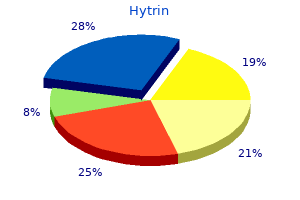
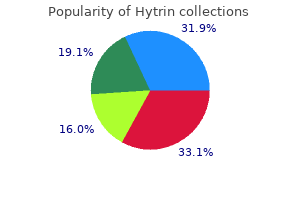
"Purchase hytrin mastercard, heart attack ncla".
By: P. Baldar, M.A., Ph.D.
Clinical Director, Palm Beach Medical College
The overall 13 pulse pressure diastolic order genuine hytrin on-line, fingerlings in the pond (N) is calculated pulse pressure test order hytrin 1 mg without prescription, number of on the basis of the sample analysis blood pressure medication headache cheap hytrin 2 mg, taking the catchability: into account (N): N nS ks where hypertension journals purchase hytrin 5 mg without prescription, n = catch per unit effort (specimens); S = area of the waterbody (m2); s = haul area (m2); and k = catch efficiency index (Kushnarenko, 1971). By default, the catch efficiency index of a fingerling trawl is considered equal to 0. In addition, a direct relation exists between fingerling weight and catchability index, which increases considerably upon specimens reaching a weight of 4 g. This can stimulate the search for feeding sites and increase the survival rate after release. The primary factors for identification of release sites are the consistent availability of sufficient food organisms and the state of the bottom (hard, sand or slightly silted beds) to avoid crowding of juveniles within limited areas. Table 49: Basic phases of sturgeon larvae, fry and fingerlings rearing under the regime of gradually increasing salinity (after transition to exogenous feeding) (Kokoza, 2004). Release of juveniles into rivers and adjacent to river mouth/sea areas should be spread out in terms of area and time. It is important to consider the state of shoreline vegetation, size of main feed items, lack of predators and pests. Prior to release of juveniles it is necessary to evaluate adequacy of key hydrochemical parameters. Thermal and salinity stratification which reduces speed of space distributation of fish should be absent at the place of release. This can cause diminishing in feeding area, an increase in predators pressure and may negatively affect thep hysiological state of the fingerlings, resulting in a decrease in survival rate (Levin, 1989). Hence, analysis of the salinity tolerance of different size- and age-graded groups enables optimization of release sites and periods, as well as the development of species-specific schemes for adaptation of hatchery-produced juveniles to various salinities. In the wild, migrating sturgeon juveniles encounter sea areas of increasing salinity in the course of their growth. The senior juveniles possess more developed mechanisms of osmotic and ionic homeostasis. The developing eggs of the ship sturgeon are the most sensitive to variations in salinity, with high mortality (up to 30 percent) occurring at water salinity as low as 2 (Kasimov, 1987). The level of morpho-functional development that determines the level of osmotic regulation in sturgeon fingerlings is primarily size and weight dependent. At large fish size, relationships between the surface area of the body and its weight and volume tend to change, as well as those between blood system size and blood volume, and gill epithelium and number of chloridesecreting cells. For larger fingerlings, a change in blood osmolarity in water of 12 salinity occurs more rapidly than in smaller fish. This proves that the osmoregulatory function in larger fingerlings is more developed. Preliminary adaptation permits their survival in water of salinity up to 16 (Krayushkina, 1983). Beluga exhibit lower adaptability and are capable of resisting 12 salinity only upon reaching 6. The developed osmoregulatory system in fingerling anadromous sturgeons is characterized by the ability to transit swiftly from a hypotonic to a hypertonic type of osmoregulation, resulting in a decrease in blood serum osmolarity in water of various salinity to basal level (Krayushkina, 2006). The functional activity of endocrine glands (interregnal and thyroid) also tends to increase in the course of adaptation (Dyubin and Kiseleva, 1983). Optimal regimes for adaptation of larvae, fry and fingerlings to gradual increase in salinity are presented in Table 49. Water temperature has proved to be an important factor during transition of fingerlings from fresh to seawater.
