in causes of death among diabetes patients in the Waikato region of New Zealand. The economic consequences of diabetes and cardiovascular disease in the United States. The burden and costs of chronic diseases in low income and middle income countries. The global economic burden of diabetes in adults aged 20-79 years: a costof-illness study. Prevention of cardiovascular disease: guidelines for assessment and management of total cardiovascular risk. Prevalence and healthcare costs of diabetic retinopathy: a population-based register study in Sweden. Cost of diabetic retinopathy and macular oedema in a population, an eight year follow up. The Effect of Intensive Treatment of Diabetes on the Development and Progression of Long-Term Complications in InsulinDependent Diabetes Mellitus.
Buy epitol once a day. Anxiety (TEST) - Do You Have Anxiety?.