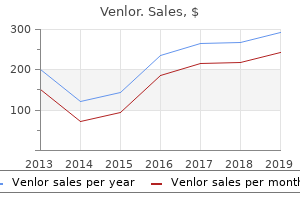
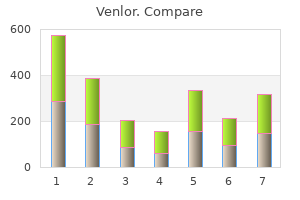
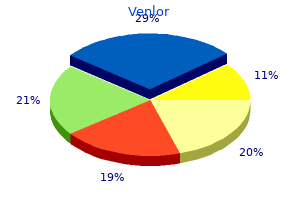
"Order venlor without a prescription, anxiety funny".
By: F. Ilja, M.B. B.A.O., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Clinical Director, Southwestern Pennsylvania (school name TBD)
Then P (C) = P (C X = 0)q 2 + P (C X = 1)(2pq) + P (C X = 2)p2 = 2pqP (C) + p2 anxiety in relationships purchase venlor on line amex, so P (C) = p2 anxiety symptoms jaw order venlor canada. Sanity check: Note that this should (and does) reduce to 1 for p = 1 anxiety 911 venlor 75 mg online, 0 for p = 0 anxiety quotes cheap venlor 75mg mastercard, and 18 1 2 Chapter 2: Conditional probability for p = 1. So the probability that Calvin wins the match is (p2 - q 2)/p2 (p2 - q 2)/p2 1 - (q/p)2 p2 = 4 = 2 = 2, 4 4)/p4 2)(p2 + q 2)/p4 1 - (q/p) (p - q (p - q p + q2 which agrees with the above. Show this is impossible (with a short proof) or find a counterexample (with a story interpreting A, B, C). Solution: (a) It is not possible, as seen using the law of total probability: P (A) = P (A C)P (C) + P (A C c)P (C c) < P (B C)P (C) + P (B C c)P (C c) = P (B). In this problem, the weights P (C) and P (C c) are the same in both expansions, so the inequality is preserved. Homer: Lisa, a guy who has lots of ivory is less likely to hurt Stampy than a guy whose ivory supplies are low. Here Homer and Lisa are debating the question of whether or not the man (named Blackheart) is likely to hurt Stampy the Elephant if they sell Stampy to him. They clearly disagree about how to use their observations about Blackheart to learn about the probability (conditional on the evidence) that Blackheart will hurt Stampy. Solution: (a) Let H be the event that the man will hurt Stampy, let L be the event that a man has lots of ivory, and let D be the event that the man is an ivory dealer. Implicitly, she suggests that this makes it likely that the man will hurt Stampy, i. It may be true that, controlling for whether or not Blackheart is a dealer, having high ivory supplies makes it less likely that he will harm Stampy: P (H L, D) < P (H Lc, D) and P (H L, Dc) < P (H Lc, Dc). In short: rich individuals (in any state) tend to vote for Republicans, while states with a higher percentage of rich people tend to favor Democrats. Is it possible that both Pnew (D B) > Pold (D B) and Pnew (D B c) > Pold (D B c) are true? If so, explain how it is possible and why it does not contradict the law of total probability P (D) = P (D B)P (B) + P (D B c)P (B c); if not, show that it is impossible. Solution: (a) Here are two tables that are as desired: Red Rich Poor Total Dem 5 20 25 Rep 25 50 75 Total 30 70 100 Blue Rich Poor Total Dem 45 35 80 Rep 15 5 20 Total 60 40 100 19 In these tables, within each state a rich person is more likely to be a Republican than a poor person; but the richer state has a higher percentage of Democrats than the poorer state. Letting D, W, B be the events that a randomly chosen person is a Democrat, wealthy, and from the Blue State (respectively), for the above numbers we have P (D W, B) < P (D W c, B) and P (D W, B c) < P (D W c, B c) (controlling for whether the person is in the Red State or the Blue State, a poor person is more likely to be a Democrat than a rich person), 20 Chapter 2: Conditional probability but P (D W) > P (D W c) (stemming from the fact that the Blue State is richer and more Democratic). Suppose with the numbers from (a) that 10 people move from the Blue State to the Red State, of whom 5 are Democrats and 5 are Republicans. Then Pnew (D B) = 75/90 > 80/100 = Pold (D B) and Pnew (D B c) = 30/110 > 25/100 = Pold (D B c). Intuitively, this makes sense since the Blue State has a higher percentage of Democrats initially than the Red State, and the people who move have a percentage of Democrats which is between these two values. This result does not contradict the law of total probability since the weights P (B), P (B c) also change: Pnew (B) = 90/200, while Pold (B) = 1/2. The phenomenon could not occur if an equal number of people also move from the Red State to the Blue State (so that P (B) is kept constant). Solution: the function P (D = j) is nonnegative and the sum over all values is 9 log10 j=1 j+1 = j 9 (log10 (j + 1) - log10 (j)). More compactly, we can also write G(x) = limtx- F (t), where the - denotes taking a limit from the left (recall that F is right continuous), and G(x) = F (x - 1), where x is the ceiling of x (the smallest integer greater than or equal to x). Let 21 22 Chapter 3: Random variables and their distributions p be the probability that A wins an individual game, and assume that the games are independent. First let us do a direct calculation: P (A wins) = P (A wins in 4 games) + P (A wins in 5 games) +P (A wins in 6 games) + P (A wins in 7 games) = p4 + 4 4 p q+ 3 5 4 2 p q + 3 6 4 3 p q. Then P (X 4) = = P (X = 4) + P (X = 5) + P (X = 6) + P (X = 7) 7 4 3 p q + 4 7 5 2 p q + 5 7 6 p q + p7, 6 which looks different from the above but is actually identical as a function of p (as can be verified by simplifying both expressions as polynomials in p). Solution: Chapter 3: Random variables and their distributions (a) Note that n - X Bin(n, 1/2) and n + 1 - Y Bin(n + 1, 1/2) (we can interpret this by thinking of counting Tails rather than counting Heads), with n - X and n + 1 - Y independent.