The third method avoids transfer of breeders from one unit to another and therefore maintains their initial physiological state prehypertension 5 mg hytrin amex, as fish can easily tolerate a wide variation in temperature (as is typical in the wild) (Rivkin and Kazansky arteria basilar discount 5mg hytrin otc, 1979) blood pressure medication for sleep generic 1mg hytrin with mastercard. Therefore blood pressure medication voltaren order hytrin canada, this method requires a more detailed scheme for integration of isolated tanks into the cooling system and obviously might be more promising for units with an increased number of tanks. The period of fish post-stress adaptation (related to their capture and transportation) is rather long (14 d). Thus, during stocking and the subsequent holding of breeders, the transfer of fish from tank to tank should be avoided. This is permissible only during the period of transition to spawning temperatures. The use of species-dependent optimal temperature regimes of accumulation provides high survival rates and hatchery success when using various seasonal forms of breeders. Statistical analysis of multiyear hatchery trial data and the physiological state of breeders has enabled the identification of optimal holding regimes for each sturgeon species and seasonal race. Only early hiemal and vernal forms of stellate sturgeon should be exposed to long-term holding (> 2 months). In the case of long-term holding, this is essential (Chebanov and Savelyeva, 1995). The rate of water exchange depends on the temperature and aeration intensity (or oxygenation). The freshwater supply rate determines the water quality and should be arranged accordingly (Table 40). Trials have demonstrated that transition of sturgeons to the final stage of the reproductive cycle after longterm holding at low temperatures cannot be routinely performed by simple linear temperature increase within a specified preplanned daily gradient (Kazansky and Molodtsov, 1974). Then, the total balance of spawning temperatures should be considered and further injection may be administered (Table 41). In this case, the target temperature is reached without intermediate phases (Figure 104). Further temperature increase should alternate with its decrease within the spawning temperature range. The sum of cumulative spawning temperature for stellate sturgeon after long-term holding at low temperatures leading to definitive functional maturity ranges between 250 and 300 degree-days (Chebanov et al. This seems to be very important, as fish kept at low temperatures respond poorly to hormonal injection if accumulation of thermal energy is insufficient, which leads to poor offspring viability (Table 41). The lowest number of females capable of producing viable progeny is observed when the spawning temperatures effect is minimal.
Best 2 mg hytrin. Blood Pressure Companion App Review.
Epimedium. Hytrin.
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- How does Horny Goat Weed work?
- Are there safety concerns?
- What is Horny Goat Weed?
- Dosing considerations for Horny Goat Weed.
- Impotence, ejaculation problems, sexual dysfunction, fatigue, memory loss, high blood pressure, heart disease, liver disease, bronchitis, joint pain, HIV/AIDS, osteoporosis, and other conditions.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96686
Differences in coping styles as they relate to gender and culture should be recognized so each can be supported for his or her strengths blood pressure quit drinking order hytrin with a mastercard, insight blood pressure ranges low normal high order 2mg hytrin, and ability during the course of the illness arrhythmia long term effects buy hytrin mastercard. On the other hand blood pressure chart diastolic low best order hytrin, some couples have felt that the strain and the magnitude of the issues they face have made them stronger together. Depression and anxiety are two uncomfortable emotions characteristics that may accompany this disease. Many parents feel anxious or depressed from the onset, unsure of what to anticipate. The ability to contain the anxiety or depression, to make decisions, to enjoy life, and to continue to function are skills to be mastered. Talking to other parents, understanding their decision-making processes, and getting support help parents to maintain the balance they need. These support groups offer parents the opportunity to be parents: to be able to compare their child to other children, to seek companionship of another parent in a similar situation, to brainstorm, to share information, and to join the fight against Fanconi anemia and become empowered in the face of the illness. Families may be viewed incorrectly as aggressive when they advocate in the interests of their children. There may be moments when families and individual physicians do not agree on treatment options and alternatives. The involved professionals must work to make the best decisions with, and not for, families. This strategy will Chapter 16: Psychosocial Issues 295 help minimize potential later regrets for families and professional staff. Helping navigate the course of the illness, and thinking through decisions can help those facing such rare illnesses feel much less isolated. Parents describe having a greater appreciation for the things they do with their children, learning how to experience each day to its fullest. This process can be financially, emotionally, and physically draining and in some cases, all-consuming. Families can benefit from talking with others who have been in this situation to help mitigate the intense emotions that can occur during this time. If parents create an environment that allows for questions, discussions, and an expression of feelings, children will feel free to ask their parents about their illness and treatment options and become active participants in the disease management. In addition to what they have been told, they pick up information from ambient conversation, have independent interactions with professionals, and surmise things from the emotional climate around them. They will ask questions when they want to know, and will often shy away from questions to which they do not want the answers. Children are good regulators of their own knowledge base, providing cues to the adults around them at all junctures. Children need to be able to confide in their parents and others when they feel limited physically or socially by Fanconi anemia. At each stage of development, children need age-appropriate explanations of their diagnosis and treatment. Information offered regularly to children will enhance their ability to understand their disease and establish trusting relationships. As they get older and medical problems emerge, groundwork set in earlier years will encourage patients to rely on health care providers. Others may have no known problems but, because of illness-related absence, may need extra assistance. School-age children develop increasingly strong relationships with their peers as they begin to differentiate themselves from their families. Each child and family must find a balance in social and family relationships, which allows for a blend of independence and dependence, nurturing and differentiation. They may, therefore, come to understand and deal with issues with which adults may not feel comfortable. Thus, they may seem more mature than their chronological ages and often are more sophisticated than their peers in matters of illness and death. They may also appreciate life, and the meaning of life, more than the adults they encounter. For adolescents, challenging the rules is age-appropriate and functional at times for emotional growth.