Similar disorders induced by other species of Solanum have been reported in cattle grazing S anxiety symptoms flushed face generic 75mg venlor mastercard. Death is uncommon and some animals have to be euthanized because of severe injuries caused by repeated falls anxiety after eating buy venlor visa. Histologic lesions include fine vacuolization and diffuse loss of Purkinje cells anxiety zoloft dosage discount venlor uk, axonal spheroids in the granular layer and white matter anxiety disorder symptoms dsm 5 purchase venlor 75 mg otc, Bergman gliosis in the molecular layer, and atrophy of molecular and granular layers. Ultrastructurally, there are numerous lipid inclusions and membranous bodies in the cytoplasm of Purkinje cells (Riet-Correa et al. A lectin histochemical study of the cerebella of two cattle experimentally poisoned with S. However, the lectinbinding patterns in cerebella of cattle naturally poisoned with S. Lectin histochemistry using paraffin-embedded sections may be useful in the identification of specific sugars and hence aid in diagnosing glycoprotein and glycolipid storage diseases (Alroy et al. The objectives of this retrospective study were to describe the clinical signs and compare the morphological and lectin histochemical findings of 33 natural cases of S. The cases originated from three municipalities of central Rio Grande do Sul State, southern Brazil. The history and clinical signs were obtained from the owners or the practicing veterinarians in all cases. At necropsy, the brains were collected and fixed in 10% buffered neutral formalin for 5 to 7 days. The following sections of the brain were evaluated histologically: medulla at the level of the obex, pons, cerebellum, midbrain at the level of the rostral colliculus, thalamus, basal nuclei, hippocampus, and frontal, parietal, and occipital lobes. For the lectin histochemical study, after deparaffination with xylene, additional samples of cerebellum were immersed in 0. They were then incubated with the eight biotinylated lectins (Vector Laboratories Inc. The horseradish peroxidase was activated by incubation for 4 to 10 min with buffered0. The following negative controls were performed: the lectins were omitted or blocked by incubating them with their blocking sugars (0. The lectin binding was analyzed using the following semiquantitative scale of stained structures and subjectively scored as follows: (0) none, (1) weakly positive, (2) moderately positive, and (3) strongly positive. Results distention of portions of the Purkinje cells; some degenerated cells had swollen and eosinophilic cytoplasm and others had peripherally placed nuclei. In some cases, the vacuoles were confluent and occupied one pole or the most of the pericarya of the neurons. Occasionally, focal gliosis and mild histiocytic perivascular cuffs were visualized in the white matter of the cerebellum of three cases. There were different lectin binding patterns between the affected and control cerebella. Lectin reactivity in Purkinje cells between cases was independent of cell damage stage (from mild to severe loss of neurons). Discussion Neurological clinical signs observed in all affected cattle included proprioceptive and cerebellar deficits such as incoordination, hypermetria, tremors, frequent falls, and transitory seizures when moved or stimulated. After these episodes, numerous animals assumed a wide base stance or appeared apparently normal. Microscopically, the lesions were restricted to the cerebellum and consisted of fine vacuolization and 30 the clinical signs and gross and microscopic findings observed in cattle in the current study are similar to those previously described in S. A fine vacuolar degeneration of neuronal perikaria with progressive axonal degeneration resulting in the death of these cells and eventual atrophy of the cerebellum are the main pathological features of this disease. Electron microscopy studies revealed lipidic inclusions and cytoplasmic membranous and lamellar bodies accompanied by ribosome disaggregation in cerebellar Purkinje cells of cattle intoxicated with S. Another typical degenerative histopathologic and ultrastructural change observed is the presence of axonal spheroids that represent swollen myelinated axons (probably by cytoskeletal distortion) filled with electron-dense residual bodies, swollen mitochondria, and an increase in the ratio of axoplasm/myelin (Riet-Correa et al.
Verification of cystic lesions in abdominal viscera can usually be well-documented with ultrasound anxiety essential oils purchase venlor 75mg with visa. Common Diagnostic Indications this section contains general abdominal anxiety quiz purchase venlor paypal, hepatobiliary anxiety symptoms 0f purchase venlor in united states online, pancreatic anxiety xanax benzodiazepines generic venlor 75mg mastercard, gastrointestinal, genitourinary, splenic, and vascular indications. These medications should be stopped whenever possible and liver chemistries repeated before performing advanced imaging Other causes for elevated liver transaminases include excessive alcohol intake, cirrhosis, hepatitis, hepatic steatosis as well as other hepatic and non-hepatic disorders. Splenic Indeterminate splenic lesion on prior imaging, such as ultrasound Note: Splenic hemangioma is the most common benign splenic tumor and may be followed with splenic ultrasound. Characteristics of common solid liver lesions and recommendations for diagnostic workup. Hemangioma-like lesions in chronic liver disease: diagnostic evaluation in patients. Multimodality imaging of neoplastic and nonneoplastic solid lesions of the pancreas. These variations or extra sequences are included within the original imaging request. Breast cancer Staging of low risk breast cancer (stage 2B or less) in the absence of signs or symptoms suggestive of metastatic disease Surveillance of breast cancer in the absence of signs or symptoms of recurrent disease Surveillance imaging of colon cancer in remission, unless one of the following high risk features is present: Lymphatic or venous invasion Lymph node involvement Perineural invasion Poorly differentiated tumor T4 tumor Associated with bowel obstruction Close, indeterminate or positive margins Fewer than 12 nodes examined at surgery Localized perforation Exclusions-advanced imaging is not indicated in the following scenarios: Colon cancer Gynecologic malignancies Surveillance imaging in patients with previously treated gynecologic malignancies including ovarian, endometrial, cervical, vaginal or vulvar cancer (Note: this exclusion does not apply to sarcoma or other rare histologies not typically associated with these structures). Italian Society of Hematology practice guidelines for the management of iron overload in thalassemia major and related disorders. Screening for hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with hepatitis C cirrhosis: a cost-utility analysis. Australian guidelines for the assessment of iron overload and iron chelation in transfusion-dependent thalassaemia major, sickle cell disease and other congenital anaemias. American College of Gastroenterology clinical guideline: the diagnosis and management of focal liver lesions. Accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosis of liver iron overload: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Computed tomographic angiography, abdomen, with contrast material(s), including non-contrast images, if performed, and image post-processing 74185. Doppler ultrasound examination is an excellent means to identify a wide range of vascular abnormalities, both arterial and venous in origin. Renal artery stenosis Note: Suspected renovascular hypertension from renal artery stenosis with at least one of the following Refractory hypertension, in patients receiving therapeutic doses of three (3) or more anti-hypertensive medications with documentation of at least two (2) abnormal serial blood pressure measurements Hypertension with renal failure or progressive renal insufficiency Accelerated or malignant hypertension Abrupt onset of hypertension Hypertension developing in patients younger than 30 years of age Deteriorating renal function on angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition Abdominal bruit, suspected to originate in the renal artery Generalized arteriosclerotic occlusive disease with hypertension Unilateral small renal size (greater than 1. In the absence of classic peripheral symptoms of claudication, then obtain a vascular surgical consultation and perform lower extremity non-invasive arterial evaluation, which may include the following: segmental systolic pressure measurements, segmental limb plethysmography, continuous wave Doppler and duplex ultrasonography. Visceral artery aneurysms Renal Celiac Splenic Hepatic Diagnosis, management, and surveillance of visceral artery aneurysms including: Superior/inferior mesenteric and their branches References 1. Renal artery aneurysm: diagnosis and surveillance with multidetector-row computed tomography. Technology Considerations Doppler ultrasound examination is an excellent means to identify a wide range of vascular abnormalities, both arterial and venous in origin. Pseudoaneurysm Of the abdominal aorta and/or branch vessel Thromboembolism Traumatic vascular injury References 1. Verification of cystic lesions in the pelvis is usually well-established with ultrasound. Common Diagnostic Indications this section contains general pelvic, intestinal, genitourinary, vascular, and osseous indications. Diagnostic evaluation of the pelvis may be performed with pelvic ultrasound (trans-abdominal and trans-vaginal), which is the initial imaging modality for most gynecologic abnormalities. Transabdominal pelvic sonography is also used for urinary bladder assessment, such as post-void residual urine volume. Endoscopy and barium examinations are well established procedures for intestinal evaluation. Common Diagnostic Indications Abnormalities detected on other imaging studies which require additional clarification to direct treatment Adenomyosis of the uterus following pelvic ultrasound Adnexal mass(es) following pelvic ultrasound Usually performed to further evaluate problematic cases which are initially detected on pelvic ultrasound.