No consistent pattern in cord blood lead levels was apparent in the few cases where they were reported interleukin 6 arrhythmia hytrin 2mg for sale. In the other cases cord blood lead levels were lower than maternal prechelation levels hypertension icd 9 buy discount hytrin line. In sev eral reports blood pressure 5020 order on line hytrin, chelation treatment was not initiated until shortly before or soon after delivery and was directed toward the newborns blood pressure medication recommendations hytrin 1 mg line. Exchange transfusion has been used, in combination with chelation therapy, to successfully lower blood lead levels in neonates (Hamilton et al. The relative benefits/risks of chelation versus exchange transfusion have not been investigated. Such decision making should weigh the lack of definitive evidence of safety for the fetus (especially in the first trimester) against the extensive safety profile 91 and experience with these drugs in children and adults. Immediate removal from the lead source is still the first prior ity and, in some cases, pregnant women may require hospitalization. When chelation is being considered, it should be performed in an inpatient setting only with close monitoring of the patient and in consultation with a physician with expertise in the field of lead chelation therapy. Data regarding the reproductive risk associ ated with chelation during pregnancy are sparse. Most case reports of infant outcomes report on the use of chelating agents after the first trimester (see Table 8-2). Reserving the use of chelating agents for later in preg nancy is consistent with the general concern about the use of unusual drugs during the period of organogen esis (National Research Council, 2000). However, severe maternal lead intoxication, such as encephalopathy, will warrant chelation regardless of the stage of pregnancy. The limited data published suggest that toxicities for 0- to 6-month-olds are no different than those of 6- to 12-month-olds. Chelation treatment must occur in an environment free of lead hazards; therefore, prior to initiating chelation therapy, the patient should be removed from further lead exposure. Very limited data are available on the use of exchange transfusion as an alternative in this age group. Published Experience with Chelating Agents During Pregnancy in Humans Authors/Location/Year Published Abendroth et al. Chronic Apgar 7/9, birthweight 2,300g, 37 wks, neonatal seizures; poor language development @2 yrs Ghafour et al. Chronic (years) Apgar 9/9, birthweight 2,280g, 35 wks; poor suck, sleepiness as neonate; @ 12 months global delay of 5-6 mos. Key Recommendations for Initiation of Breastfeeding Measurement of levels of lead in breast milk is not recommended. These reccomendations are not appropriate in countries where infant mortality from infec tious diseases is high (World Health Organization Collaborative Study Team on the Role of Breastfeeding on the Prevention of Infant Mortality 2000). These infants should have blood lead tests at birth and be followed according to the schedule in Chapter 5. Flush the tap for at least 3 minutes before use and then heat the water or use bottled or filtered tap water known to be free of lead. Breastfeeding is an optimal infant feeding practice compared with other infant feeding practices which carry risks. With regard to short-term risks, lack of breastfeeding is associated with increases in common childhood infections, such as diarrhea (Chien and Howie 2001) and ear infections (Ip et al. Lack of breastfeeding also increases the risk for some relatively rare but severe infections and diseases, such as severe lower respiratory infections (Bachrach et al.