Step 4 in the system of the spine is evaluating the neuroforamina anxiety nos icd 10 buy venlor 75mg with amex, and this is most important in the cervical spine in which they are well seen in oblique views anxiety vs panic attack 75mg venlor overnight delivery. When associated with degenerative disc disease the findings are termed spondylosis (not to be confused with spondylolysis anxiety symptoms women discount venlor 75 mg on-line, the defect mentioned previously) anxiety symptoms reddit purchase venlor visa. Figures 142 (previous) and 159 (next page) show normal neuroformina as opposed to a patient with cervical spondylosis. White arrows point to normal neuroforamina, as opposed to the encroachment by enosteophytes as indicated by the red arrow. This is a common finding in patients with osteoarthritis and may be the cause of parathesias In the cervical spine, alignment evaluation is extremely important in evaluating trauma victims. In this projection one should check the upper portion of the cervical spine in relation to the clivus, the extended line of which should intersect the odontoid in its posterior one third. Also the posterior and anterior vertebral margins should align fairly close in this view, as should the facets, pedicles and neuroformina in the oblique projections. Remember that position and alignment of cervical vertebrae are maintained by ligaments, which may be stretched or fractured, and there may not be an associated bone injury. If flexion and extension views are provided, keep in mind there is a great deal of "normal" subluxation in children, whose ligaments are much more elastic than adults. In fact up to 40% of pediatric cervical spines will show a pseudosubluxation, most often at C2-3. Differentiating pseudosubluxation from the real thing, especially with a history of trauma can be difficult. Swischuk defined a line drawn from the posterior arch of C-1 to the posterior arch of C-3. The line should pass through or be no more than 1-2mm anterior to the posterior arch cortex of C-2 (yellow line). The turquoise lines indicate the position of the posterior arches of C-4 and C-5 so you get some idea of how to locate posterior arch margins. Sometimes in neck injuries like whiplash, all that can be seen is a loss of or straightening of the usual lordotic curvature. When the curvature reverses with angulation of the posterior vertebral margin, the injury is more severe and may involve an intervertebral disc or fracture. One is due to the gap between the two frontal maxillary incisors causing a vertically oriented pseudofracture. The inferior edge of these same incisors or sometimes the posterior arch of C-1 can also simulate a transverse fracture at the base of the odontoid. If the gap between the frontal incisors (red arrow in Figure # 165 right) superimposes the odontoid on the open mouth view, it causes the appearance of a vertically oriented fracture. Likewise, the inferior edge of these same incisors can fool you into thinking there is a transverse fracture across the odontoid (dens). The odontoid view also gives you a good look at the alanto-atlas articulation and normal spacings. Compare the normal odontoid view above with figure 167 on the next page and see if you can spot the abnormality before reading the answer. Note the lateral edges of C-1, the atlas, (red arrows) are lateral to the edges of C-2, the axis, white arrows). Failure of the posterior arch to fuse is a common congenital defect representing spina bifida occulta as shown in previous figures, but complete absence of the posterior spinous process or complete failure of the posterior arch to fuse can occur anyplace in the spine. White arrows indicate another case of spina bifida occulta, this time involving two levels at the cervical dorsal junction (C-7 and T-1). Red arrow points to an os ligamentum nuchae which is a normal sesmoid sometimes seen in the neck. The position of the os nuchae in this case might be mistaken for an avulsion fracture of the posterior spinous process. Small black arrow shows an un-united apophysis which can also be mistaken for a fracture. Ignoring the vertebrae which are not very well reproduced on this image, scrutinize the soft tissues for a specific abnormality and diagnosis.
Question #9 A 22-year-old man is brought to the emergency department after he sustained a gunshot wound to the left thigh anxiety 24 hour helpline order genuine venlor online. Pulse rate is 122/min anxiety meditation discount 75mg venlor amex, respirations are 18/min anxiety symptoms similar to heart attack order venlor american express, and blood pressure is 128/88 mmHg anxiety symptoms rocking discount venlor 75 mg online. Physical examination shows a bleeding wound in the left upper thigh, just below the inguinal ligament. The most appropriate management is debridement of the wound and which of the following? The patient has several hard signs of vascular injury, which include the following: evidence of distal ischemia, absent or diminished pulses, expanding hematoma, palpable thrill, pulsatile bleeding, and a bruit. Repair with an interposition vein graft is the most appropriate management considering these factors because of the potential for contamination and the length of the arterial damage. Appropriate surgical repair of an arterial injury depends on the extent of the vascular injury. Option (A), end-to-end anastomosis, and Option (B), end-to-side anastomosis, are incorrect because although these procedures are used for extensive injuries requiring some debridement of the artery, they are only appropriate when there is no significant loss of the original length of the artery. Option (C), repair with an interposition artery graft, is incorrect because repairing an artery with an artery can cause stenosis and is not favorable. Option (D), repair with an interposition prosthetic graft, is incorrect because use of a prosthetic graft is contraindicated in a wound that is infected or contaminated. Sample Cardiovascular/Thoracic Surgery Questions & Critiques Question #10 A 66-year-old man is recovering in the hospital five hours after undergoing three-vessel coronary artery bypass grafting. Initial output from the mediastinal chest tube was 300 mL of bloody drainage per hour. Despite repeated intravenous bolus administration of fluid, mean arterial pressure has decreased from 80 to 40 mmHg. Central venous pressure is increased at 20 mmHg (N=2-6 mmHg), and administration of dopamine has been required for maintenance of blood pressure. In the patient described, cardiac tamponade secondary to postoperative bleeding is evidenced by significant blood loss noted in the drainage from the chest tube as well as persistent hypotension and decrease in mean arterial pressure despite repeated intravenous hydration. Returning the patient to the operating room for surgical exploration is needed for evacuation of blood from the pericardium and mediastinum. After this has been accomplished, blood flow will return to the right side of the heart and cardiac output will improve. Sample Cardiovascular/Thoracic Surgery Questions & Critiques Option (A), administration of phenylephrine via intravenous drip, Option (B), infusion of streptokinase into the mediastinal chest tube, and Option (E), transfusion of two units of packed red blood cells, are incorrect because these interventions will not relieve cardiac tamponade. Option (C), placement of an intra-aortic balloon pump, is incorrect because this intervention would be appropriate only if ventricular failure were present. Question #11 A 40-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by his wife one hour after he had sudden onset of shortness of breath. Medical history includes chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and prior spontaneous right pneumothorax. After placement of an appropriately sized chest tube, which of the following is the most definitive management? The patient has characteristic risk factors for primary spontaneous pneumothorax: male gender, 20 to 40 years of age, history of cigarette smoking, history of lung disease, and prior spontaneous pneumothorax. The cause of primary spontaneous pneumothorax is rupture of a small air blister or bleb on the anterior surface of the lung. Sample Cardiovascular/Thoracic Surgery Questions & Critiques patients who have had a prior primary spontaneous pneumothorax, risk of recurrence within three years is greater than 50%. To prevent recurrence of spontaneous pneumothorax, the bleb must be surgically removed. Option (B), initiate patient-controlled anesthesia, is incorrect because this will not correct the underlying condition of recurrent spontaneous rupture of the bleb. Option (C), perform pleurodesis with doxycycline, is incorrect because it would not prevent future recurrence of pneumothorax. Option (E), wait for the lung to seal on continuous suction, is incorrect because this intervention would reexpand the current pneumothorax but would not prevent future recurrence. Question #12 A 58-year-old man is undergoing three-vessel coronary artery bypass grafting with replacement of the aortic valve. Multiple attempts to separate the patient from the heart-lung machine are unsuccessful.
Purchase genuine venlor on-line. What Does Depersonalization / Derealization Feel Like?.